Simulation Zone
Simulation zones allow the result of one frame to influence the next one. That way even a set of simple rules can lead to complex results, with the passing of time. The most common type of them is physics simulation, with specific solvers for physical phenomena.
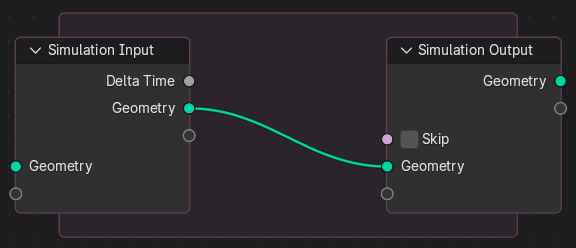
Nós de simulação iniciais e zona de simulação.
Ao adicionar uma simulação, dois nós são adicionados, definindo entre eles uma «Zona de Simulação».
As entradas que são conectadas ao nó Simulation Input são calculadas apenas uma vez, no início da simulação, passadas para o próximo estado da simulação e eventualmente gerado. Outros nós podem ser conectados dentro da região de simulação a partir de fora. Esses são re-calculados a cada passo baseados em seu valor em determinado quadro.
It is not possible to have any link going towards outside. The result of the simulation can only be accessed via the Simulation Output node. This also allows sub-frame interpolation for motion blur.
Nota
This node cannot be used in the Tool context—only in the Modifier context.
Clock
The simulation is tied to the animation system, with support for sub-steps. It will only be evaluated while the animation frame changes, and is cached like the existing physics simulations in Blender.
Properties
In the Node Editor the inputs can be renamed, shuffled and removed. This is also the place where sub-steps can be defined for a simulation.
Inputs
- Skip
Forward the output of the simulation input node directly to the output node and ignore the nodes in the simulation zone.
Gerar e gravar
The simulation is automatically cached during playback. The valid cache can be seen as a strong yellow line in the timeline editor. This allows for animators to quickly inspect all the previous frames of a simulation.
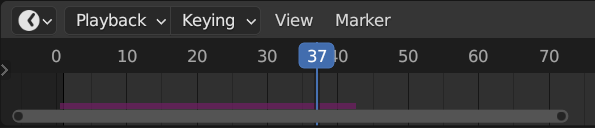
Cached frames in the Timeline.
For the cases where the current frame is the only one relevant, users can opt-out of «Cache» to save memory.
When the result is ready to be sent to a render-farm, it can be baked to disk. This allows for the simulation to be rendered in a non-sequential order.
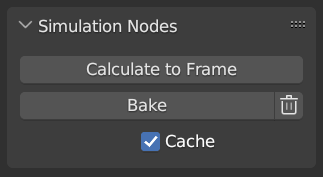
Simulation and Physics, Simulation Nodes user interface.
Nota
Baking the simulation will bake all the simulations in all modifiers for the selected objects.
Examples
Combined with the Index of Nearest, this can be used for a number of sphere-based simulations.
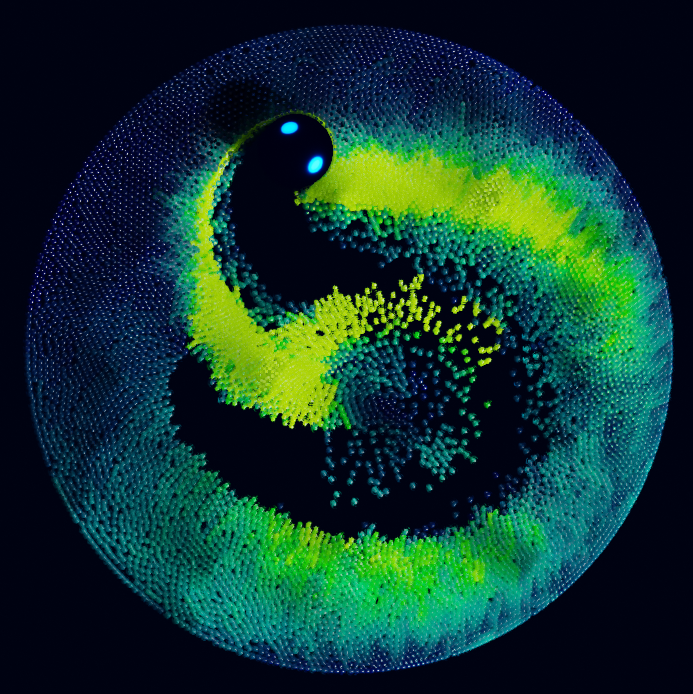
Index of Nearest sample file CC-BY Sean Christofferson.