Common¶
Target¶
The Target Data ID field lets you link the constraint to a Target object of your choosing. This link provides data to the constraint so that it can begin to function. For example, the Copy Location Constraint needs location data to function. Fill in the Target field, and the Copy Location constraint will begin to use location data from the Target object.
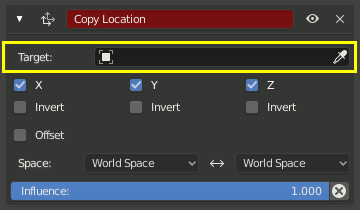
El Target field debe ser completado para que el constraint funcione.¶
By default, the Target will use the object origin as the target point.
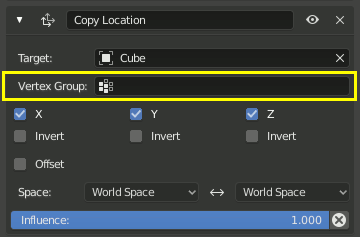
If the Target field links to a mesh or lattice object, a Vertex Group field will appear. Enter the name of a vertex group and the constraint will target the median point of this vertex group instead of the object’s origin.
If the Target field links to an Armature, a Bone field will appear along with a Head/Tail slider. Enter the name of a bone and the constraint will target the bone instead of the entire armature object origin.
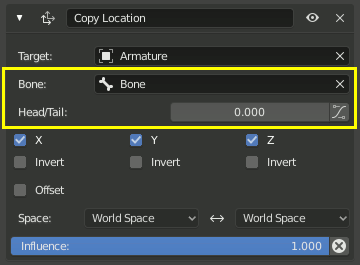
The slider moves the precise position of the target between the head and tail of the bone. Some constraints have a button next to the slider that enables using the curved shape of Bendy Bones.
Space¶
Constraints necesitan de un marco de referencia para funciónar. Este marco dede referencia es el llamado «space» de el constraint. La elección de un espacio frente a otro va a cambiar este marco de referencia y alterar sustancialmente el comportamiento de una restricción»
Para entender cómo cambiar el espacio de cambiar el comportamiento de elconstraint, considere la posibilidad de experimentar con dos empties. Asegúrese de que mostrar como flechas, de modo que usted puede ver a los ejes locales de cada uno de los empty. Asegúrese de que el tamaño de un empty sea un poco más grande que el otro, de manera que ambos están siempre visible incluso si directamente en la parte superior de uno al otro. A continuación, agregue un constraint a un vacío que se dirige a los otros y experimentar a fondo por el movimiento, la rotación y el escalado de la target en muchas maneras diferentes.
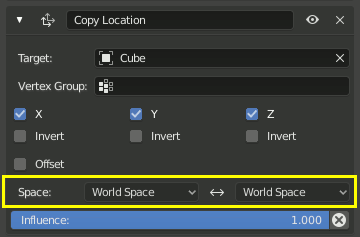
Este constraint está configurado para utilizar el World Space como marco de referencia para la tanto en su Target Space y sus Owner Space.¶
Target Space & Owner Space¶
The space used to evaluate the target of the constraint is called the Target Space. The space used to evaluate the constrained object (the object that owns the constraint) is called the Owner Space. Hover over the space select menu(s) to learn whether it affects the space of the target or the space of the owner.
When the constraints use a Target and/or/nor an Owner space there will be no, one or two selector(s). The Copy Location constraint in example use both Target and Owner space.
Cuando un constraint utiliza tanto Target y Owner space, el Target y Owner puede ser cualquier combinación de los tipos de espacio.
Space Types¶
- World Space
En este tipo de espacio el world es el marco de referencia para el objeto (ohueso). La ubicación es relativa al mundo de origen. La rotación y la Escala orientado al mundo de los axes. Las transformaciones en el objeto, el objeto los padres y cualquier otra restricción más arriba en la restricción de pila tomados en cuenta»
- Local Space
In this space type the parent of the object (or bone) is the frame of reference. Location is relative to the parent object origin. Rotation and Scale are oriented to the parent object axes. Only transformations to the object itself are taken into account. Transformations to the object’s parent are not taken into account.
- Local Con Parent (huesos sólo)
The bone properties are evaluated relative to its rest pose location and orientation, thus including both its own transformations and those caused by a possible parent relationship (i.e. the chain’s transformations above the bone).
- Pose Space (huesos sólo)
Las propiedades de los huesos se evalúan en el objeto armadura espacio local (i.e. independientemente de la armadura transformaciones en Object Mode). Por lo tanto, si el objeto armadura ha null transformaciones Pose Space tienen el mismo efecto como World Space.
Influencia¶
El control de influencia deslizante determina el constraint afectará de el objeto (target).
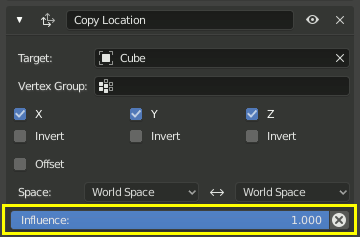
Influencia de 0.0 no tendrá ningún efecto. Una influencia de 1.0 es efecto completo.
Values between (0.0 and 1.0) will have a partial effect, but be careful. These partial effects can be difficult to control, especially as the constraint stack grows in complexity.
El valor de influencia puede ser animada, permitiendo constraints ser desactivado,o prendido parcialmente según sea necesario.
The X button after the influence slider can be used to disable the constraint while trying to
preserve the current object position. This may not work perfectly if other constraints remain active.