Principled BSDF
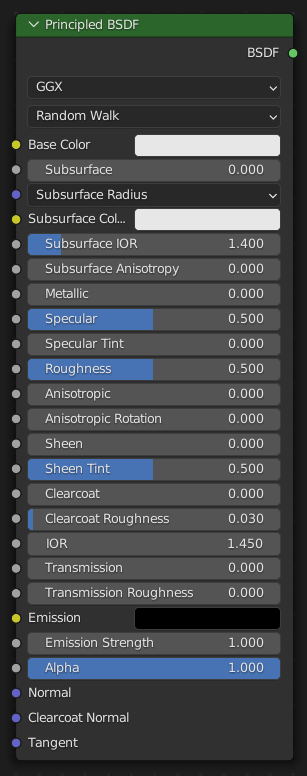
The Principled BSDF that combines multiple layers into a single easy to use node. It is based on the Disney principled model also known as the «PBR» shader, making it compatible with other software such as Pixar’s Renderman® and Unreal Engine®. Image textures painted or baked from software like Substance Painter® may be directly linked to the corresponding parameters in this shader.
This «Uber» shader includes multiple layers to create a wide variety of materials. The base layer is a user controlled mix between diffuse, metal, subsurface scattering and transmission. On top of that there is a specular layer, sheen layer and clearcoat layer.
Obs
The emphasis on compatibility with other software means that it interprets certain input parameters differently from older Blender nodes.
Inputs
- Base Color
Diffuse or metal surface color.
- Subsurface
Mix between diffuse and subsurface scattering. Rather than being a simple mix between Diffuse and Subsurface Scattering, it acts as a multiplier for the Subsurface Radius.
- Subsurface Radius
Average distance that light scatters below the surface. Higher radius gives a softer appearance, as light bleeds into shadows and through the object. The scattering distance is specified separately for the RGB channels, to render materials such as skin where red light scatters deeper. The X, Y and Z values are mapped to the R, G and B values, respectively.
- Subsurface Color
Subsurface scattering base color.
- Subsurface IOR Cycles Only
Index of refraction for Subsurface Scattering.
- Subsurface Anisotropy Cycles Only
Controls the directionality of subsurface scattering.
- Metallic
Blends between a non-metallic and metallic material model. A value of 1.0 gives a fully specular reflection tinted with the base color, without diffuse reflection or transmission. At 0.0 the material consists of a diffuse or transmissive base layer, with a specular reflection layer on top.
- Specular
