Thực Thể (Instances)
Ba thể loại thực thể.
In addition to storing real data like a mesh or a curve, a geometry can store instances, which themselves can reference more geometry, or an object, or a collection. The purpose of instancing is to allow including much more geometry in the result, without duplicating the actual data. This is because renderer like Cycles can handle the same geometry data in many different locations better than when the data is duplicated.
Each instance keeps track of which geometry it corresponds to, and a Transform.
Instances can also store the id attribute, used for correct motion blur when instances
move in an animation.
The main node used to create instances in geometry nodes is the Nút Thực Thể Hóa trên Điểm (Instance on Points Node).
Cảnh báo
Hiện tại, quá trình thực thể hóa từ các nút hình học không thể hòa trộn với quá trình thực thể hóa từ bảng điều khiển Thực Thể Hóa (Instancing) trong trình biên soạn tính chất được.
Thực Thể Hóa Lồng Nhau (Nested Instancing)
Since instances can store a geometry, and a geometry can contain instances, nested instancing is possible. In other words, it is possible to instance an instance, or even a collection of instances. By default, the Nút Thực Thể Hóa trên Điểm (Instance on Points Node) will create nested instances by instancing on the points real geometry and instanced geometry.
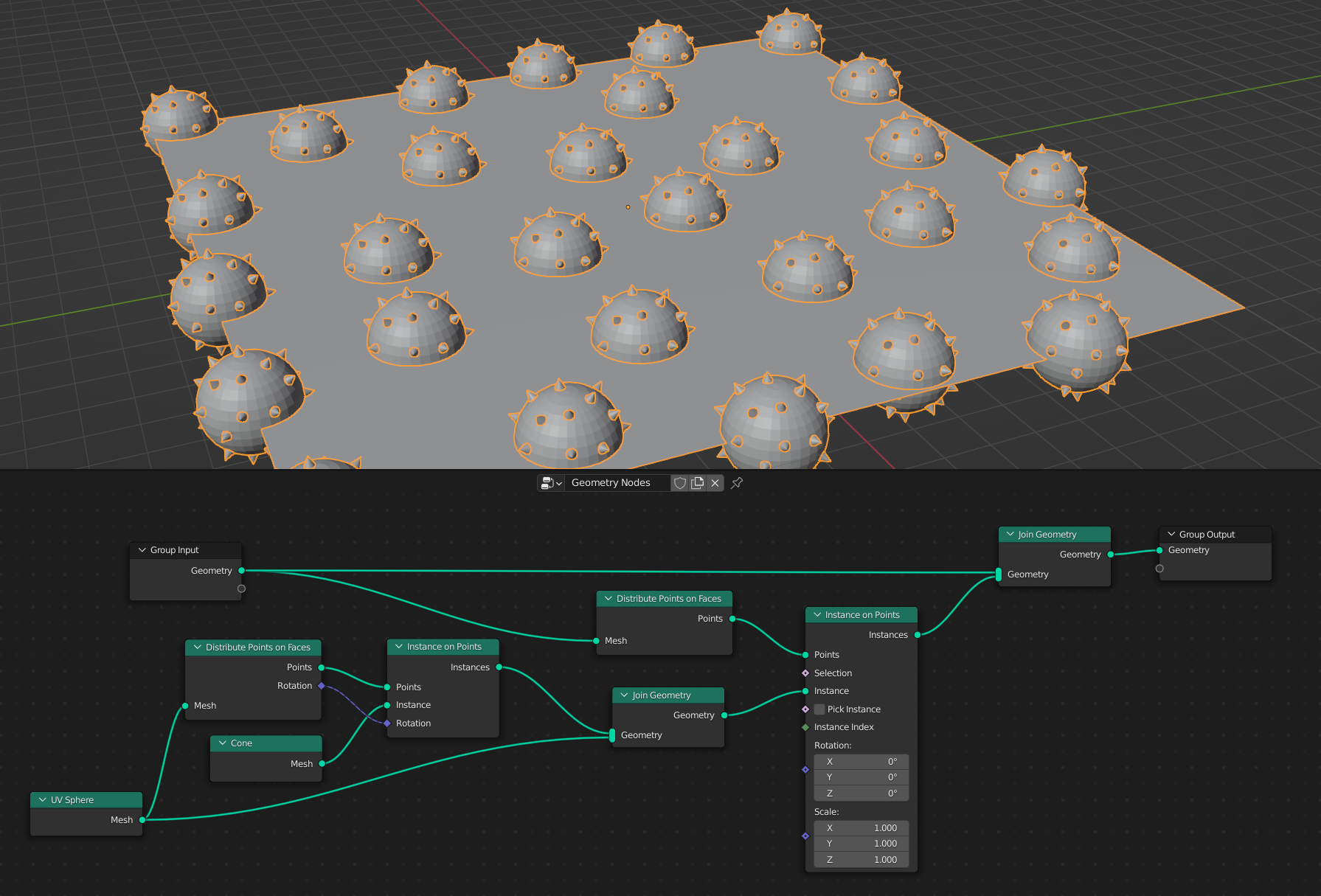
Một nhóm nút kiến tạo thực thể hóa đệ quy bằng cách nối nút thực thể hóa trên điểm (instance on points).
