Hook Modifier
The Hook modifier is used to deform a mesh, curve or lattice using another object (usually an empty or a bone but it can be any object). As an object specified as hook moves, it pulls vertices or control points from the geometry with it. You can think of it as animated Proportional Editing.
While hooks do not give you the fine control over vertices movement that shape keys do, they have the advantage that you can select vertices directly for manipulation.
To assign selected vertices (in Edit Mode) you can use the Assign button on the modifier panel or use the Add Hook menu.
Options
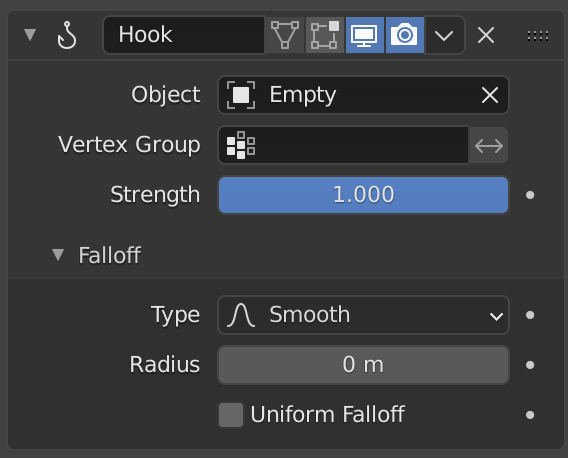
The Hook modifier.
- 오브젝트
The name of the object to hook vertices to.
- 버텍스 그룹
Allows you to define the influence per vertex.
Useful when you want something other than a spherical field of influence.
- Invert
<-> Inverts the influence of the selected vertex group, meaning that the group now represents vertices that will not be deformed by the modifier.
The setting reverses the weight values of the group.
- Invert
- Strength
Adjust this hooks influence on the vertices, were (0.0 to 1.0) (no change to fully follows the hook).
Since multiple hooks can work on the same vertices, you can weight the influence of a hook using this property.
The following settings are only available in Edit Mode:
- Reset
Recalculate and clear the offset transform of the hook.
- Recenter
Set the hook center to the 3D cursor position.
- Select
Select the vertices affected by this hook.
- Assign
Assigns selected vertices to this hook.
경고
The Hook Modifier stores vertex indices from the original mesh to determine what to affect. This means that modifiers that generate geometry, like Subdivision Surface, should always be put after the Hook one in the stack. Otherwise, the generated geometry will be left out of the hook’s influence.
Falloff
- Type
This can be used to adjust the kind of influence curve that the hook has on the mesh. You can also define a custom curve to get a much higher level of control.
- Radius
The size of the hooks influence.
- Uniform Falloff
This setting is useful when using hooks on scaled objects, especially in cases where non-uniform scale would stretch the result of the hook.
This is especially useful for lattices, where it is common to use non-uniform scaling.
Example
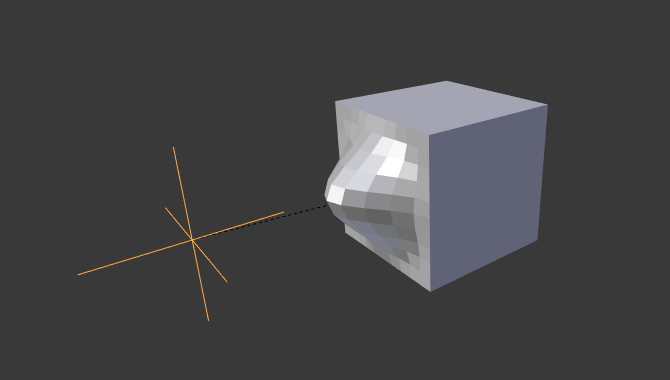
Empty used as Hook to deform a subdivided cube.