Amount of dielectric specular reflection. Specifies facing (along normal) reflectivity in the most common 0 - 8% range.
Hint
To compute this value for a realistic material with a known index of refraction, you may use this special case of the Fresnel formula: \(specular = ((ior - 1)/(ior + 1))^2 / 0.08\)
For example:
water: ior = 1.33, specular = 0.25
glass: ior = 1.5, specular = 0.5
diamond: ior = 2.417, specular = 2.15
Since materials with reflectivity above 8% do exist, the field allows values above 1.
- Specular Tint
Tints the facing specular reflection using the base color, while glancing reflection remains white.
Normal dielectrics have colorless reflection, so this parameter is not technically physically correct and is provided for faking the appearance of materials with complex surface structure.
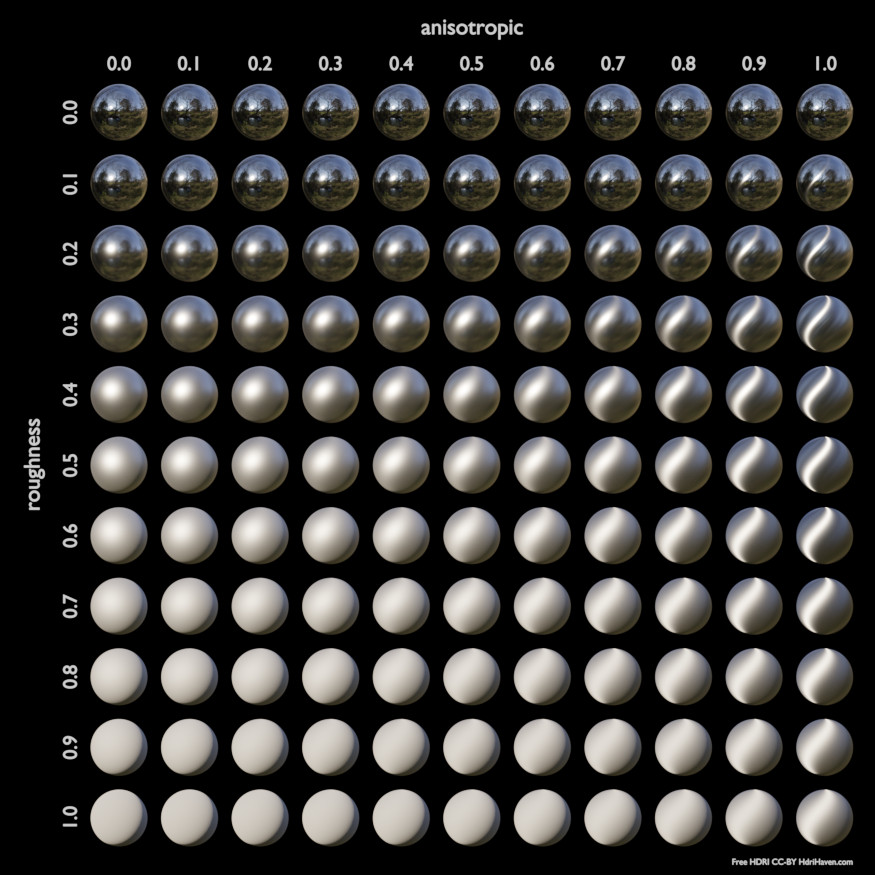
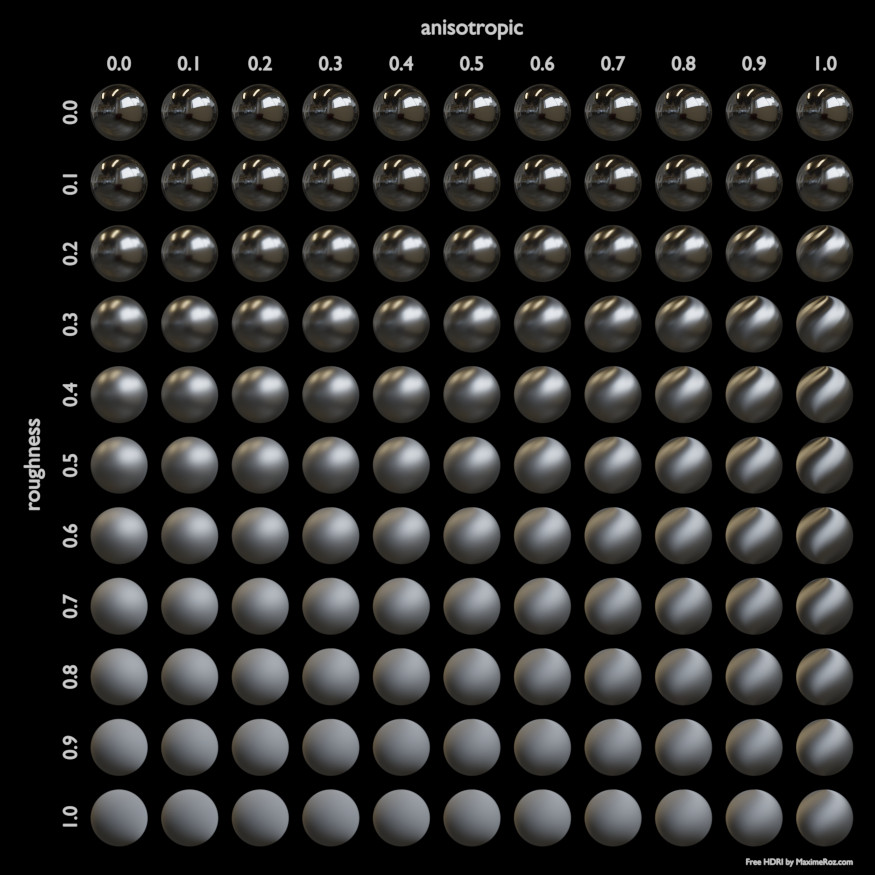
- Roughness
Specifies microfacet roughness of the surface for diffuse and specular reflection.
- Anisotropic Cycles Only
Amount of anisotropy for specular reflection. Higher values give elongated highlights along the tangent direction; negative values give highlights shaped perpendicular to the tangent direction.
- Anisotropic Rotation Cycles Only
Rotates the direction of anisotropy, with 1.0 going full circle.
Hint
Compared to the Anisotropic BSDF node, the direction of highlight elongation is rotated by 90°. Add 0.25 to the value to correct.
- Sheen
Amount of soft velvet like reflection near edges, for simulating materials such as cloth.
- Sheen Tint
Mix between white and using base color for sheen reflection.
- Clearcoat
Extra white specular layer on top of others. This is useful for materials like car paint and the like.
- Clearcoat Roughness:
Roughness of clearcoat specular.
- IOR
Index of refraction for transmission.
- Transmission
Mix between fully opaque surface at zero and fully glass like transmission at one.
- Transmission Roughness Cycles Only
With GGX distribution controls roughness used for transmitted light.
- Emission
Light emission from the surface, like the Emission shader.
