Вузол «Математика» – Math Node¶
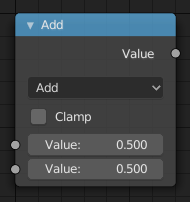
Вузол «Математика» – Math node.¶
Вузол «Математика» – Math здійснює математичні операції.
Уводи – Inputs¶
The inputs of the node are dynamic. Some inputs are only available in certain operations. For instance, the Addend input is only available in the Multiply Add operator.
- Значення – Value
Input Value. Trigonometric functions read this value as radians.
- Addend
Input Addend.
- Base
Input Base.
- Exponent
Input Exponent.
- Epsilon
Input Epsilon.
- Distance
Input Distance.
- Min
Input Minimum.
- Max
Input Maximum.
- Increment
Input Increment.
- Scale
Input Scale.
- Degrees
Input Degrees.
- Radians
Input Radians.
Властивості – Properties¶
- Операція – Operation
The mathematical operator to be applied to the input values:
- Functions
- Add
The sum of the two values.
- Subtract
The difference between the two values.
- Multiply
The product of the two values.
- Divide
The division of the first value by the second value.
- Multiply Add
The sum of the product of the two values with Addend.
- Power
The Base raised to the power of Exponent.
- Logarithm
The log of the value with a Base as its base.
- Square Root
The square root of the value.
- Inverse Square Root
One divided by the square root of the value.
- Absolute
The input value is read with without regard to its sign. This turns negative values into positive values.
- Exponent
Raises Euler’s number to the power of the value.
- Comparison
- Minimum
Outputs the smallest of the input values.
- Maximum
Outputs the largest of two input values.
- Less Than
Outputs 1.0 if the first value is smaller than the second value. Otherwise the output is 0.0.
- Greater Than
Outputs 1.0 if the first value is larger than the second value. Otherwise the output is 0.0.
- Sign
Extracts the sign of the input value. All positive numbers will output 1.0. All negative numbers will output -1.0. And 0.0 will output 0.0.
- Compare
Outputs 1.0 if the difference between the two input values is less than or equal to Epsilon.
- Smooth Minimum
- Smooth Maximum
- Rounding
- Round
Round the input value to the nearest integer.
- Floor
Rounds the input value down to the nearest integer.
- Ceil
Rounds the input value up to the nearest integer.
- Truncate
Outputs the integer part of the value.
- Fraction
- Modulo
Outputs the remainder once the first value is divided by the second value.
- Wrap
Outputs a value between Min and Max based on the absolute difference between the input value and the nearest integer multiple of Max less than the value.
- Snap
Round the input value to down to the nearest integer multiple of Increment.
- Ping-pong
The output value is moved between 0.0 and the Scale based on the input value.
- Trigonometric
- Sine
The Sine of the input value.
- Cosine
The Cosine of the input value.
- Tangent
The Tangent of the input value.
- Arcsine
The Arcsine of the input value.
- Arccosine
The Arccosine of the input value.
- Arctangent
The Arctangent of the input value.
- Arctan2
Outputs the Inverse Tangent of the first value divided by the second value measured in radians.
- Hyperbolic Sine
The Hyperbolic Sine of the input value.
- Hyperbolic Cosine
The Hyperbolic Cosine of the input value.
- Hyperbolic Tangent
The Hyperbolic Tangent of the input value.
- Conversion
- To Radians
Converts the input from degrees to radians.
- To Degrees
Converts the input from radians to degrees.
- Затиск – Clamp
Limits the output to the range (0.0 to 1.0). See Clamp.
Виводи – Outputs¶
- Значення – Value
Вивід числового значення.
Приклади – Examples¶
Ручна Z-Маска – Manual Z-Mask¶
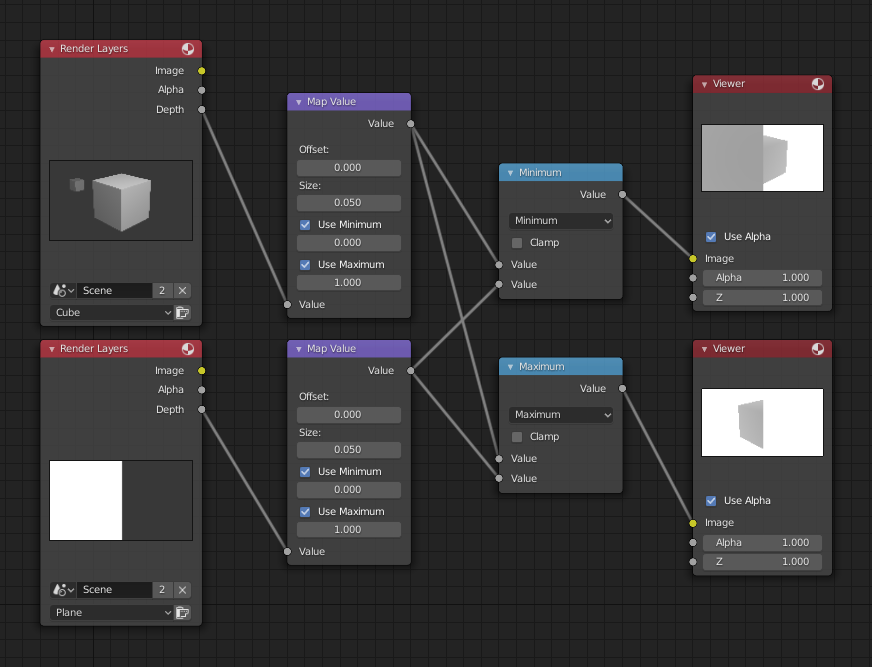
Приклад функції мінімуму та максимуму.¶
Цей приклад має один увід зі сцени, поданий вузлом «Шари Рендера» – Render Layers, який має куб, що знаходиться близько 10 одиниць від камери. Нижній вузол «Шари Рендера» – Render Layers уводить сцену з площиною, що покриває ліву половину огляду та є на 7 одиниць від камери. Обидва подаються через відповідні їм вузли «Розкладка Значень» – Map Value, що ділять їх значення Z-буфера на 20 (або множать на 0.05, як показано у полі устави «Розмір» – Size), та затискають ці значення у діапазон мінімуму/максимуму 0.0/1.0 відповідно.
