运算
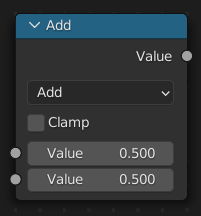
运算 节点的功能是执行数学运算。
输入
The inputs of the node are dynamic. Some inputs are only available in certain operations. For instance, the Addend input is only available in the Multiply Add operator.
- 数值
输入值。可以输入三角法则定义的弧度数值。
- 加数
输入加数。
- 基础(基数)
输入底数。
- 指数
输入幂(指数)。
- Epsilon
输入对数的基数。
- 距离
输入距离。
- 最小值
输入最小值。
- 最大值
输入最大值。
- 增量
输入增量。
- 缩放
输入比例。
- 角度
输入角度。
- 弧度
输入弧度。
属性
- 运算
数学运算符将两侧的输入值按运算符表示的含义进行数学运算:
- 函数
- 相加:
将运算符两侧的数值进行加法运算。
- 相减:
对两侧的输入值进行减法运算。
- 正片叠底(相乘):
将两个输入值进行相乘运算。
- 相除:
将第一个输入值作为被除数,第二个值作为除数进行相除数学运算。
- 乘后再加:
将两个乘积值再次进行 相加 运算。
- 能量(乘方):
将 底数 进行 乘方 运算。
- 对数:
以 基数 为基数的值的对数。
- 平方根:
求输入值的平方根。
- 平方根取倒:
即用数字1除以一个数值的平方根所得的结果。
- 绝对:
读取输入值而不考虑其符号。这会将负值转换为正值。
- 指数:
提升欧拉数为输入值的N次幂。备注:e,作为数学常数,是自然对数函数的底数。有时称它为欧拉数(Euler number)。
- 比较
- 最小值:
比较输入值,将其中最小值作为结果输出。
- 最大值:
将两个输入值比较,将最大的一个作为结果输出。
- 小于:
如果第一个值小于第二个值,输出 1.0,反之输出 0.0 。
- 大于:
如果第一个值大于第二个值,输出 1.0,反之输出 0.0 。
- 符号:
识别输入值的符号情况,所有正数将输出值为 1.0。所有负数将输出值为 -1.0。0 值本身输出为 0。
- 比较:
比较两个输入值的差值是否小于或等于参数 Epsilon(备注:Epsilon 是希腊语第五个字母艾普西隆的小写,写作 ϵ 或 ε,常用于数学参数等的命名。),符合即输出值为 1.0。
- 平滑最小值:
- 平滑最大值:
- 圆滑(舍入)
- 圆(四舍五入):
将输入值四舍五入到最接近的整数值。
- 基面:
将输入值向下取最接近的整数值。
- 向上取整:
将输入值向上取整到最接近的整数值。
- 截断:
将一个 输入值 的整数部分进行输出,小数部分舍弃。
- 分数:
返回输入 值 的分数部分。
- 模数:
第一个输入值除以第二个输入值,输出所得结果的余数值(备注:取模运算("Modulus Operation")和取余运算("Remainder Operation")两个概念有重叠的部分但又不完全一致。主要的区别在于对负整数进行除法运算时操作不同。取模主要是用于计算机术语中。取余则更多是数学概念。参看百度百科 "取模运算")。
- 循环:
在输入值和小于最大值的最大整数倍数值之间,最小值 和 最大值 绝对值的差值之间取值进行输出。
- 吸附:
将输入值向下舍入为最接近 增量 的整数倍。
- 乒–乓:
The output value is moved between 0.0 and the Scale based on the input value.
