Empties¶
The « empty » is a single coordinate point with no additional geometry. Because an empty has no volume and surface, it cannot be rendered. Still it can be used as a handle for many purposes.
Sélection et édition¶
An empty can only be edited in Object Mode, which includes its transformation and parenting properties. For other tools see the Object section.
- Apply Scale Ctrl-A
While empties don’t exactly have any object data attached to them which can be used for supporting « true » apply scale (i.e. with non-uniform scaling), they do have Display Size which controls how large the empties are displayed (before scaling). This works by taking the scale factor on the most-scaled axis, and combines this with the existing empty Display Size to maintain the correct dimensions on that axis.
Propriétés¶
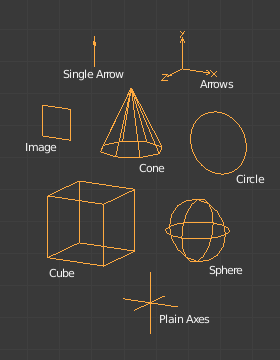
Empty Display Types.¶
- Display
- Plain Axes
Représenté par 6 lignes, initialement avec une ligne pointant dans chaque direction des axes +X, -X, +Y, -Y, +Z, et -Z.
- Arrows
Représenté par des flèches, initialement pointant dans les directions des axes positifs X, Y, et Z, chacune ayant une étiquette.
- Single Arrow
Représenté par une flèche unique, initialement pointant dans la direction de l’axe +Z.
- Circle
Représenté par un cercle initialement dans le plan XZ.
- Cube
Représenté par un cube, initialement aligné sur les axes XYZ.
- Sphere
Représenté par une sphère implicite définie par trois cercles. Initialement, les cercles sont alignés, chacun sur un des axes X, Y et Z.
- Cone
Représenté par un cône, initialement pointant dans la direction de l’axe +Y.
- Image
Empties can display images. This can be used to create reference images, including blueprints or character sheets to model from. The image is displayed regardless of the 3D display mode.
Empty Displays settings can be accessed from panel.
- Use Alpha
Use alpha blending instead of alpha-test (blends with the background but can have depth sorting artifacts).
- Opacity
Fade the image to make it transparent (uses the object Color’s alpha component).
- Offset X, Y
Offset the image origin (where 1.0 represents the width/height of the image).
- X=0.5, Y=0.5
Object origin at image center.
- X=0.0, Y=0.0
Object origin at image bottom, left.
- X=1.0, Y=1.0
Object origin at image top, right.
- Depth
- Default
Use normal depth behavior.
- Front
Afficher toujours au dessus des autres objets.
- Back
Afficher toujours derrière les autres objets.
Astuce
When using the image as a reference for modeling, it can be useful to set the depth to Front, with a low Opacity.
- Side
- Both
Afficher à la fois l’avant et l’arrière de l’empty.
- Front
Afficher seulement le devant de l’image.
- Back
Afficher seulement l’arrière de l’image.
Astuce
This is useful if you’re using an image as a reference where you have photos from both the front and back, so two empty images can be set only to show when viewed from the correct side.
- Display Orthographic
Montrer en vue orthographique.
- Display Perspective
Montrer en vue perspective.
Indication
C’est souvent pour désactiver ceci, ainsi les images de référence ne sont pas un obstacle lors de la visualisation d’un modèle.
- Display Only Axis Aligned
Only displays the image contents when the view is aligned with the object’s local axis.
- Size
Contrôle la taille de visualisation des empties. Ceci ne change pas son échelle, mais fonctionne comme un décalage.
Utilisation¶
Les empties peuvent servir de poignées de transformation. Quelques exemples d’utilisation comprennent :
Objet parent pour un groupe d’objets
An empty can be parented to any number of other objects. This gives the user the ability to control a group of objects easily, and without affecting a render.
Cible pour des contraintes
Un empty peut aussi être utilisé comme cible pour des contraintes normales ou des contraintes d’os. Ceci donne à l’utilisateur bien plus de contrôle ; par exemple, un rig peut être facilement installé pour permettre à une caméra de pointer vers un empty en utilisant la contrainte Track to,
Array offset
Un empty peut être utilisé pour décaler un modificateur Array, ce qui signifie que des déformations complexes peuvent être réalisées par le déplacement d’un seul objet.
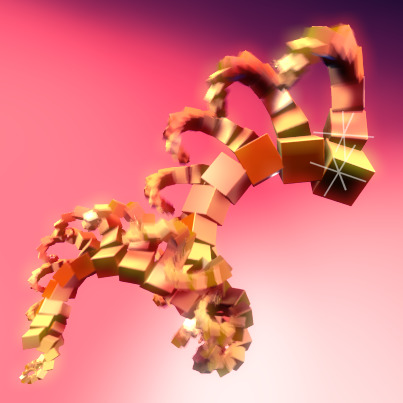

Exemple d’un empty utilisé pour contrôler un array.¶ |
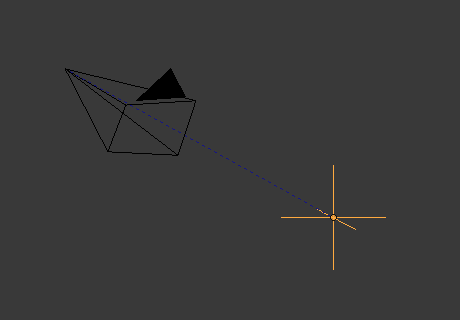
An example of an empty being used to control the Track To constraint.¶ |
Autres utilisations habituelles :
Placeholders
Contrôles de rigging
DOF distances
Images de référence