Laplacian Deform Modifier¶
The Laplacian Deform modifier allows you to pose a mesh while preserving geometric details of the surface.
The user defines a set of „anchor“ vertices, and then moves some of them around. The modifier keeps the rest of the anchor vertices in fixed positions and calculates the optimal locations of all the remaining vertices to preserve the original geometric details.
This modifier captures the geometric details with the use of differential coordinates. The differential coordinates capture the local geometric information, the curvature and direction of a vertex based on its neighbors.
Bemerkung
You must define an Anchors Vertex Group. Without it the modifier does nothing.
Options¶
The Laplacian Deform modifier.¶
- Repeat
How many iterations to do to improve the found solution. The objective is to find the rotation of the differential coordinates preserving the best possible geometric details. Details are retained better if more iterations are used, however, it will take longer to calculate.
Deform horse example blend-file.¶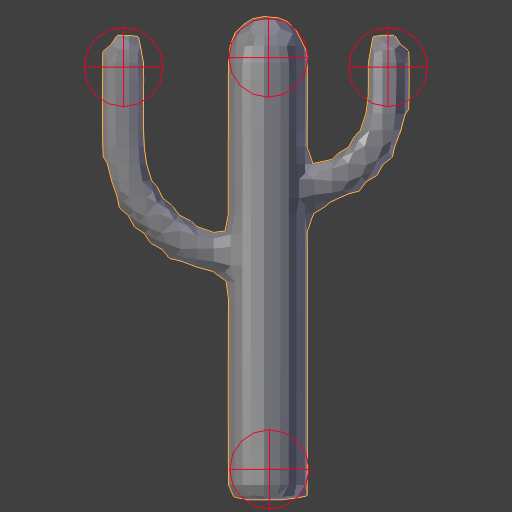 
Original Model.¶
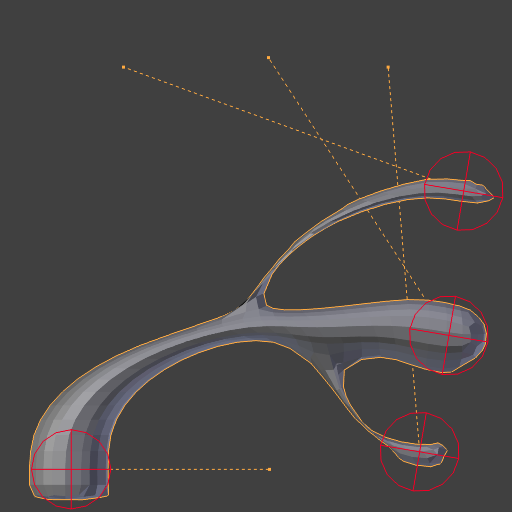
Repeat: 1.¶
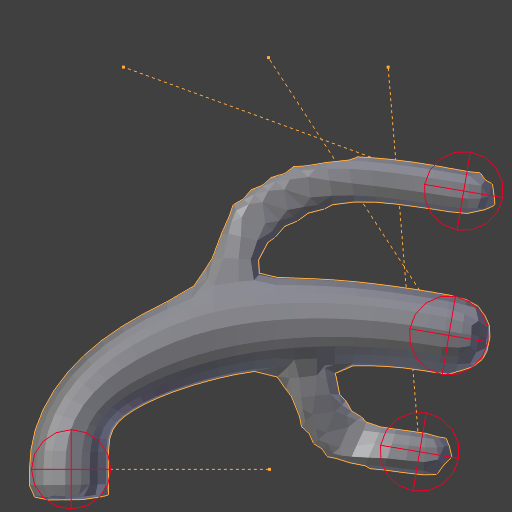
Repeat: 2.¶
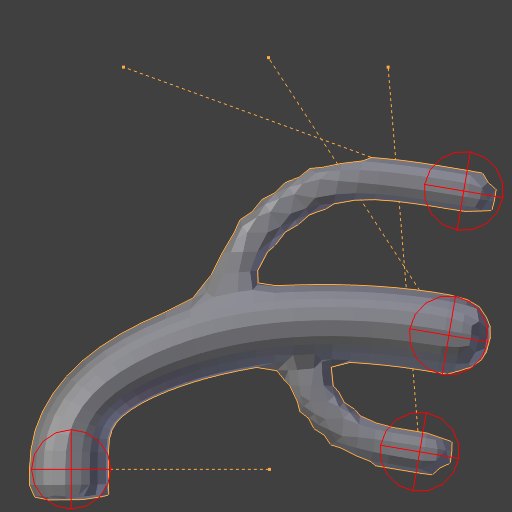
Repeat: 5.¶
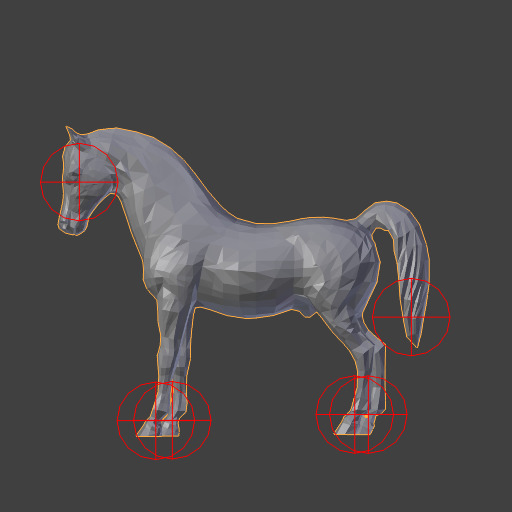
Original Model.¶
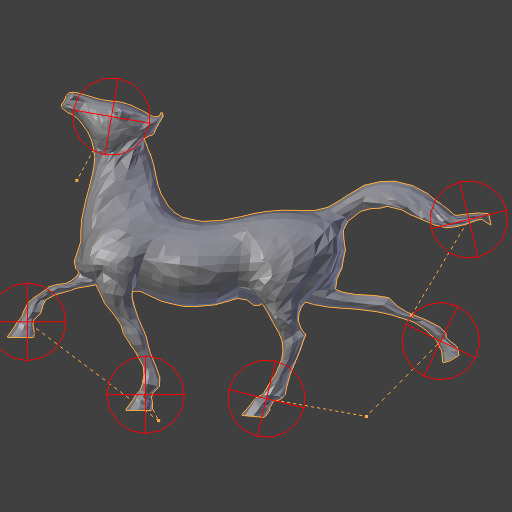
Repeat: 1.¶
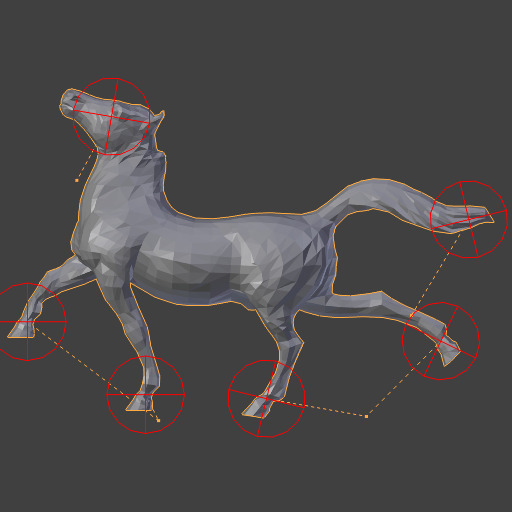
Repeat: 2.¶
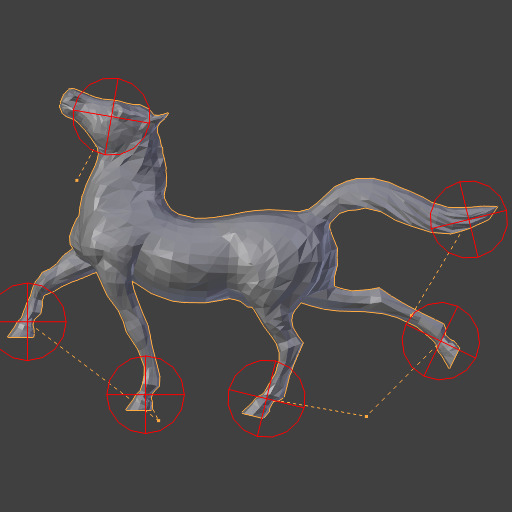

Repeat: 10.¶
- Anchors Vertex Group
