Displacement¶
Reference
- Panel
Detail can be added to the shape of a surface with displacement shaders.
To create displacement, connect a Displacement or Vector Displacement node to the displacement input of the Material Output node. Procedural, painted or baked textures can then be connected to these nodes.
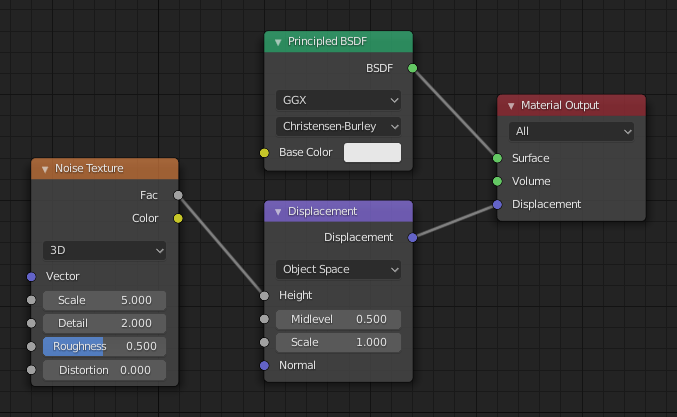
Typical displacement node setup.¶
Three displacement methods exist, with varying accuracy, performance and memory usage.
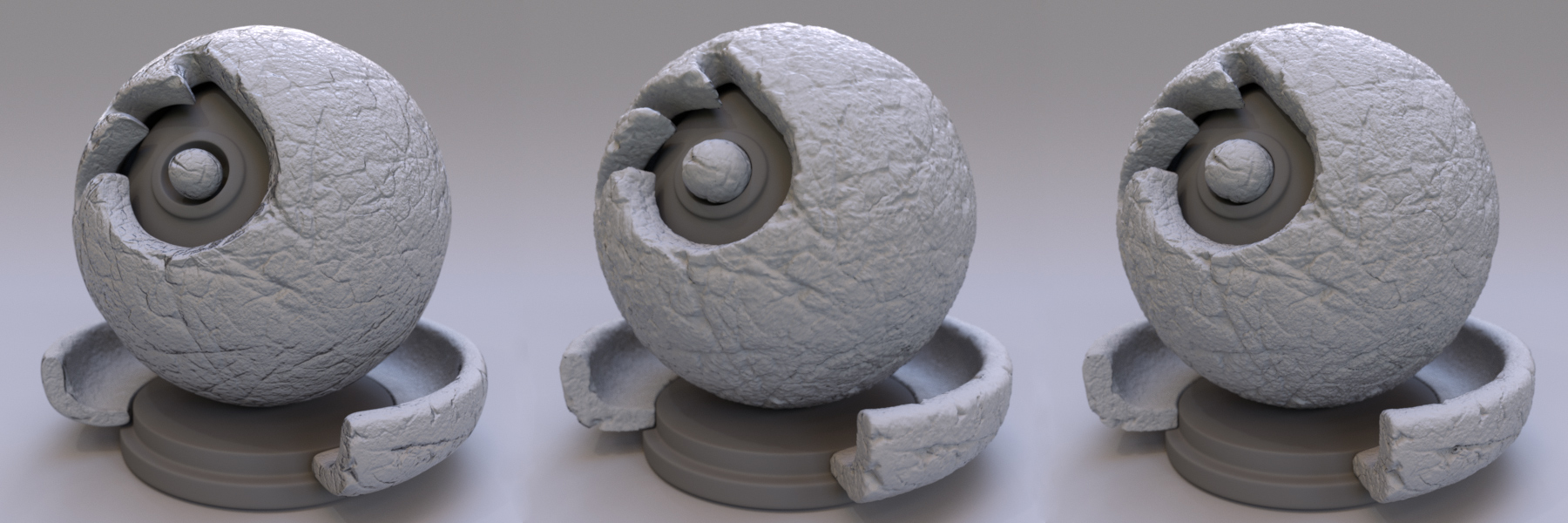
Bump only, displacement only and displacement and bump combined.¶
Bump Only¶
The least accurate but most memory efficient method is bump mapping. This method does not actually alter the mesh surface, but merely changes the shading to make it seem so.
Bump maps are often used to add smaller details on a model, for example pores or wrinkles on skin.
For baked bump maps, 8-bit images are commonly used. However, 16 or 32-bit float maps can provide better looking results. When using image textures use Cubic interpolation to avoid stepping artifacts, these are more visible for bump maps than other types of textures.
Tärkeä
Because bump mapping is a fake effect, it can cause artifacts if the actual shape of the geometry is too different from the bump mapped shape. If this happens the strength of bump mapping should be reduced or actual displacement should be used.
Displacement Only¶
Cycles Only
The most accurate and memory intensive displacement method is to apply true displacement to the mesh surface.
It requires the mesh to be finely subdivided, which can be memory intensive. Adaptive Subdivision is the best way to subdivide the mesh, so that exactly the right amount of subdivision is used depending on the distance of the object to the camera.
For baked displacement maps, best results are achieved with 16 or 32-bit float maps, as 8-bit images often can not represent all the necessary detail.
Katso myös
The Displace Modifier can also be used to displace a mesh.
Displacement and Bump¶
Cycles Only
Both methods can be combined to use actual displacement for the bigger displacement and bump for the finer details. This can provide a good balance to reduce memory usage.
Once you subdivide the mesh very finely, it is better to use only actual displacement. Keeping bump maps will then only increase memory usage and slow down renders.