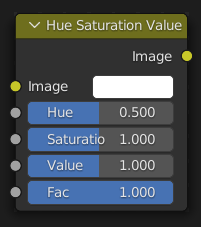
Hue Saturation Value Node
The Hue Saturation Value Node applies a color transformation in the HSV Color Model.
Inputs
- Factor
Controls the amount of influence the node exerts on the output image.
- 이미지
Standard color input.
특성
The transformations are relative shifts. In the shader and texture context the following properties are available as input sockets.
- Hue
Specifies the hue rotation of the image. 360° are mapped to (0 to 1). The hue shifts of 0 (-180°) and 1 (+180°) have the same result.
- Saturation
A saturation of 0 removes hues from the image, resulting in a grayscale image. A shift greater than 1.0 increases saturation.
- 값(value)
Value is the overall brightness of the image. De/Increasing values shift an image darker/lighter.
Outputs
- 이미지
Standard color output.
Hue/Saturation Tips
Some things to keep in mind that might help you use this node better:
- Hues are vice versa
A blue image, with a Hue setting at either end of the spectrum (0 or 1), is output as yellow (recall that white, minus blue, equals yellow). A yellow image, with a Hue setting at 0 or 1, is blue.
- Hue and Saturation work together.
So, a Hue of 0.5 keeps the blues the same shade of blue, but Saturation can deepen or lighten the intensity of that color.
- Gray & White are neutral hues
A gray image, where the RGB values are equal, has no hue. Therefore, this node can only affect it with Value. This applies to all shades of gray, from black to white; wherever the values are equal.
- Changing the effect over time
The Hue and Saturation values can be animated with a Time Node or by animating the property.
참고
Tinge
This HSV node simply shifts hues that are already there. To colorize a gray image, or to add a tint to an image, use a Mix node to add in a static color from an RGB input node with your image.
HSV Example
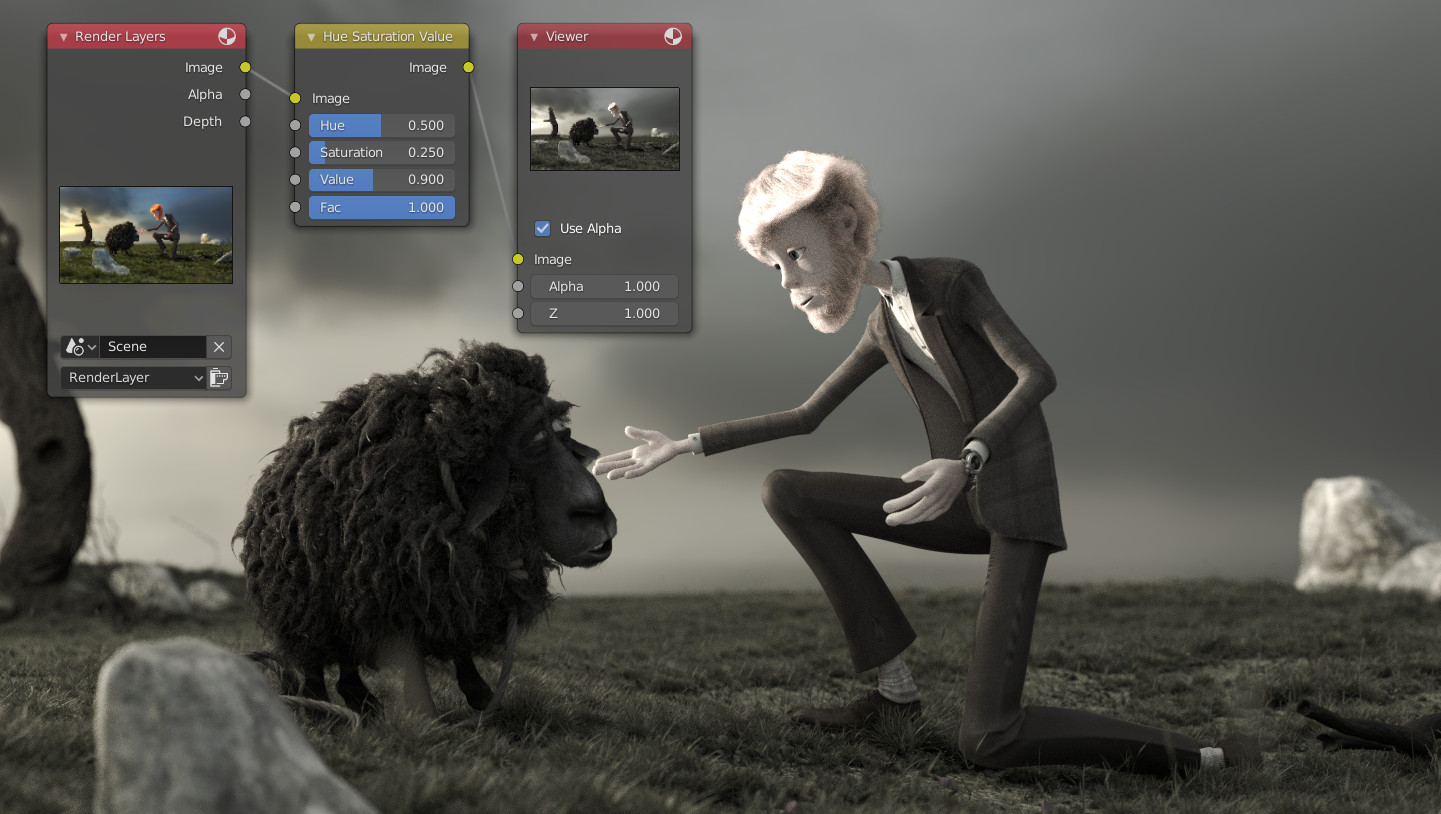
A basic example.
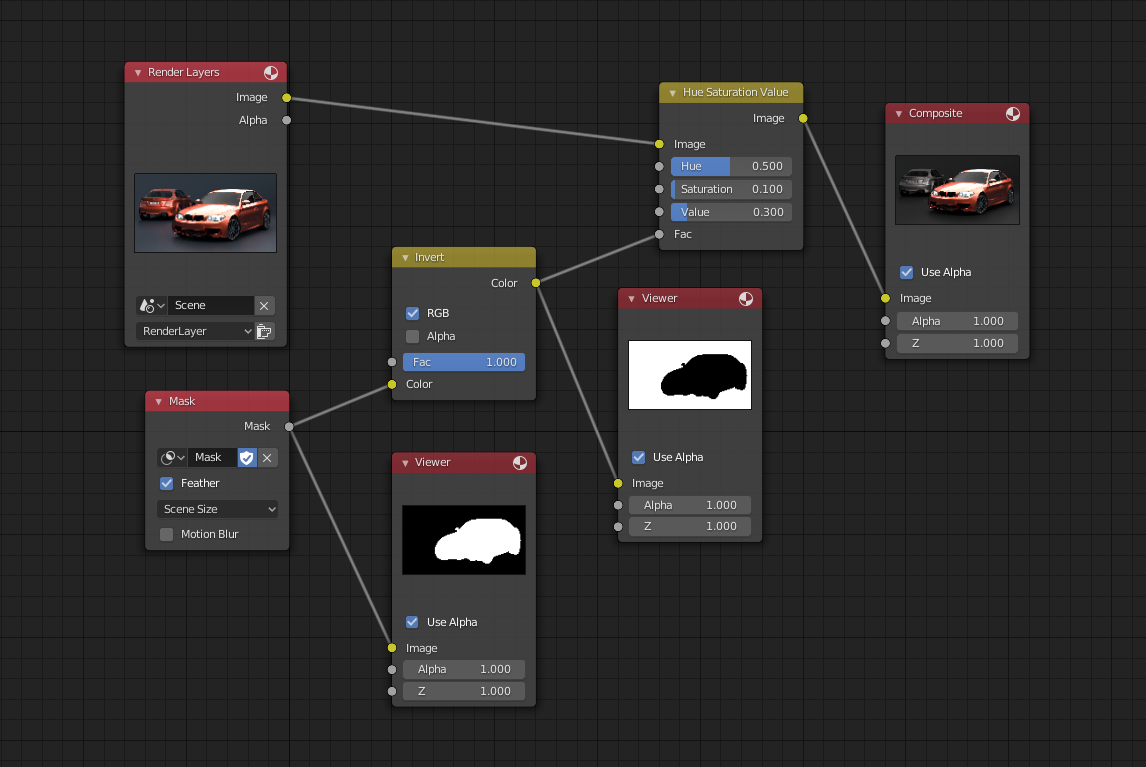
An example of using the Factor input for masking.