Dilate/Erode Node¶
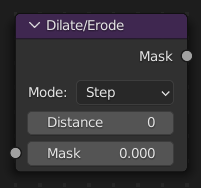
The Dilate/Erode node expands and shrinks masks, using a morphological operator.
Inputs¶
- Mask
Single color channel (or a black-and-white image) input.
Properties¶
- Mode
Step, Threshold, Distance, Feather
- Distance
The Distance is the filter radius. A positive value of Distance dilates (expands) the influence of a pixel on its surrounding pixels. A negative value erodes (shrinks) its influence.
- Edge
Edge to inset.
- Falloff
Falloff type the feather.
Outputs¶
- Mask
The filtered mask output.
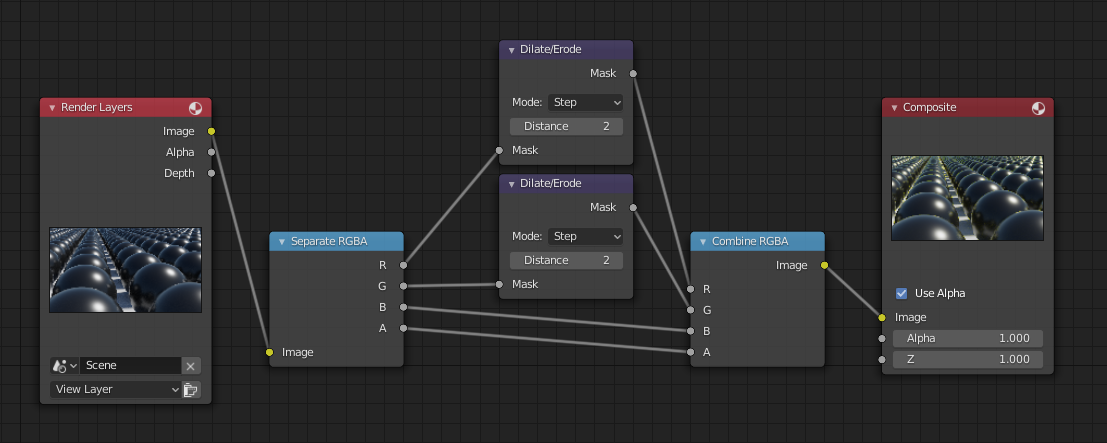
Example¶
In this example, we wanted to take the rather boring array of ball bearings and add some variation to it. So, we dilated the red and eroded the green, leaving the blue alone. If we had dilated both red and green… (hint: red and green make yellow). The amount of influence is increased by increasing the Distance values. Blend-file available here.