Window System Introduction
After starting Blender and closing the Splash Screen, the Blender window should look similar to the image below.
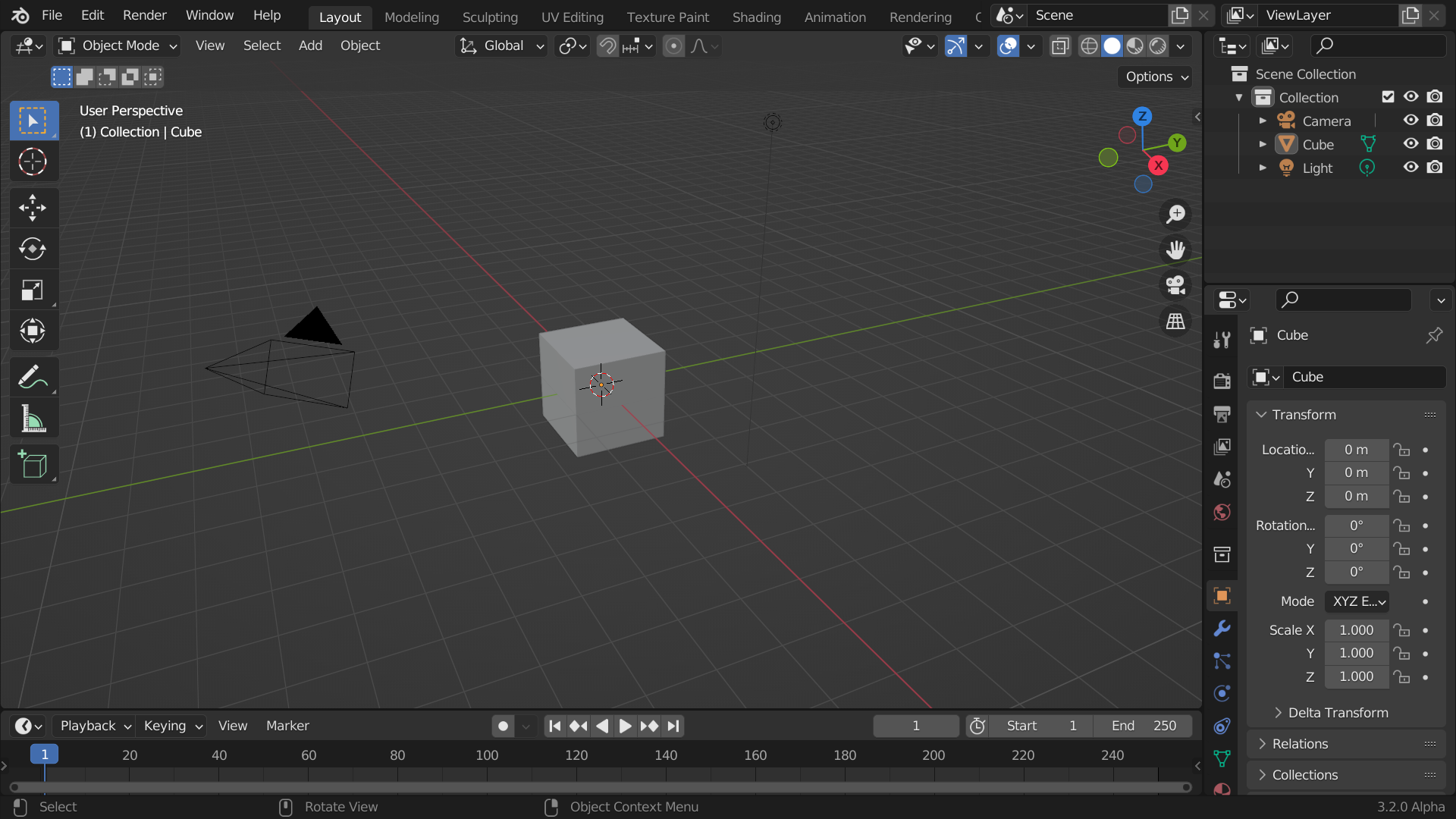
The default startup Blender window.
Blender’s interface is separated into three main parts:
The Topbar at the very top, consists of the main menu, which is used for saving, importing and exporting files, configuring settings, and rendering among other functions.
Areas in the middle, which is the main workspace
The Status Bar at the bottom, which displays shortcut suggestions and relevant statistics.