- 三角函数
- 转换
- 到弧度:
将输入值从角度数值转换为弧度数值。
- 到角度:
将输入值从弧度数值转换为角度数值。
- 钳制
限定输出数值的范围(0 到 1)。参见钳制。
输出
- 数值
数值输出。
示例
自定义Z深度通道节点设置
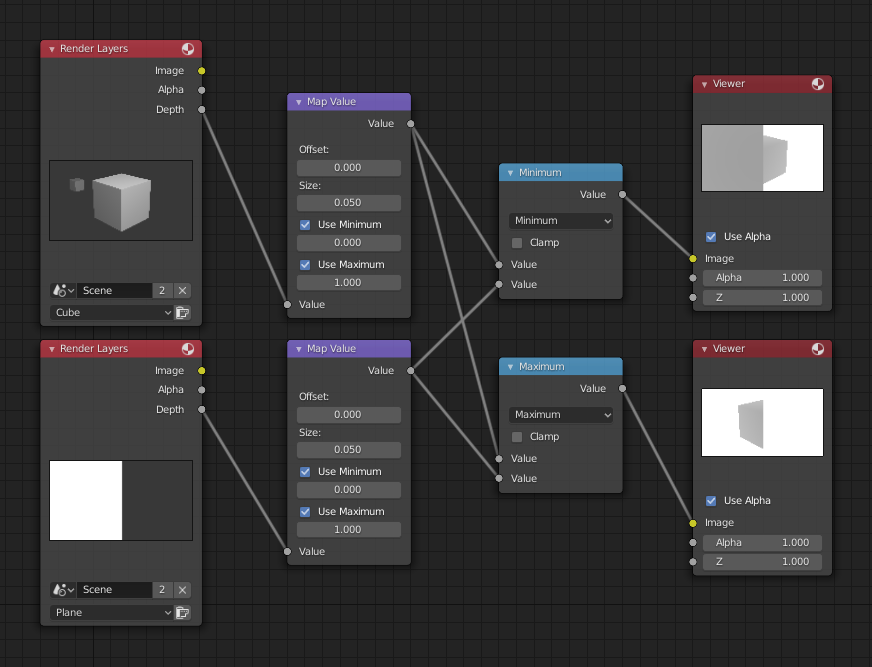
最大值与最小值功能举例。
This example has one scene input by the top Render Layers node, which has a cube that is about 10 units from the camera. The bottom Render Layers node inputs a scene with a plane that covers the left half of the view and is 7 units from the camera. Both are fed through their respective Map Value nodes to divide the Z-buffer by 20 (multiply by 0.05, as shown in the Size field) and clamped to be a min/max of 0.0/1.0 respectively.
For the minimum function, the node selects those Z values where the corresponding pixel is closer to the camera; so it chooses the Z values for the plane and part of the cube. The background has an infinite Z value, so it is clamped to 1.0 (shown as white). In the maximum example, the Z values of the cube are greater than the plane, so they are chosen for the left side, but the plane Render Layers Z are infinite (mapped to 1.0) for the right side, so they are chosen.
使用正弦功能得到不断循环的变化数
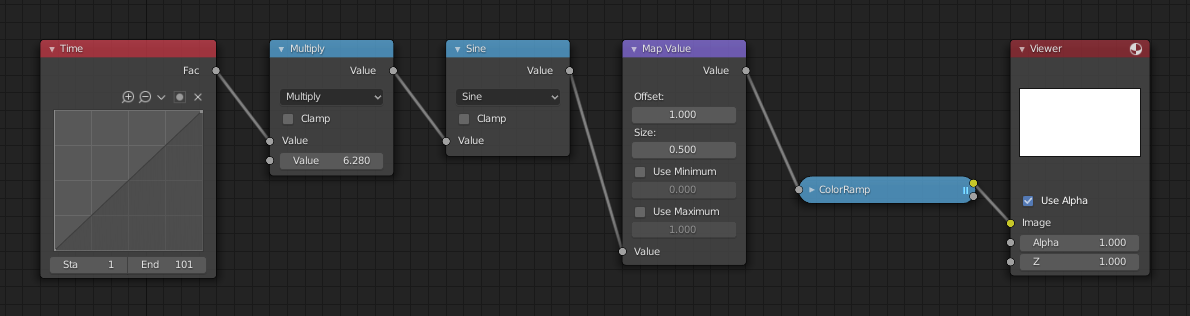
使用正弦功能举例。
范例中采用一个 时间 节点,其时间范围从 1 到 101 之间。在第 25 帧,输出为 0.25。此数值转为由 2 × pi (6.28) 进行相乘运算并由正弦函数转换映射到 1.0 范围,用数学公式表示为
Since the sine function can put out values between (-1.0 to 1.0),
the Map Value node scales that to 0.0 to 1.0 by taking the input (-1 to 1), adding 1
(making 0 to 2), and multiplying the result by one-half (thus scaling the output between 0 to 1).
The default Color Ramp converts those values to a gray-scale.