Here, nested instancing is used to distribute geometry that contains both a mesh and instances. The output geometry contains a "real" mesh, and a group of instances. Each instance contains a sphere mesh and many instances of a cone geometry.
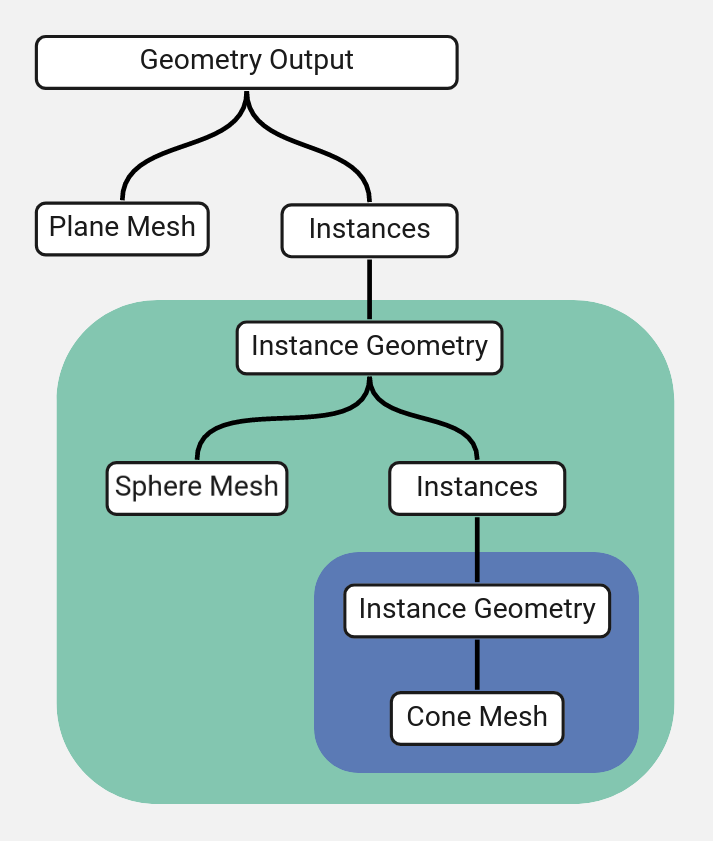
Cấu trúc cây của hình học thực thể cho ví dụ trên.
What makes this method helpful is that the output geometry only contains three unique meshes: the plane, the sphere, and the cone. This would make the performance much better if the meshes were more complicated.
Cảnh báo
Only eight levels of nested instancing are supported for rendering and the viewport currently. Though deeper trees of instances can be made inside geometry nodes, they must be realized at the end of the node tree.
Xử Lý Thực Thể (Instance Processing)
Almost all nodes that process geometry do so by processing each unique geometry in their input's tree of instances separately. For example, if a Nút Bề Mặt Phân Hóa (Subdivision Surface Node) was placed at the end of the example above, it would only have to subdivide three meshes, rather than each instance of a mesh. Another important example is processing with the output of the Nút Chuỗi Ký Tự thành Đường Cong (String to Curves Node), where each unique character only has to be processed once.
Phương pháp này có thể cải thiện hiệu suất hoạt động rất nhiều, nhưng nó có nghĩa là đối với mọi trường hợp của một hình học nhất định, kết quả của một thao tác sẽ giống nhau. Để có kết quả đơn nhất cho mọi trường hợp, chúng ta có thể sử dụng nút Nút Chuyển các Thực Thể thành Thật (Realize Instances Node).