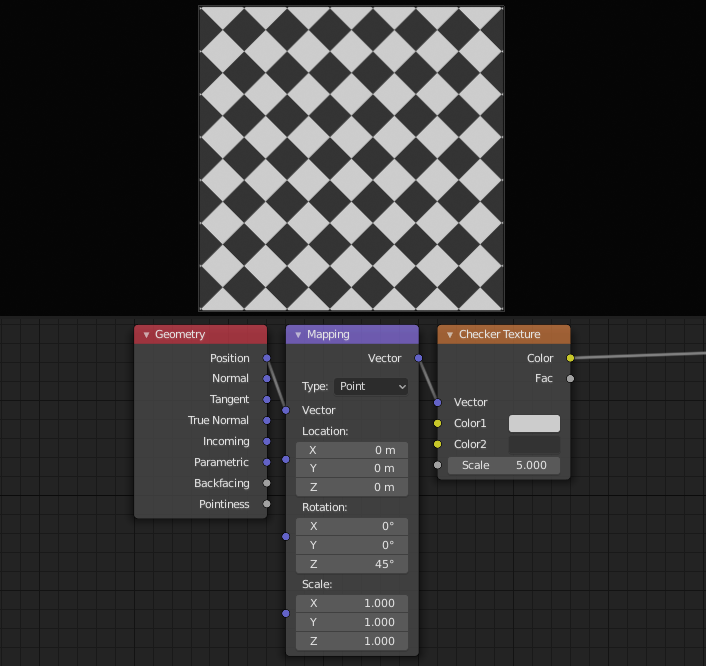
Mapping Node¶
The Mapping node transforms the input vector by applying translation, rotation, and scaling.
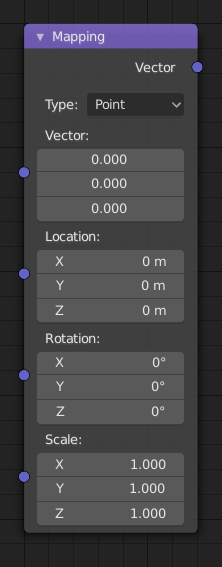
Mapping node.¶
Inputs¶
The inputs of the node are dynamic. In particular, the Location input is only available in the Texture and Point vector types.
- Vector
The vector to be transformed.
- Location
The amount of translation along each axis.
- Rotation
The amount of rotation along each axis. XYZ order.
- Scale
The amount of scaling along each axis.
Properties¶
- Vector type
The node applies the transformation differently depending on the semantic type of the input vector.
- Point
For this vector type, the node performs a straightforward transformation.
Transforming a texture coordinates is analogous to transforming a UV map. For instance, translating the texture coordinates along the positive X axis would result in the evaluated texture to move in the negative X axis, much like if one translated a UV map. Similarly, scaling the texture coordinates up would result in the evaluated texture to scale down. So transforming the texture coordinates would appear to have the opposite effect on the evaluated texture.
The order of transformation is: Scale –> Rotate –> Translate, which means:
Translation moves the input along the local rotation axis.
Rotation rotates the input around the origin of the space.
Scaling scales the input along the global axis.
- Texture
For this vector type, the node performs an inverse transformation.
Inverse transforming a texture coordinates would, as opposed to the Point type, transform the evaluated texture itself. For instance, translating the texture coordinates along the positive X axis would result in the evaluated texture to move in the positive X axis, as one would expected. Similarly, scaling the texture coordinates up would result in the evaluated texture to scale up, as one would expect.
The order of transformation is: Translate –> Rotate –> Scale, which means:
Translation moves the input along the global axis.
Rotation rotates the input around the translation vector.
Scaling scales the input along the local rotation axis.
- Vector
For this vector type, a Point transformation is performed, but with zero translation.
- Normal
For this vector type, the node performs the inverse transpose of the transformation and normalize the result. Such transformation ensures correct normals after non-uniform scaling. So this type should be used when transforming normals.
Outputs¶
- Vector
The input vector after transformation.