Shrinkwrap Modifier¶
The Shrinkwrap modifier allows an object to «shrink» to the surface of another object. It moves each vertex of the object being modified to the closest position on the surface of the given mesh (using one of the four methods available).
It can be applied to meshes, lattices, curves, surfaces and texts.
Options¶
The Shrinkwrap modifier in Nearest Surface Point mode.¶
- Target
Shrink target, the mesh to shrink to/wrap around.
- Offset
The distance that must be kept from the calculated target position.
- Vertex Group
The vertex group to control whether and how much each vertex is displaced to its target position. If a vertex is not a member of this group, it is not displaced (same as weight 0).
Mode¶
This selector specifies the method to be used to determine the nearest point on the target’s surface for each vertex of the modified object. Some options will add some extra, specific controls to the panel.
Nearest Surface Point¶
This will select the nearest point over the surface of the shrunk target.
Project¶
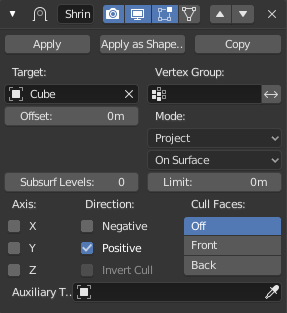
Project mode.¶
This will project vertices along a chosen axis until they touch the shrink target. Vertices that never touch the shrink target are left in their original position.
- Subdivision Surface Levels
This applies a (temporary) Catmull-Clark subdivision to the modified object’s geometry, before computing the wrap.
- Limit
This is a distance limit between original vertex and surface. If the distance is larger than this limit vertex would not be projected onto the surface.
- Axis X/Y/Z
Along which local axis of the modified object the projection is done. These options can be combined with each other, yielding a «median axis» of projection. If none are selected, the normal direction is used.
- Direction Negative/Positive
This allows you to select the allowed direction(s) of the shrink along the selected axis. If both options are enabled, the modifier tries both ways and selects the closest hit.
- Cull Faces Off/Front/Back
Allows you to prevent any projection over the «front side» (respectively the «back side») of the target’s faces. The «side» of a face is determined by its normal (front being the side «from where» the normal «originates»).
- Invert Cull
If Cull Faces is enabled, and Negative direction along axis is allowed, this option can be used to invert the Front or Back cull choice for the Negative direction. This is useful when projecting in both directions.
- Auxiliary Target
An additional object to project over.
Nearest Vertex¶
Nearest Vertex mode.¶
This will snap vertices to the nearest vertex of the shrunk target. It adds no extra options.
This method doesn’t support the Snap Mode setting described below.
Target Normal Project¶
Target Normal Project mode.¶
This mode is similar to Nearest Surface Point, but produces a much smoother projection in return for being significantly slower.
Instead of finding the closest point, it searches for the nearest point that has its interpolated smooth normal pointing towards or away from the original vertex position. Non-manifold boundary edges are specially handled as infinitely thin cylinders that emit normals in all perpendicular directions. Ignores flat shading and auto smooth settings.
Snap Mode¶
Most modes support an additional setting to control how the vertex is moved to the target point selected by the methods described above. Some of the choices only differ if Offset is not zero.
- On Surface
The vertex is always moved. The offset is applied along the projection line connecting the original vertex and selected target point towards the original position.
- Outside Surface
Like On Surface, but the offset is always applied towards the outside of the target.
- Above Surface
Like On Surface, but the offset is applied along the smooth normal of the target.
- Inside
The vertex is not moved if it is already inside the target. Offset shrinks the allowed volume towards the inside along the projection line.
- Outside
The vertex is not moved if it is already outside the target. Offset expands the exclusion volume towards the outside along the projection line.
The Inside and Outside options can be used for very crude collision detection. The inside vs outside determination is done based on the target normal and is not always stable near 90 degree and sharper angles in the target mesh.
Ver también