Для мінімуму функції цей вузол вибирає ті значення Z, де відповідний піксель є ближчим до камери; тому, він вибрав значення Z для площини та частини куба. Задньоплан має безкінечне значення Z, а тому він затискається значенням 1.0 (показується білим кольором). У прикладі з максимумом значення Z куба є більшим, ніж площини, а тому вони вибираються з лівого боку, але Z вузла Render Layers із площиною є безкінечним (розкладеним на 1.0) для правого боку, і тому вони обоє є обраними.
Використання функції синуса для отримання ефекту пульсації – Using Sine Function to Pulsate¶
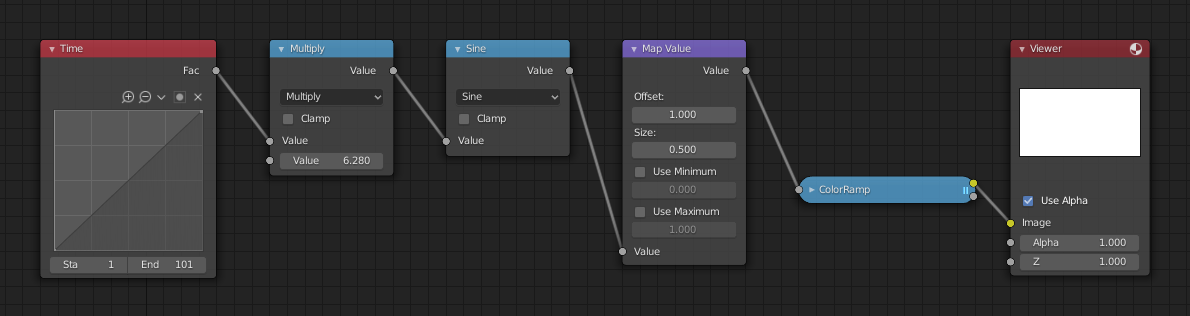
Приклад використання функції синуса.¶
This example has a Time node putting out a linear sequence from 0 to 1 over the course of 101 frames. At frame 25, the output value is 0.25. That value is multiplied by 2 × pi (6.28) and converted to 1.0 by the Sine function, since \(sin(2 × pi/ 4) = sin(pi/ 2) = +1.0\).
Оскільки функція синуса може викладати значення між (-1.0 до 1.0), то вузол «Розкладка Значень» – Map Value масштабує це у діапазон від 0.0 до 1.0, беручи увід (-1 до 1), додаючи 1 (робить 0 до 2) та множачи результат на половину (таким чином масштабуючи вивід між 0 до 1). Стандартний Градієнт Кольорів – Color Ramp конвертує ці значення у сіровідтінкове. Таким чином, середній сірий відповідає виводу 0.0 за синусом, чорний – значенню -1.0 та білий – значенню 1.0. Як ви можете бачити, \(sin(pi/ 2) = 1.0\). Ніби у вас є свій візуальний калькулятор колір! Анімування цього укладу вузлів забезпечує плавну циклічну послідовність через діапазон сірих відтінків.
Використовуйте цю функцію для варіювання, наприклад, альфа-каналу зображення для отримання ефекту появи/щезання. Змінюйте значення цього каналу Z для переміщування сцени у/поза фокус. Змінюйте значення колірного каналу для зроблення «пульсації» кольору.