The group of vertices that the user will use to transform the model. The weight of each vertex does not affect the behavior of the modifier, the method only takes into account vertices with weight greater than 0.
- Bind
The Bind button is what tells the Laplacian Deform modifier to actually capture the geometry details of the object, so that altering the anchor vertices actually alters the shape of the deformed object.
- Unbind
After binding the modifier, you may later decide to make changes to the Anchors Vertex Group. To do so you will first need to Unbind the modifier before binding it again.
Error Messages¶
- Vertex group group_name is not valid
This message is displayed when a user deletes the vertex group or changes its the name.
- Vertices changed from X to Y
This message is displayed when a user adds or deletes vertices to/from the mesh.
- Edges changed from X to Y
This message is displayed when a user adds or deletes edges to/from the mesh.
- The system did not find a solution
This message is displayed if the solver could not find a solution for the linear system.
Bemerkung
If the mesh is dense, with a number of vertices greater than 100,000, then it is possible that the nonlinear optimization system will fail.
History¶
Laplacian Surface Editing is a method developed by Olga Sorkine and others in 2004. This method preserves geometric details as much as possible while the user makes editing operations. This method uses differential coordinates corresponding to the difference between a vector and the weighted average of its neighbors to represent the local geometric detail of the mesh.
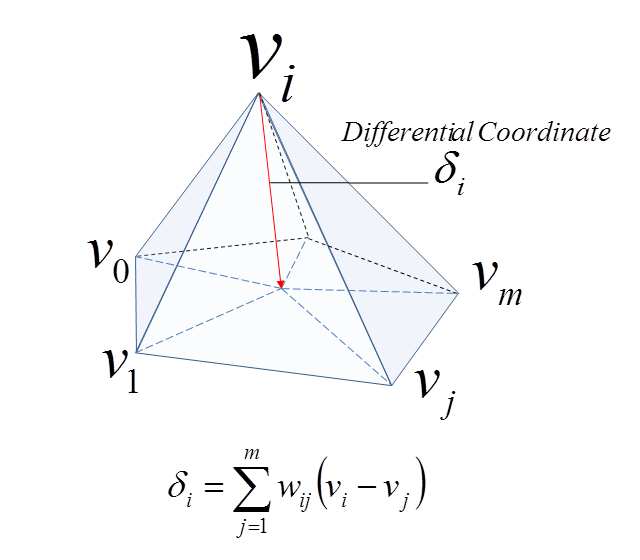
Differential Coordinate.¶