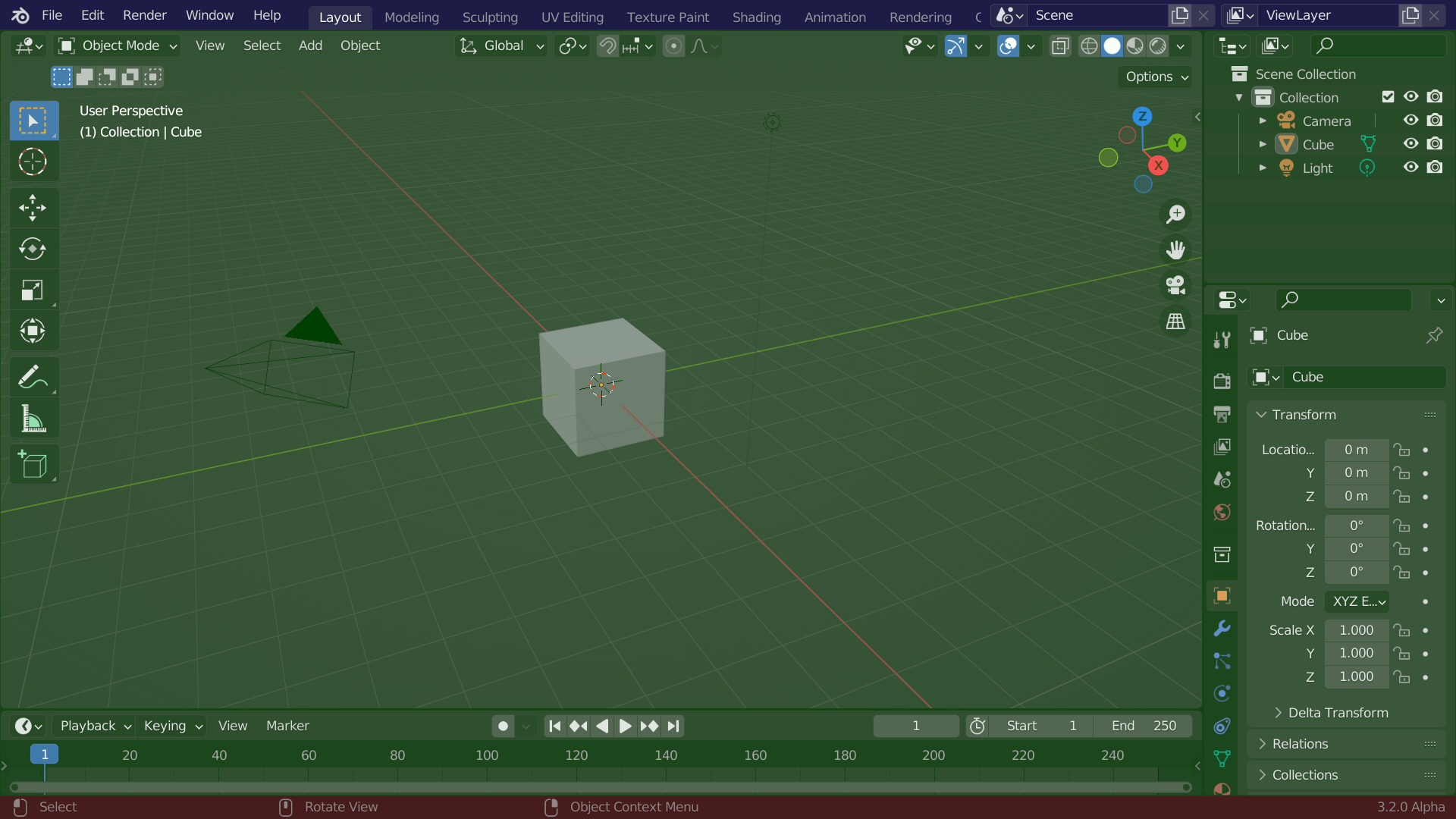
Blender’s default Screen Layout. Topbar (blue), Areas (green) and Status Bar (red).
Customization
Keyboard shortcuts
Blender makes heavy use of keyboard shortcuts to speed up work. These can be customized in the Keymap Editor.
Theme colors
Blender allows for most of its interface colors to be changed to suit the needs of the user. If you find that the colors you see on screen do not match those in the Manual, it could be that your default theme has been altered. Creating a new theme or selecting/altering a preexisting one can be done by opening the Preferences and clicking on the Themes tab.
Accessibility
Blender has several options for visibility customization, including resolution scale, and the ability to load custom fonts. These settings can be configured in the Interface Preferences.