Introduction¶
In addition to modeling and animation, Blender can be used to edit video. There are two possible methods for this, one being the Compositor. However, this chapter describes the other, the Video Sequence Editor (VSE), sometimes shortened to just "Sequencer". The Sequencer within Blender is a complete video editing system that allows you to combine multiple video channels and add effects to them. You can use these effects to create powerful video edits, especially when you combine it with the animation power of Blender!
To use the VSE, you load multiple video clips and lay them end-to-end (or in some cases, overlay them), inserting fades and transitions to link the end of one clip to the beginning of another. Finally, you can add audio and synchronize the timing of the video sequence to match it.
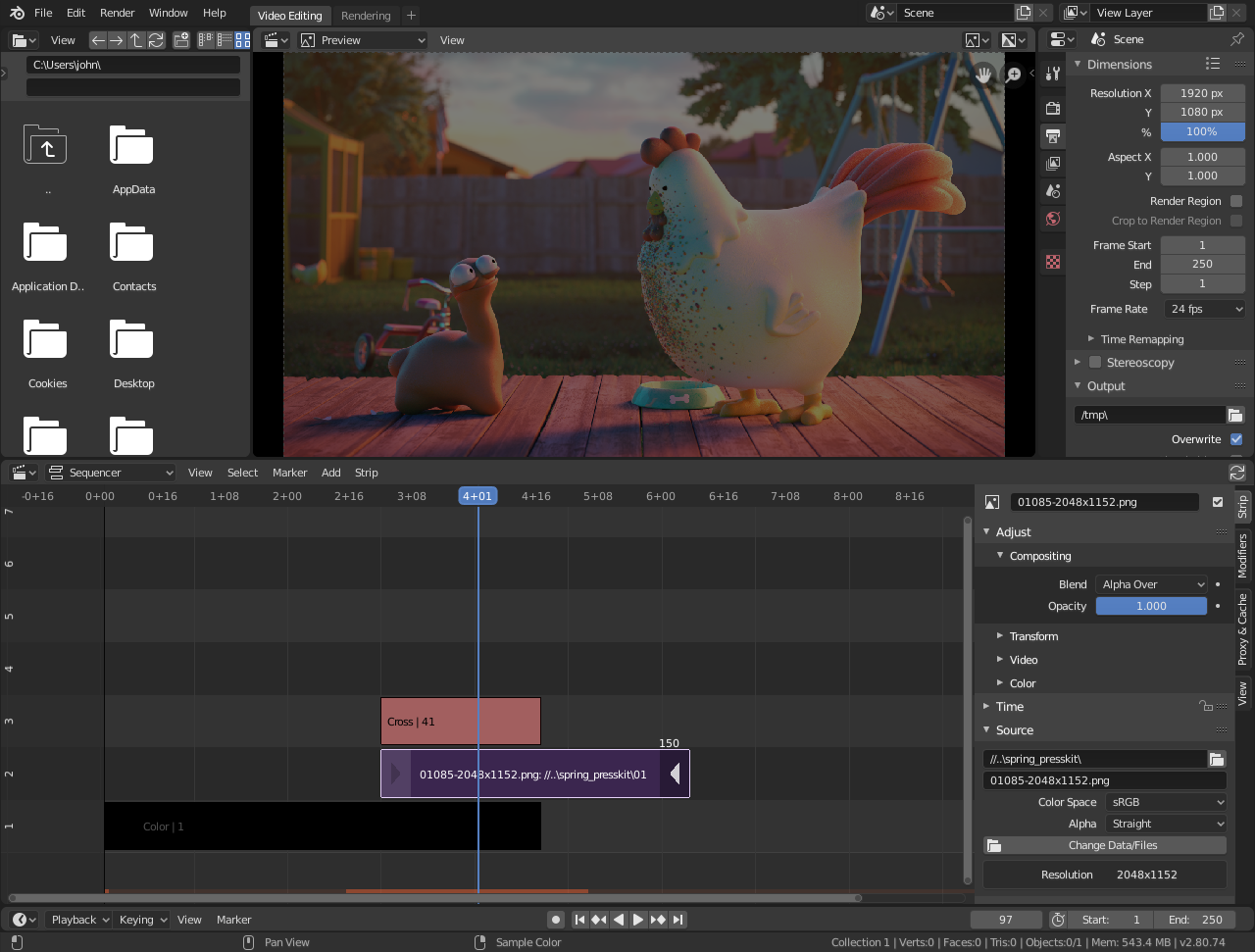
Default Video Editing screen layout.¶
View Types¶
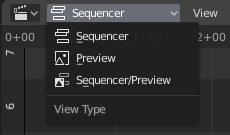
The Video Sequence Editor has three view types for the main view:
- Sequencer
View timeline and strip properties.
- Preview
View preview window and preview properties.
- Sequencer/Preview
Combined view of preview and timeline and properties of both.
It is possible to create multiple instances of any view type in single workspace.
注釈
By default the Sequencer is enabled, however, it can be disabled in the Post Processing Panel.
Performance¶
Playback performance can be improved through several ways. The biggest impact on performance is to allow the Video Sequencer to cache the playback. There are two levels of cache, the first is a RAM cache, this is enabled by default but can be increased based on the amount of RAM available. The next level of cache is a disk cache which stores cached strips on disk. A disk cache can generally cache more than a RAM cache, but it can be slower. Both of these cache options can be configured in the Preferences.
Another way to improve performance is by using Strip Proxies These are used to cache images or movies in a file that is easier to playback by reducing the image quality by either decreasing the resolution and/or compressing the image.