Options de sortie¶
La première étape du processus de rendu est de déterminer et de définir les options de sortie. Celles-ci comprennent la taille de rendu, la fréquence de trames, l’aspect ratio du pixel et le type de fichier.
Panneau Dimensions¶
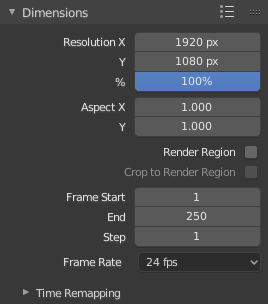
Panneau Dimensions.
- Préréglages de rendu
- Préréglages de format pour les TV et les écrans.
- Resolution
- X/Y
- Le nombre de pixels horizontaux et verticaux dans l’image.
- Percentage
- Curseur pour réduire ou d’augmenter la taille de l’image rendue par rapport aux valeurs X/Y ci-dessus. C’est utile pour des petits rendus test qui ont les mêmes proportions que l’image finale.
- Aspect Ratio
Les plus anciens téléviseurs peuvent avoir des pixels non carrés, aussi ceci peut être utilisé pour contrôler la forme des pixels sur l’axe respectif. Ceci les images qui apparaîtront étirées sur un écran d’ordinateur, mais qui s’affichera correctement sur une TV. C’est important que vous utilisiez l’aspect ratio de pixel correct pour le rendu pour prévenir une remise à l’échelle, qualité d’image réduite.
See Video Output for details on pixel aspect ratio.
- Render Region
Renders just a portion of the view instead of the entire frame. See the Render Region documentation to see how to define the size of the render region.
Note
Ceci désactive l’option Save Buffers dans les options Performance et Full Sample dans Anti-Aliasing.
- Crop Render Region
- Crops the rendered image to the size of the render region, instead of rendering a transparent background around it.
- Frame Range
- Set the Start and End frames for Rendering Animations. Step controls the number of frames to advance by for each frame in the timeline.
- Frame Rate
- For an Animation the frame rate is how many frames will be displayed per second.
- Time Remapping
- Utiliser pour remapper la longueur d’une animation.
Panneau Output¶
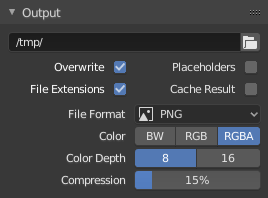
Panneau Output.
Ce panneau offre des options pour définir la position des trames rendues pour les animations, et la qualité des images sauvegardées.
- File Path
Choisir la position où sauvegarder les trames rendues.
Pendant le rendu d’une animation, le numéro de trame est ajouté à la fin du nom du fichier avec un padding de quatre zéros (ex.
image0001.png). Vous pouvez définir une taille de padding personnalisée en ajoutant le nombre approprié de#n’importe où dans le nom du fichier (ex.image_##_test.pngtraduit enimage_01_test.png).This setting expands Relative Paths where a
//prefix represents the directory of the current blend-file.- Overwrite
- Écraser les fichiers existants pendant le rendu.
- Placeholders
- Create empty placeholder frames while rendering.
- File Extensions
- Ajoute les extensions de fichier correctes par type de fichier dans les fichiers de sortie.
- Cache Result
- Saves the rendered image and passes to a multi-layer EXR file in temporary location on your hard drive. This allows the compositor to read these to improve the performance, especially for heavy compositing.
- File Format
Choisir le format de fichier pour la sauvegarde. Selon le format utilisé, d’autres options telles que les canaux, la profondeur de bits et le niveau de compression sont disposibles.
For rendering out to images see: saving images, for rendering to videos see rendering to videos.
- Color Mode
Choisir le format de couleur dans lequel sauvegarder l’image. Notez que RGBA ne sera pas disponible pour tous les formats d’image.
BW, RGB, RGBA
Indication
Primitive Render Farm
Une manière aisée d’avoir plusieurs machines pour partager la charge de travail est de :
- Configurer un dossier partagé sur le système de fichier de réseau.
- Désactiver Overwrite, activez Placeholders dans le panneau Render Output.
- Démarrer autant de machines que vous souhaitez pour le rendu dans ce dossier.
Post Processing Panel¶
Reference
| Panel: |
|---|
The Post Processing panel is used to control different options used to process your image after rendering.
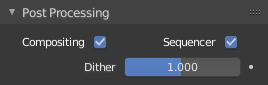
Post Processing panel.
- Sequencer
- Renders the output of the Video Sequence editor, instead of the view from the 3D scene’s active camera. If the sequence contains scene strips, these will also be rendered as part of the pipeline. If Compositing is also enabled, the Scene strip will be the output of the Compositor.
- Compositing
- Renders the output from the compositing node setup, and then pumps all images through the Composite node map, displaying the image fed to the Composite Output node.
Dithering¶
Dithering is a technique for blurring pixels to prevent banding that is seen in areas of gradients, where stair-stepping appears between colors. Banding artifacts are more noticeable when gradients are longer, or less steep. Dithering was developed for graphics with low bit depths, meaning they had a limited range of possible colors.
Dithering works by taking pixel values and comparing them with a threshold and neighboring pixels then does calculations to generate the appropriate color. Dithering creates the perceived effect of a larger color palette by creating a sort of visual color mixing. For example, if you take a grid and distribute red and yellow pixels evenly across it, the image would appear to be orange.
The Dither value ranges from 0 to 2.