Autodesk 3DS
Reference
- Category:
Import-Export
- Menu:
- Version:
2.3.4
- Blender:
3.6
- Authors:
Bob Holcomb, Campbell Barton, Sebastian Schrand
- Maintainer:
Sebastian Sille (NRGSille)
- Support Level:
Community
Usage
This add-on can be used to import and export objects to/from the 3DS Studio file format, the native file format of the 3D Studio DOS releases R1 to R4. This format is one of the first 3D file formats beside OBJ and was commonly used to exchange files from Autodesk® 3ds MAX®.
Properties
Import
Include
- Image Search
This enables a recursive file search if an image file can’t be found.
- Read Keyframe
Reads the keyframe tracks from a 3ds file and transforms the objects to the data wich was found. Usually only one frame is found in static scenes, it will be imported to the timeline. If the 3ds scene is animated, the complete animation will be imported to the timeline.
Transform
- Forward / Up Axis
Since many applications use a different axis for ‘Up’, these are axis conversions for Forward and Up axes – By mapping these to different axes you can convert rotations between applications default up and forward axes. Blender uses Y forward, Z up (since the front view looks along the +Y direction). For example, its common for applications to use Y as the up axis, in that case -Z forward, Y up is needed.
- Size Constraint
Scales the imported objects by 10 scene units until it reaches the size defined here. To disable set the Size Constraint to zero.
- Apply Transform
Applies object transformations after importing. If unchecked, all objects will stay at its origins.
- World Space
Use world matrix instead of local matrix to transform the objects. This is useful for older 3ds files from 3D Studio DOS wich only used world space to transform the objects. It is also useful if the object was exported without apply transform.
Export
Include
- Selection Only
When checked, only selected objects are exported. Otherwise export all objects in the scene.
Transform
- Forward / Up
Since many applications use a different axis for pointing upwards, these are axis conversion for these settings, Forward and up axes – By mapping these to different axes you can convert rotations between applications default up and forward axes. Blender uses Y forward, Z up (since the front view looks along the +Y direction). For example, it is common for applications to use Y as the up axis, in that case -Z forward, Y up is needed.
Materials
Materials in 3ds are defined in various color and percent chunks wich can include either integer percent and 24bit color values or float color and percent values, both can be read by the importer and will be converted to blender values. The exporter uses the integer values, since this is used from 3ds version 3 and above. The material definitions wich Blender can use are the following:
3ds Diffuse Color <-> blender Base Color
3ds Specular Color <-> blender Specular Color
3ds Ambient Color <-> blender Emission Color
3ds Mat Shininess <-> blender Roughness inverted
