Surface Deform Modifier¶
The Surface Deform modifier allows an arbitrary mesh surface to control the deformation of another, essentially transferring its motion/deformation. One great use for this is to have a proxy mesh for cloth simulation, which will in turn drive the motion of your final and more detailed mesh, which would otherwise not be suitable for simulation.
Options¶
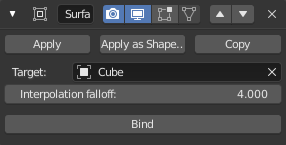
The Surface Deform modifier.¶
- Target
The object to which to bind (this setting is unavailable after binding).
- Interpolation falloff
How much a vertex bound to one face of the target will be affected by the surrounding faces (this setting is unavailable after binding). This essentially controls how smooth the deformations are.
Nota
While lower values result in smoother deformations, they may also introduce slight artifacts.
- Bind
Bind the current state of the modified mesh to the current state of the target mesh, such that any later change in the target mesh will deform the modified mesh as well. Note that until the bind has been executed, this modifier will have no effect at all.
- Unbind
Once the mesh is bound, the Bind button changes to Unbind. Executing this frees the modified mesh from the target, and resets it to its original shape.
Nota
The meshes are bound with regard to global coordinates, but later transformations on the objects are ignored. This means that one can freely transform the target or modified object after binding, without affecting the modified object. The modified mesh will only pick up changes to the target object’s mesh itself.
Nota
The further a mesh deviates from the target mesh surface, the more likely it is to get undesirable artifacts. This is an inherent characteristic of surface binding in general, so it is recommended to have reasonably well matching meshes, in order to get a good bind.
Advertencia
Target Mesh Validity
While there are no restrictions with regard to the modified mesh, the target object’s mesh has a few constraints, which if not followed, will prevent a successful binding:
It must not contain edges with more than two faces.
It must not contain concave faces.
It must not contain overlapping vertices (doubles).
It must not contain faces with collinear edges.