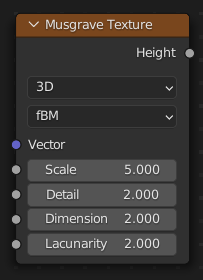
Musgrave Texture Node
Note
This node is ported from shader nodes. The manual and images are
referencing the shader version of the node.
This node accepts field inputs and outputs.
When not connected the Vector input has an implicit position attribute value.
The Musgrave Texture node evaluates a fractal Perlin noise at the input texture coordinates. Unlike the Noise Texture, which is also a fractal Perlin noise, the Musgrave Texture allows greater control over how octaves are combined.
Inputs
The inputs are dynamic, they become available if needed depending on the node properties.
- Vector
Texture coordinate to evaluate the noise at; defaults to Generated texture coordinates if the socket is left unconnected.
- W
Texture coordinate to evaluate the noise at.
- Scale
Scale of the base noise octave.
- Detail
Number of noise octaves. The fractional part of the input is multiplied by the magnitude of the highest octave. Higher number of octaves corresponds to a higher render time.
- Dimension
The difference between the magnitude of each two consecutive octaves. Larger values corresponds to smaller magnitudes for higher octaves.
- Lacunarity
The difference between the scale of each two consecutive octaves. Larger values corresponds to larger scale for higher octaves.
- Offset
An added offset to each octave, determines the level where the highest octave will appear.
- Gain
An extra multiplier to tune the magnitude of octaves.
Properties
- Dimensions
The dimensions of the space to evaluate the noise in.
- 1D:
Evaluate the noise in 1D space at the input W.
- 2D:
Evaluate the noise in 2D space at the input Vector. The Z component is ignored.
- 3D:
Evaluate the noise in 3D space at the input Vector.
- 4D:
Evaluate the noise in 4D space at the input Vector and the input W as the fourth dimension.
Higher dimensions corresponds to higher render time, so lower dimensions should be used unless higher dimensions are necessary.
- Type
Type of the Musgrave texture.
- FBM (Fractal Brownian Motion):
Produces an unnatural homogeneous and isotropic result. Uses an additive cascade, the values are simply added together.
- Multifractal:
