Selecting¶
Selection determines which elements will be the target of our actions. Selections work on the current scene visible objects. Blender has advanced selection methods. Both in Object Mode and in Edit Mode.
Selections and the Active Object¶
Blender distinguishes between two different states of selection:
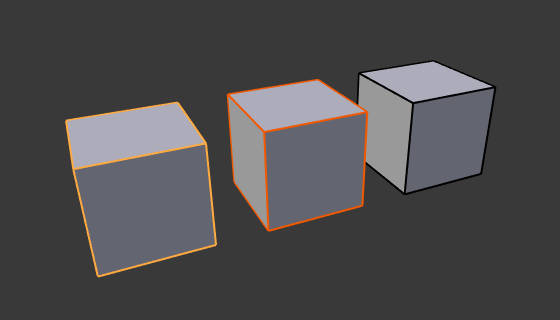
Active object in yellow, selected object in orange, and unselected object in black.¶
In Object Mode the last (de)selected item is called the "Active Object" and is outlined in yellow (the others are orange). There is at most one active object at any time.
Many actions in Blender use the active object as a reference (for example linking operations). If you already have a selection and need to make a different object the active one, simply reselect it with Shift-LMB.
All other selected objects are just selected. You can select any number of objects. In order to change a property or to perform an operation on all selected objects (bones, and sequencer strips) hold Alt, while confirming.