Image Texture Node
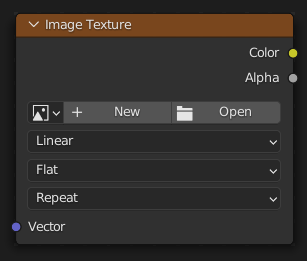
The Image Texture is used to add an image file as a texture.
Inputs
- Vector
Texture coordinate for texture look-up. If this socket is left unconnected, UV coordinates from the active UV render layer are used.
Properties
- Image
Image data-block used as the image source. More settings can be found in : These include options to control the alpha channel along with addition options for the color space. These addition options are documented with the rest of Common Image Settings.
- Interpolation
Method to scale images up or down for rendering.
- Linear:
Regular quality interpolation.
- Cubic:
Smoother, better quality interpolation. For bump maps this should be used to get best results.
- Closest:
No interpolation, use only closest pixel for rendering pixel art.
- Smart:
Cycles Only Only for Open Shading Language. Use cubic interpolation when scaling up and linear when scaling down, for a better performance and sharpness.
- Projection
Projection to use for mapping the textures.
- Flat:
Uses the XY coordinates for mapping.
- Box:
Maps the image to the six sides of a virtual box, based on the normal, using XY, YZ and XZ coordinates depending on the side.
- Blend
For Box mapping, the amount to blend between sides of the box, to get rid of sharp transitions between the different sides. Blending is useful to map a procedural-like image texture pattern seamlessly on a model. 0.0 gives no blending; higher values give a smoother transition.
- Sphere:
Sphere mapping is the best type for mapping a sphere, and it is perfect for making planets and similar objects. It is often very useful for creating organic objects.
- Tube:
Maps the texture around an object like a label on a bottle. The texture is therefore more stretched on the cylinder. This mapping is of course very good for making the label on a bottle, or assigning stickers to rounded objects. However, this is not a cylindrical mapping so the ends of the cylinder are undefined.
- Extension
Extension defines how the image is extrapolated past the original bounds:
- Repeat:
Will repeat the image horizontally and vertically giving tiled-looking result.
- Extend:
Will extend the image by repeating pixels on its edges.
- Clip:
Clip to the original image size and set all the exterior pixels values to transparent black.
- Mirror:
Repeatedly flip the image horizontally and vertically.
- Color Space
Type of data that the image contains, either Color or Non-Color Data. For most color textures the default of Color should be used, but in case of e.g. a bump or alpha map, the pixel values should be interpreted as Non-Color Data, to avoid doing any unwanted color space conversions.
The list of color spaces depends on the active OCIO config. The default supported color spaces are described in detail here: Default OpenColorIO Configuration
- Alpha
If the source file has an Alpha (transparency) channel, you can choose how the alpha channel is encoded in the image.
Outputs
- Color
RGB color from image. If the image has alpha, the color is premultiplied with alpha if the Alpha output is used, and unpremultiplied or straight if the Alpha output is not used.
- Alpha
Alpha channel from image.
Examples

Image texture from GoodTextures.com.