Node Parts¶
All nodes in Blender are based on a similar construction. This applies to any type of node. These parts include the Title, Sockets, Preview and more.
Title¶
The Title shows the name/type of the node. It can be overridden by changing the value of Label in the Node section of the Sidebar region N. On the left side of the title is the collapse toggle which can be used to collapse the node this can also be done with H.
How a node appears when collapsed.¶
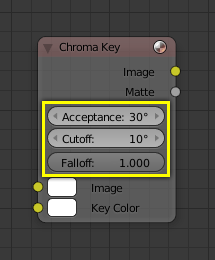
Sockets¶
The Sockets input and output values from the node. They appear as little colored circles on either side of the node. Unused sockets can be hidden with Ctrl-H. There are two kinds of sockets: inputs and outputs.
Each socket is color-coded depending on what type of data it handles.
- Color (yellow)
Indicates that color information needs to be input or will be output from the node. Depending on the node tree type, the color has an alpha channel or not.
- Numeric (gray)
Indicates numeric value’s information. It can either be a single numerical value or a so-called „value map“. (You can think of a value map as a gray-scale map where the different amount of bright/dark reflects the value for each point.) If a single value is used as an input for a „value map“ socket, all points of the map are set to this same value. Common use: Alpha maps and value options for a node.
- Vector (blue)
Indicates vector, coordinate and normal information.
- Shader (green)
Inputs¶
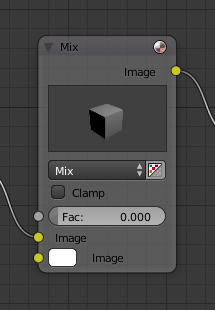
The Inputs are located on bottom left side of the node, and provide the data the node needs to perform its function. Each input socket, except for the green shader input, when disconnected, has a default value which can be edited via a color, numeric, or vector interface input. In the screenshot of the node above, the second color option is set by a color interface input.
Outputs¶
The Outputs are located on the top right side of the node, and can be connected to the input of nodes further down the node tree.