- Emission Strength
Strength of the emitted light. A value of 1.0 will ensure that the object in the image has the exact same color as the Emission Color, i.e. make it ’shadeless’.
- Alpha
Controls the transparency of the surface, with 1.0 fully opaque. Usually linked to the Alpha output of an Image Texture node.
- Normal
Controls the normals of the base layers.
- Clearcoat Normal
Controls the normals of the Clearcoat layer.
- Tangent
Controls the tangent for the Anisotropic layer.
Properties
- Distribution
Microfacet distribution to use.
- GGX:
A method that is faster than Multiple-scattering GGX but is less physically accurate. Selecting it enables the Transmission Roughness input.
- Multiple-scattering GGX:
Takes multiple bounce (scattering) events between microfacets into account. This gives a more energy conserving results, which would otherwise be visible as excessive darkening.
- Subsurface Method
Rendering method to simulate subsurface scattering.
Obs
Eevee does use not support the Random Walk methods.
- Christensen-Burley:
An approximation to physically-based volume scattering. This method is less accurate than Random Walk however, in some situations this method will resolve noise faster.
- Random Walk (Fixed Radius):
Provides accurate results for thin and curved objects. Random Walk uses true volumetric scattering inside the mesh, which means that it works best for closed meshes. Overlapping faces and holes in the mesh can cause problems.
- Random Walk:
Behaves similarly to Random Walk (Fixed Radius) but modulates the Subsurface Radius based on the Color, Subsurface Anisotropy, and Subsurface IOR. This method thereby attempts to retain greater surface detail and color than Random Walk (Fixed Radius).
Outputs
- BSDF
Standard shader output.
Examples
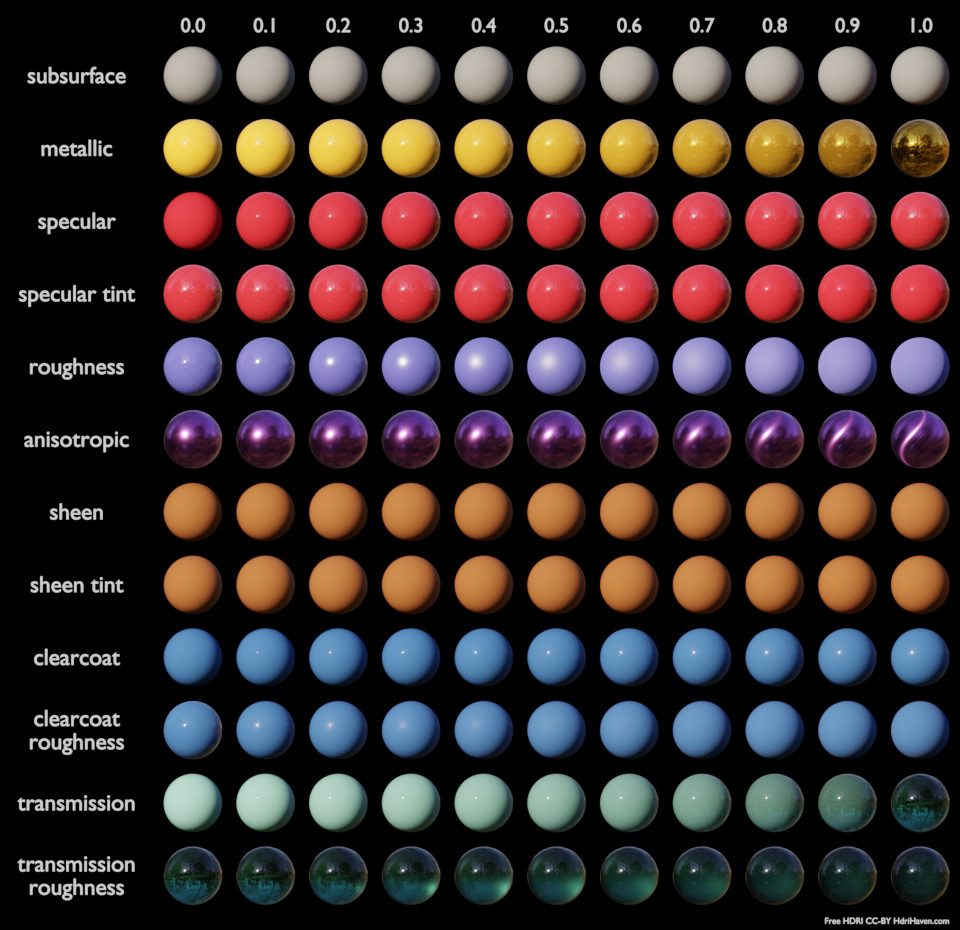
Below are some examples of how all the Principled BSDF’s parameters interact with each other.