Збільшення яскравості (Масштабування) Каналу – Brightening (Scaling) a Channel¶
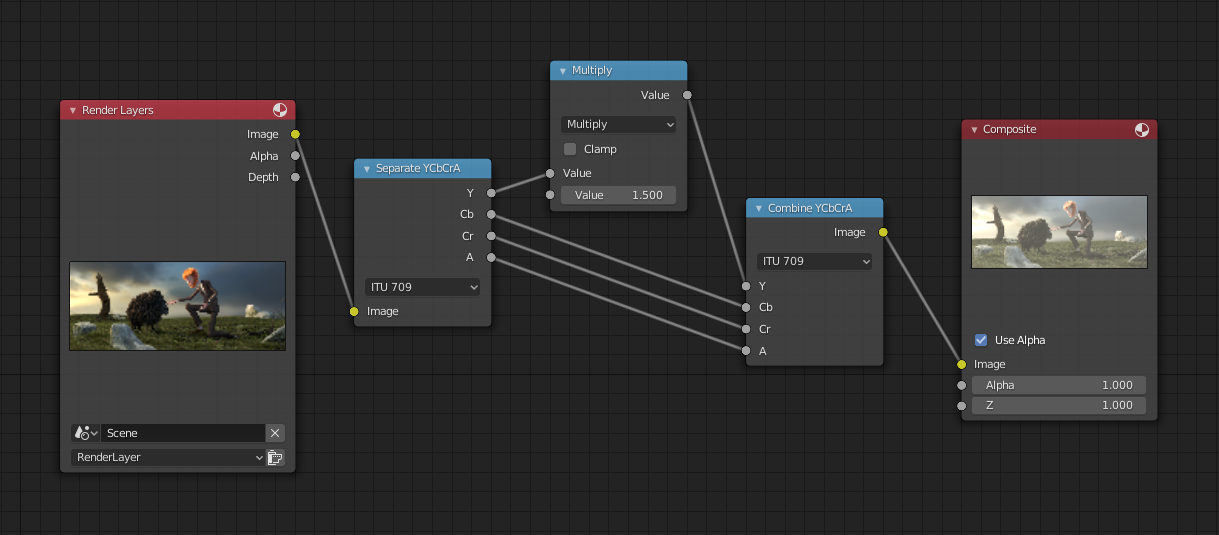
Приклад масштабування каналу.¶
Цей приклад має вузол «Математика (Множення)» – Math (Multiply), що збільшує значення каналу світності (Y) зображення для зроблення його яскравішим. Зауважте, що ви повинні використати вузол «Розкладка Значень» – Map Value node з увімкненими опціями «Вжити Мінімум» – Use Minimum min() та «Вжити Максимум» – Use Maximum max() для затиску виводу у дійсні значення. З цим підходом ви можете використати логарифмічну функцію для зроблення зображення з високим динамічним діапазоном. Для цього конкретного прикладу там є також вузол «Яскравість/Контраст» – Brighten/Contrast, що може давати простіший контроль за яскравістю.
Обмеження Вибору Кольору (Постеризація) – Restrict Color Selection (Posterization)¶
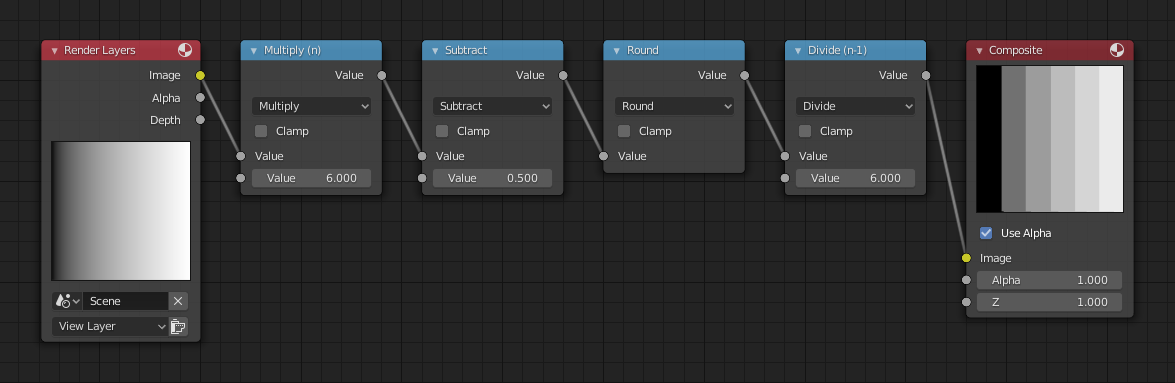
Приклад постеризації.¶
У цьому прикладі, ми обмежили значення кольору одним із шести значень: 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.
To split up a continuous range of values between 0 and 1 to certain set of values, the following function is used: \(round(x × n - 0.5) / (n - 1)\), where «n» is the number of possible output values, and «x» is the input pixel color. Read more about this function.
To implement this function in Blender, consider the node setup above. We string the Math nodes into a function that takes each color (values from 0 to 1), multiplies it up by six, the desired number of divisions (values become from 0 to 6), offsets it by 0.5 (-0.5 to 5.5), rounds the value to the nearest whole number (produces 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5), and then divides the image pixel color by five (0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0).
У випадку кольорового зображення вам необхідно розокремити його на окремі канали RGB, використавши вузли Separate/Combine RGBA та здійснити цю операцію на кожному каналі незалежно.