Introduction¶
Note
The texture node system is legacy and will be replaced soon by a new system. Due to this, the manual is not up to date with the latest version of Blender.
Blender includes a node-based texture generation system, which enables textures creation by combining colors, patterns and other textures in the same way as shader writing with material nodes.
These textures can be used for brushes, compositing and inside particle systems.
Using Texture Nodes¶
To use texture nodes with the current texture, open the Texture Node editor.
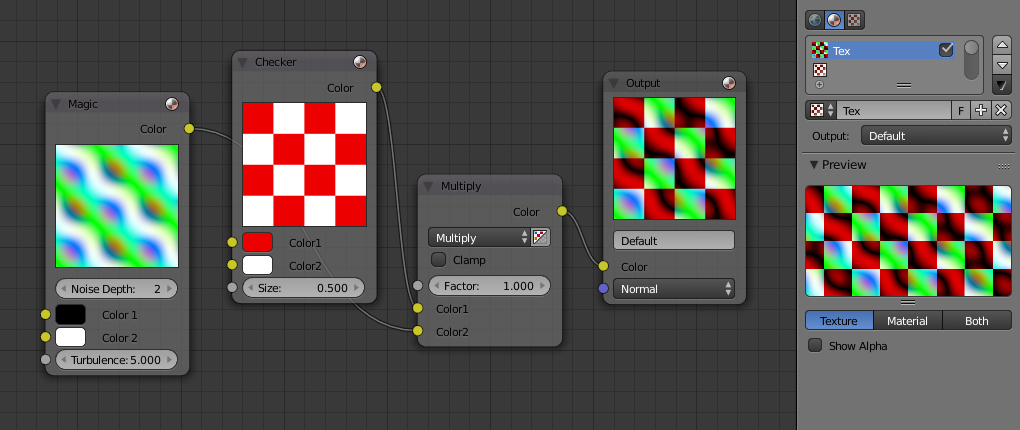
A new texture can be created by either clicking the New button in the Texture Node editor, or the New button in the Texture panel. Once a texture is selected, it can be toggled to a function as a regular texture or a node texture by clicking the Use Nodes option in the Texture Node editor.
The default node setup will appear: a red-and-white checkerboard node connected to an Output named “Default”. For texture nodes, multiple Outputs can exist in the node setup. Compare to other types of node contexts, which are limited to one active Output node. See the next section for details.
For instructions on how to add, remove and manipulate the nodes in the tree, see the nodes reference.
Using Multiple Outputs¶
Each texture defined with texture nodes can have several outputs, which can then be used for different things. For example, a texture that defines both a diffuse (color) map and a normal map. This can be done by:
- Create two texture slots in the texture list, and set them to the same texture data-block.
- Add two Output nodes to the node tree, and type new names into their Name text fields: e.g. “Diffuse” for one and “Normal” for the other.
- Underneath the texture list view in the Texture panel, a selector with the names of the outputs is shown. For each entry in the Texture list, select the desired output by changing the menu entry (e.g. set one to Diffuse and the other to Normal).
These named outputs could be used, when the material is defined with material nodes. In this case, Texture Channels are probably not used. Instead, insert the texture nodes into the material node tree by using . Inside the just added texture node the output to use can then be selected (e.g. Diffuse or Normal).