The result is more uneven (varies with location), more similar to a real terrain. Uses a multiplicative cascade.
- Hybrid Multifractal:
Creates peaks and valleys with different roughness values, like real mountains rise out of flat plains. Combines the additive cascade with a multiplicative cascade.
- Ridged Multifractal:
Creates sharp peaks. Calculates the absolute value of the noise, creating “canyons”, and then flips the surface upside down.
- Hetero Terrain (Heterogeneous Terrain):
Similar to Hybrid Multifractal creates a heterogeneous terrain, but with the likeness of river channels.
Outputs
- Height
Texture value.
Examples
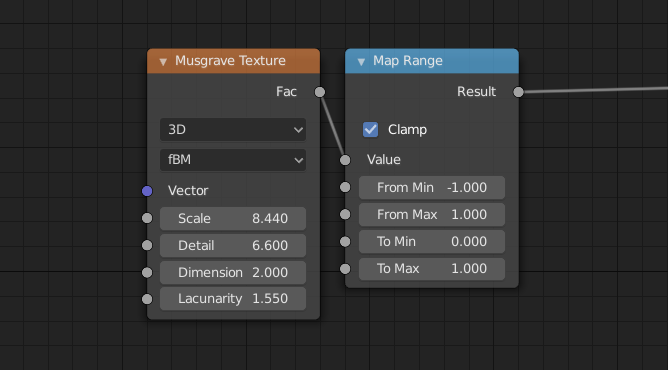
Nodes for the image to the right. |
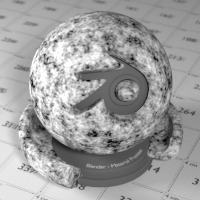
Musgrave texture. |
Musgrave Types
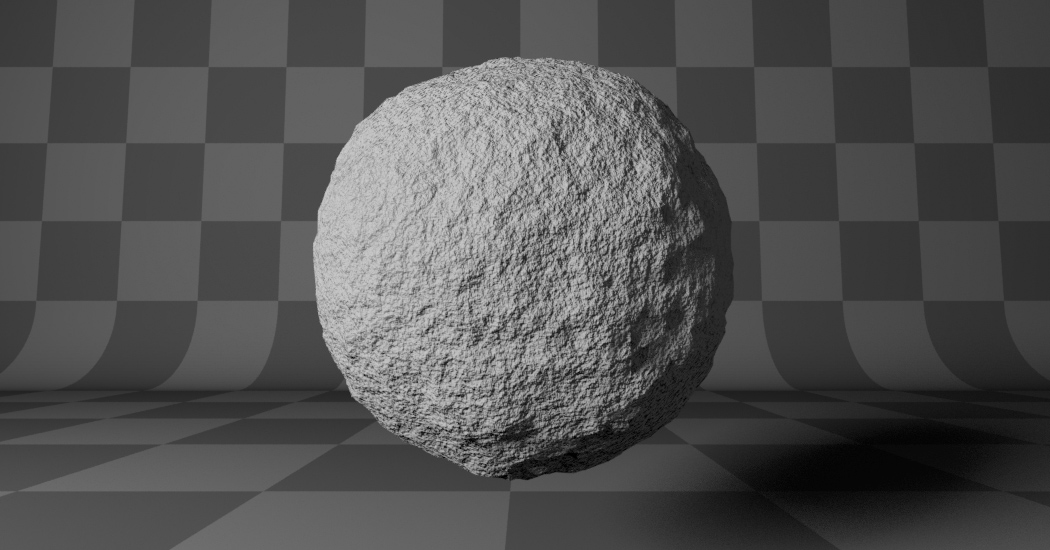

fBM (fractal Brownian Motion). |
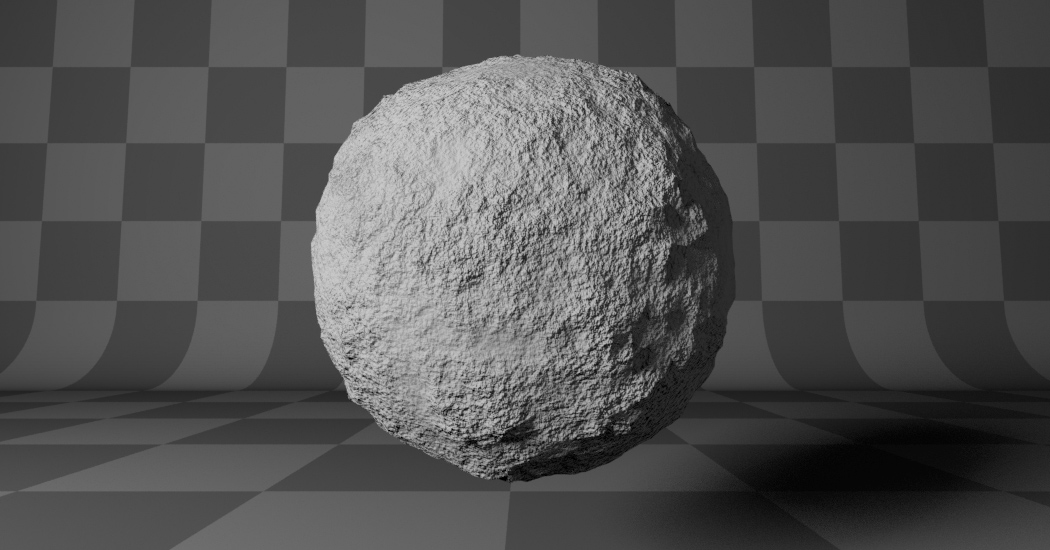

Multifractal. |
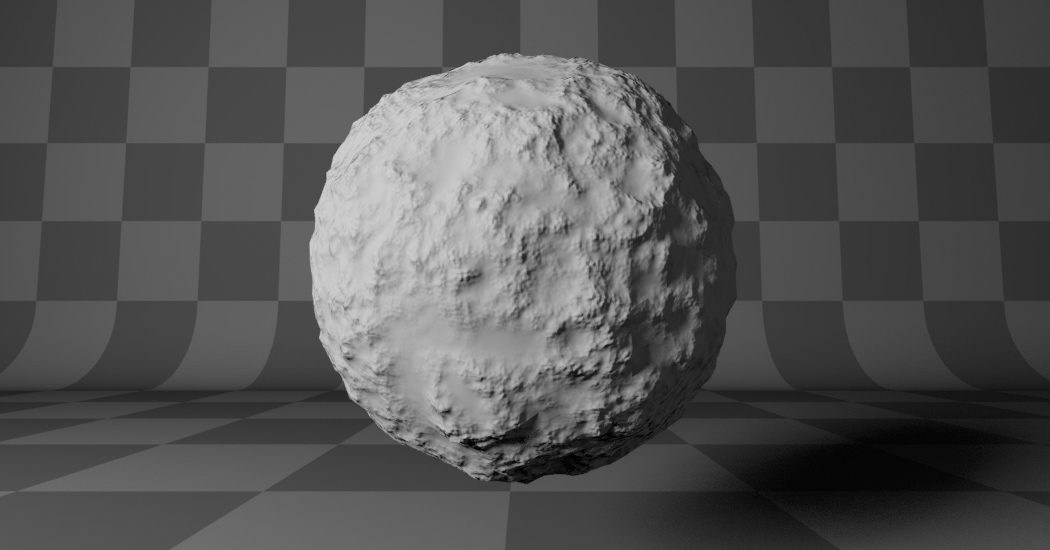

Hybrid Multifractal. |
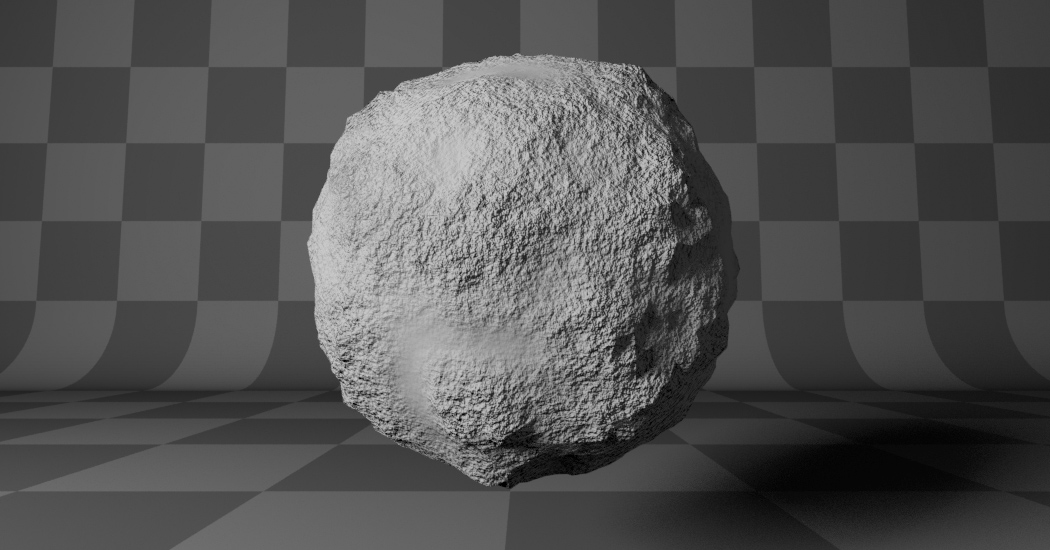

Heterogeneous Terrain. |
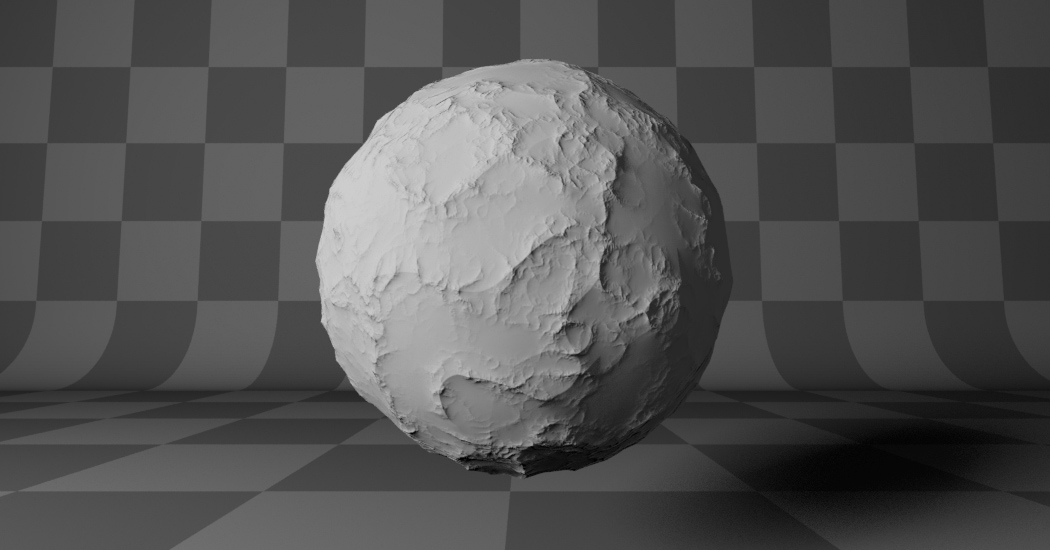
Ridged Multifractal. |
See also