Image Settings¶
Image Panel¶
- Image
Data-block menu.
- New
+ The New Image button opens a pop-up to configure a Generated image.
- New
Source¶
See about supported Supported Graphics Formats.
Single Image¶
Still image or a single frame.
Image Sequence¶
Each frame is stored in a separate file. How to Opening an Image Sequence.
- Frame
A label showing the current frame.
- Further options
See Movie below.
Movie¶
Frames packed into a container.
- Deinterlace
Removes fields in a video file. For example, if it is an analog video and it has even or odd interlacing fields.
- Frame
- Frames
Sets the range of frames to use.
- Start
Global starting frame of the sequence, when the playback should start. This is a global setting which means it affects all clip users such as the Movie Clip editor itself, motion tracking constraints and Compositor nodes.
- Offset
Offsets the first frame of the clip. It adds an extra offset to the frame number when converting a scene frame to the frame number in the file name. This option does not affect tracking data or any other associated data.
- Match Movie Length
This button sets the movies frames to the length of the selected movie.
- Auto Refresh
Automatically refresh images on frame changes.
- Cyclic
Start over and repeats after the last frame to create a continuous loop.
Generated¶
Image generated in Blender.
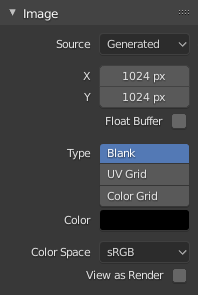
Image panel for Generated source.¶ |
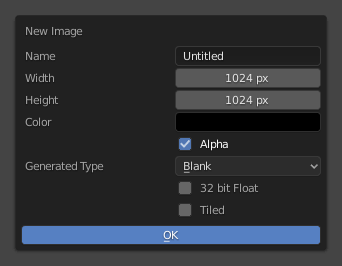
The New Image pop-up menu.¶ |
- Width, Height
The size of image in pixels.
- Color
Sets the fill color if creating a blank image.
- Type
- Blank
Creates a Blank image of a single specified color.
- UV Grid
Creates a checkerboard pattern with a colored cross (+) in each square.
- Color Grid
Creates a more complex colored grid with letters and numbers denoting locations in the grid. It could be used for testing how the UVs have been mapped and to reduce stretching or distortion.
- 32-bit Float
Creates a 32-bit image. This is a larger file size, but holds much more color information than the standard 8-bit image. For close-ups and large gradients, it may be better to use a 32-bit image.
- Tiled
Creates an image with support for UDIMs. This option creates the first
1001tile; more tiles can be added later in the UDIM Tiles panel.
Common Options¶
- File
Use for replacing or packing files.
- Pack
Embed the resource into the current blend-file.
- Path
Path to the linked file.
- Open
Opens the File Browser to select a file from a drive.
- Reload
Reloads the file. Useful when a file has been reworked in an external application.
- Color Space
-
- sRGB
Standard RGB display space.
- Linear
Linear 709 (full range). Blender native linear space.
- Linear ACES
ACES linear space.
- XYZ
Standard linear XYZ space.
- Non-Color
Color space used for images which contains non-color data (e.g. normal maps).
- Raw
Same as Non-Color.
- Filmic Log
Intermediate log color space of Filmic view transform.
- Half Float Precision
Load the image as having only a Bit Depth of 16 bits per channel instead of 32 bits which saves memory.
- View as Render
Applies color transform when displaying this image on the screen.
- Use Multi-View
See Multi-View.
- Alpha
Representation of alpha in the image file, to convert to and from when saving and loading the image. See Alpha Channel.
- Straight
Store RGB and alpha channels separately with alpha acting as a mask, also known as unassociated alpha. Commonly used by image editing applications and file formats like PNG. This preserves colors in parts of the image with zero alpha.
- Premultiplied
Store RGB channels with alpha multiplied in, also known as associated alpha. The natural format for renders and used by file formats like OpenEXR. This can represent purely emissive effects like fire correctly, unlike straight alpha.
- Channel Packed
Different images are packed in the RGB and alpha channels, and they should not affect each other. Channel packing is commonly used by game engines to save memory.
- None
Ignore alpha channel from the file and make image fully opaque.