数据块
任何 Blender 项目的基本单元都是数据块。数据块的例子包括:网格(meshes)、物体(objects)、材质(materials)、纹理(textures)、节点树(node-trees)、场景(scenes)、文本(texts)、笔刷(brushes),甚至是工作区(Workspaces)。
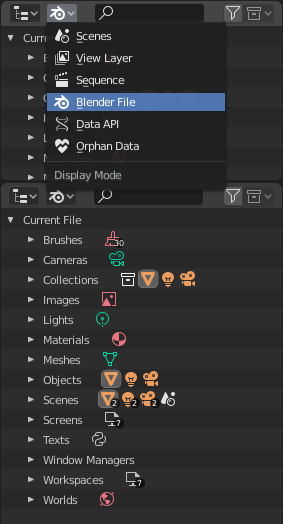
Blender 文件的大纲视图。
一个数据块是不同类型数据的一种通用抽象,具有一组共同的基本特征、属性和行为。
通用特性:
各种数据块是组成
.blend文件的主要内容。可以互相关联,以便于重复利用和实例化。(父/子、物体/物体数据,材质/图像,以及修改器和约束等方式)
对于同一个
.blend文件中的给定的数据块类型,其名字是唯一的。允许添加、删除、修改和复制。
数据块能在文件之间相互关联(仅限部分数据块)。
可以有自己的动画数据。
They can have Custom Properties.
用户通常会与更高级别的数据类型(物体、网格等)进行交互。在执行更复杂的项目时,管理数据块变得更加重要,尤其是在相互关联 blend 文件时。主要的编辑器是大纲。
并非 Blender 中的每个数据都是数据块,例如骨骼、序列片段或顶点组就不是数据块,它们分别从属于骨架、场景和网格类型。
数据块类型
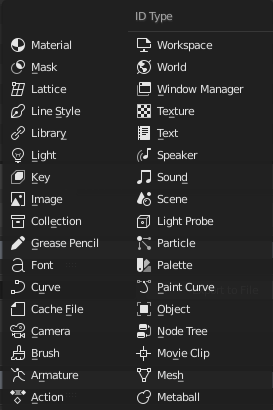
数据块类型及其图标。
这里有一张表格,列出了 .blend 文件中存储的数据类型,仅供参考。
- 关联
库关联,支持关联到其他
.blend文件中。- 打包
文件打包,支持将文件内容打包到 blend 文件中( 不 适用于大多数没有文件引用的数据块)。
类型 |
关联 |
打包 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
✓ |
— |
Stores animation F-Curves.
Used as data-block animation data,
and the Nonlinear Animation editor.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Skeleton used to deform meshes.
Used as data of armature objects, and by the Armature Modifier.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Used by paint tools.
|
|
✓ |
— |
用于相机物体的数据。
|
|
✓ |
— |
用于网格缓存修改器。
|
|
✓ |
— |
用作曲线、字体和曲面物体的数据。
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
References font files.
Used by curve object-data of text objects.
|
|
✓ |
— |
2D/3D sketch data used by Grease Pencil objects.
Used as overlay helper info, by the
3D Viewport, Image, Sequencer & Movie Clip editors.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Group and organize objects in scenes.
Used to instance objects, and in library linking.
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
Image files.
Used by shader nodes and textures.
|
|
✗ |
— |
Geometry shape storage, which can be animated.
Used by mesh, curve, and lattice objects.
|
|
✓ |
— |
用作灯光物体的数据。
|
|
✗ |
✓ |
References to an external blend-file.
Access from the Outliner's Blender File view.
|
|
✓ |
— |
用于 FreeStyle 渲染引擎。
|
|
✓ |
— |
Grid based lattice deformation.
Used as data of lattice objects, and by the Lattice Modifier.
|
|
✓ |
— |
2D animated mask curves.
Used by compositing nodes & sequencer strip.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Set shading and texturing render properties.
Used by objects, meshes & curves.
|
|
✓ |
— |
An isosurface in 3D space.
Used as data of metaball objects.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Geometry made of vertices/edges/faces.
Used as data of mesh objects.
|
|
✓ |
✗ |
Reference to an image sequence or video file.
Used in the Movie Clip editor.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Groups of re-usable nodes.
Used in the node editors.
|
|
✓ |
— |
An entity in the scene with location,
scale, rotation.
Used by scenes & collections.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Stores a paint or sculpt stroke.
Access from the paint tools.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Store color presets.
Access from the paint tools.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Particle settings.
Used by particle systems.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Help achieve complex real-time lighting in Eevee.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Primary store of all data displayed and animated.
Used as top-level storage for objects & animation.
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
Reference to sound files.
Used as data of speaker objects.
|
|
✓ |
— |
Sound sources for a 3D scene.
Used as data of speaker object.
|
|
✓ |
✗ |
Text data.
Used by Python scripts and OSL shaders.
|
|
✓ |
— |
2D/3D textures.
Used by brushes and modifiers.
|
|
✗ |
— |
The overarching manager for all of Blender's user interface.
Includes Workspaces, notification system, operators, and keymaps.
|
|
✓ |
— |
定义全局渲染环境的设置项。
|
|
✗ |
— |
UI layout.