Thus, medium gray corresponds to a 0.0 output by the sine, black to -1.0,
and white to 1.0. As you can see,
将这个功能引申,比如,图片的 alpha 通道形成渐入/渐出特效。改变Z深度通道的景深位置。改变颜色通道值使其有规律的进行色彩变化。
提亮(缩放)通道
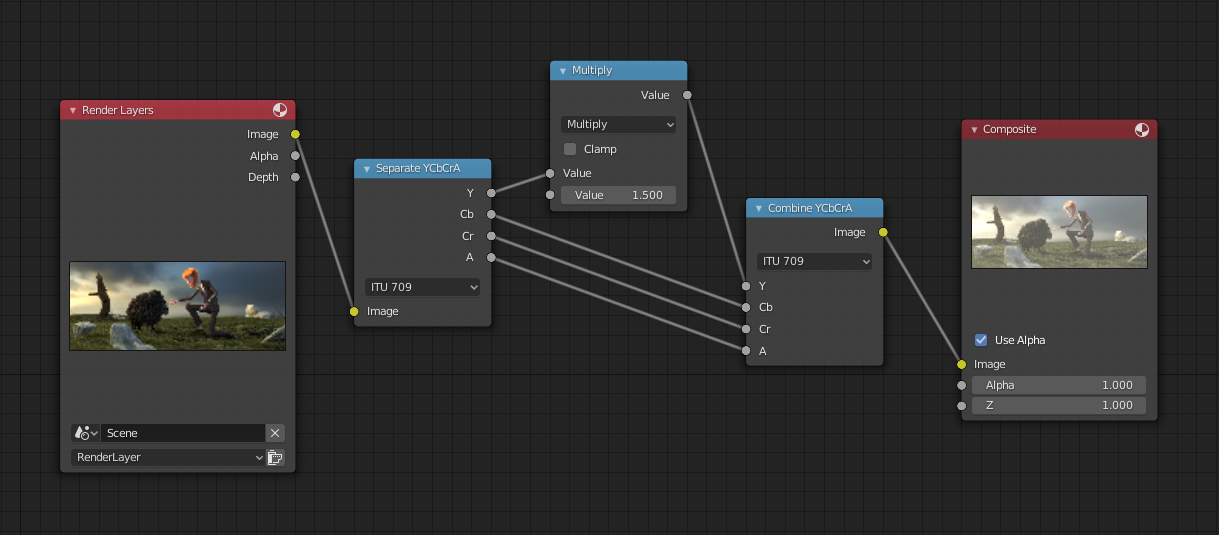
比例缩放单一通道范例。
本例中的 运算(相乘) 节点增加了图像的亮度通道(Y),使图像更加明亮。请注意,您应该使用一个 映射值节点,并启用最大值和最小值,以便将输出限制在有效值范围内。通过这种方法,您可以使用对数函数来制作高动态范围图像。在这个特定的范例中,还有一个 亮度/对比度节点,可以更简单地控制亮度。
重新限定颜色选择(色调分离)
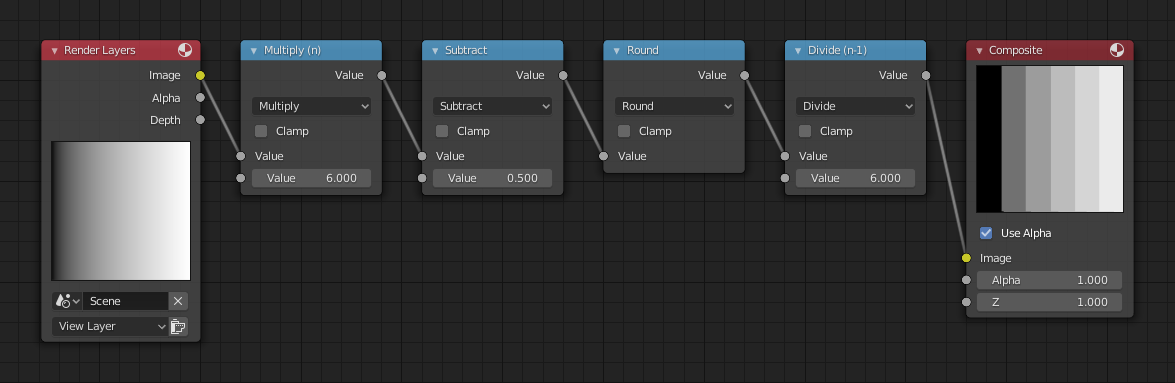
色调分离范例。
此范例中,我们重新限定颜色值为以下数值中之一:0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1 。
To split up a continuous range of values between 0 and 1 to certain set of values,
the following function is used:
要在 Blender 中执行该运算,可以考虑上图中的节点连线方式。我们通过将运算节点串连为一个函数,接受颜色值输入(取值范围从 0 到 1),分别乘以 6,则现有的数值分布(取值范围从 0 到 6),再将此结果偏移 0.5 (-0.5 到 5.5),然后四舍五入数值到最邻近的整数 (结果值为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5),然后将颜色像素值除以 5,得到 (0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0)。
In the case of a color image, you need to split it into separate RGB channels using Separate/Combine RGBA nodes and perform this operation on each channel independently.