3ds Mat Shin2 <-> blender Specular Intensity
3ds Mat Shin3 <-> blender Metallic
3ds Mat Opacity <-> blender Alpha inverted
3ds Mat Bump PCT <-> blender Normalmap Strength
3ds Self Illum PCT <-> blender Emission Strength
Textures
Each 3ds material can include different texture mappings, which are all imported to Blender material nodes including texture coordinates. The 3ds exporter basically takes the images and coordinates, wich are directly connected to the Principled BSDF shader, if an image is connected to a colormix shader, it will exported as secondary texture. Shininess maps to roughness and opacity to the alpha channel, they must be color inverted afterwards to match with Blender definition. The material mappings are defined as following:
3ds Diffuse Map <-> blender Base Color Texture
3ds Specular Map <-> blender Specular Texture
3ds Shininess Map <-> blender Roughness Texture
3ds Reflection Map <-> blender Metallic Texture
3ds Opacity Map <-> blender Alpha Texture
3ds Self Illum Map <-> blender Emission Texture
3ds Bump Map <-> blender Normal Map (tangent space)
3ds Tex2 Map <-> blender Color Texture (connect to mixshader)
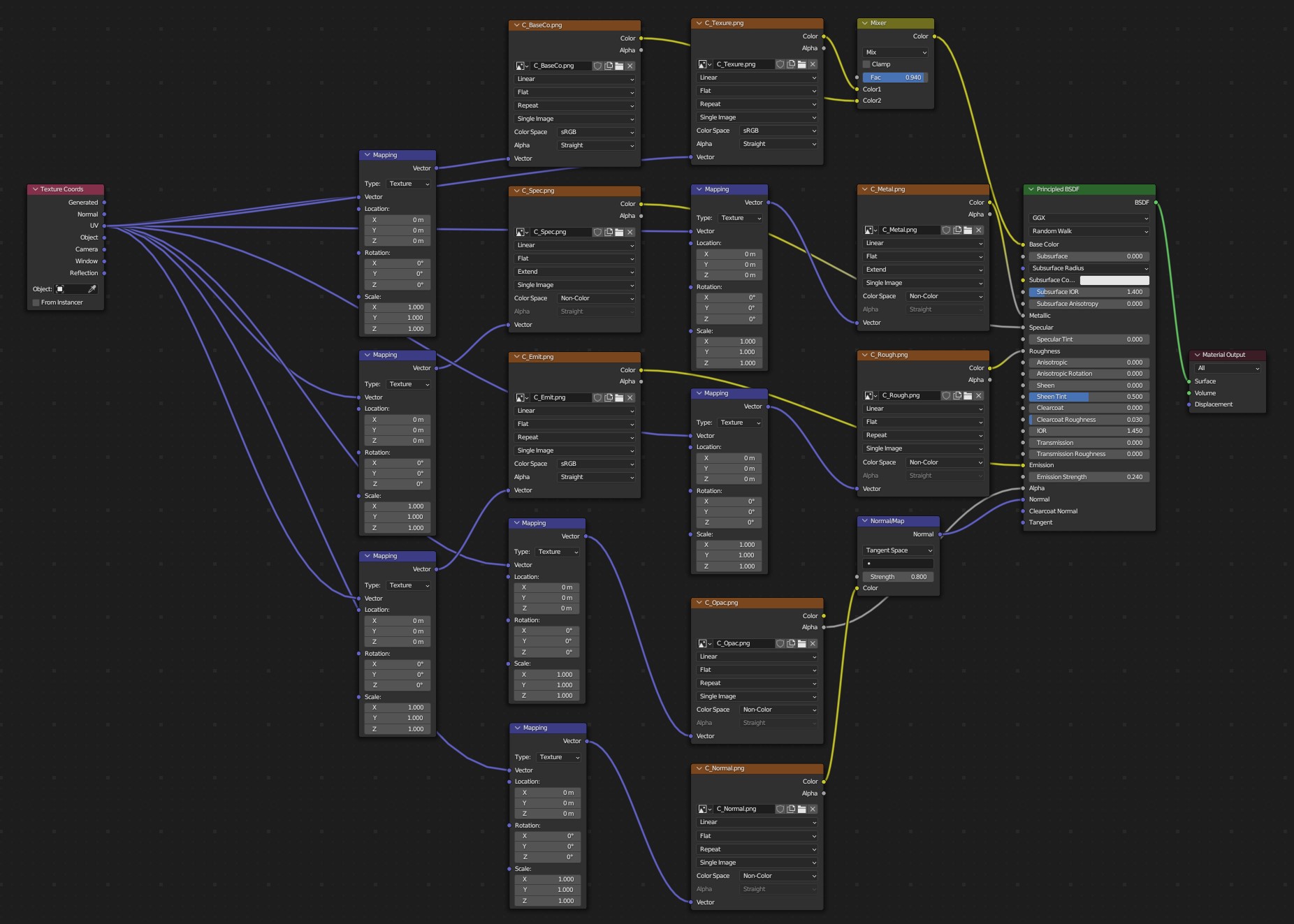
An example of a 3ds file with all image maps imported.
Note
All texture filenames are limited to the 8.3 DOS format, means that the name of the image texture can only be 8 characters long, others will be stripped away.
Meshes
Meshes are made of triangles only, no quads are supported, 3ds Studio uses edge visibilty flags to hide and show edges, many 3ds files use them to mark the quads. The Blender 3ds importer and exporter will use those flags to mark edges sharp, this can be used to convert the triangles back to quads. The importer can read the smoothchunk and shades a face smooth if it belongs to a smoothgroup, the exporter creates a smooth chunk if the mesh contains any smooth faces. 3ds only supports one pair of UV coordinates per vertex. If any vertex has more UVs, it will be dublicated.
Ambient
If ambient chunks are found by the importer, a new world with the ambient color will be created. Ambient keyframes will be imported to the timeline. The exporter creates an ambient chunk with the color of the active world if there is any.
Lights
Lights in 3DS Studio can be a point source or a spotlight, they can be animated, using color and energy data and a target for the spotlight. The lights can be imported and exported, target data is calculated to Z and X axis angle for pan and tilt, Y is used for the roll angle.
Cameras
Cameras can be imported and exported to 3ds files. They can be animated with field of view (converted to focal length), position and target data, calculated to X and Z axis angle for pitch and yaw, Y is used for the roll angle.
Keyframes
The importer can read the keyframes, they will be added to the timeline. Most animations will play, but the transformations may not be correct, some axes or rotations can be inverted. It depends on how it was exported from other applications.