Used by each window, which has its own workspace.
|
生命周期
每个数据块都有其使用计数(引用计数),当有多个数据块时,您可以在界面中其名称右侧看到数据块的当前用户数。Blender 遵循一般规则,即未使用的数据最终被删除。
由于在工作时添加和删除大量数据是很常见的,因此这样做的好处是不必手动管理每个数据块。这通过在写入 blend 文件时跳过零用户数据块来实现。
保护
由于零用户的数据块不会被保存,但有时你可能想要强制保留这些数据,而无需关心其使用者。
如果要构建一个 blend 文件作为要关联到其他文件和从其他文件关联的资产库,则需要确保它们不会意外地从库文件中删除。
要保护数据块,请使用其名称旁边带有盾牌图标的按钮。然后,Blender 将永远不会静默删除数据块,但如果需要,您仍然可以手动删除它。
生成单用户
在多个用户之间共享数据块时,可以通过单击其名称右侧的用户计数按钮为指定的用户生成数据块的副本。这会复制该数据块并将新创建的副本分配给这个用法。
Note
物体具有一组更高级的操作,可以成为单用户,请参阅其文档。
删除数据块
如生命周期中所述,当数据块不再使用时,通常会将其删除。它们也可以被手动 取消关联 或 删除。
取消关联数据块意味着其用户将不再使用它。这可以通过单击数据块名称旁边的 “X” 图标来实现。如果您取消与所有用户的关联数据块,则最终将被 Blender 删除,如上所述(除非它是受保护的)。
删除数据块将直接从 .blend 文件中删除它,自动将其与所有用户断开连接。这可以通过在其名称旁边的 “X” 图标上点击 Shift-LMB 来实现。
Warning
删除某些数据块可能会导致某些用户被删除,如果没有这些数据块这些用户将无效。常见的例子比如删除物体数据(如网格、曲线、摄像机……)也将删除使用它的所有物体。
这两种操作也可以在上下文菜单中使用 RMB - 单击 大纲视图 中的数据块。
自定义属性
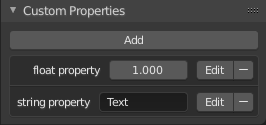
自定义属性面板。
自定义属性是一种在 Blender 的数据块中存储您自己的数据的方法。它可用于绑定(骨骼和物体可以具有驱动其他属性的自定义属性)和 Python 脚本,其中定义 Blender 中不可用的新设置是很常见的。还可以通过属性节点从材质访问自定义属性。
只有这些数据支持自定义属性:
所有数据块类型。
骨骼和姿态骨骼。
序列片段。
要添加自定义属性,请搜索大多数属性或侧栏区域底部的 自定义属性 面板,然后单击 新建。可以使用删除图标从同一位置删除属性。属性添加后,可以通过编辑图标进行配置,以处理特定用例;有关详细信息,请参阅编辑属性。
编辑属性
用户界面
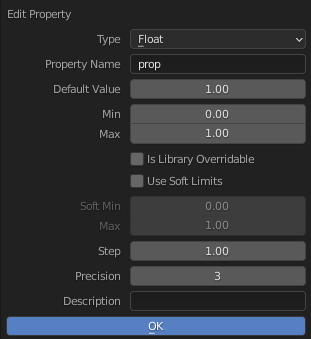
编辑自定义属性的弹框。
自定义属性可以使用可用于支持它的数据类型的面板进行编辑。编辑属性允许您配置默认值、范围,甚至添加自定义工具提示。
- 类型
属性的数据类型;不同的数据类型只能具有特定的数据属性。
- 浮点
小数位数值,例如 3.141、5.0 或 6.125 。
- 浮点数列
多个浮点数据类型的集合,例如
[3.141, 5.0, 6.125]。这种数据类型还可用于可表示为诸如颜色的浮点数组的数据。这些特殊的浮点数组可以在 子类型 选择器中设置。- 整数
没有任何小数位数的数值,例如 1、2、3 或 4 。
- 整数数列
多个整数数据类型的集合,例如
[1, 2, 3, 4]。- 字符串
一个字符序列,如 "一些文本"。
- Python
直接编辑 Python 数据类型,用于不支持的数据类型。
Note
Boolean values must be handled as integers and only work when using Min/Max values that are integers and that are no more than 1 apart.
At this point, the Boolean values will still look like integers but behave like a Boolean having one lower, off, value and a higher, on, value.
- 阵列偏移
数组中的元素数。请注意,如果数组长度大于 7,则无法直接编辑其元素,则必须按 编辑值 编辑数组的元素。
- 属性名
显示在值左侧的文本。此名称还用于通过 Python 访问属性。
- 默认值
This sets the default value of the property used by the Reset to Default Value operator.
Warning
默认值用作 NLA 混合 的基础,而用于作为关键帧的属性上的无意义默认值(例如,用于缩放的属性为 0)可能会导致问题。
- 最小值,最大值
自定义属性可以采用的最小/最大值。
- 库重写
当数据块被关联时,允许属性重写。
- 软限制
开启通过滑块调整 属性值 的限制,而无需以数字方式输入值。
- 软限制最小值、最大值
软限制的最小/最大值。
- 步长
用于控制数据类型一次增量的乘数。浮点的内部步长为 0.01,因此 步长 值为 5 将以 0.05 的速率递增,步长 值为 100 将递增 1.0。对于整数,内部步长为 1。
- 精度
要在用户界面中显示的浮点数据类型的小数后面的位数。
- 子类型
Specifies the type of data the property contains, which affects how it appears in the user interface. In order for this property to appear the Property Value must be a vector of floats. For either of the color subtypes to work the Property Value must be a vector with three or four values depending on the availability of an Alpha Channel.
- 描述
允许你为你的自定义属性编写提示。
Python 脚本访问
可以通过与字典类似的方式访问自定义属性,其中键值只能是字符串,而值只能是字符串、数字、数组或嵌套属性。
有关详细信息,请参阅 API 文档。