关系
参考
- 模式:
所有模式
- 面板:
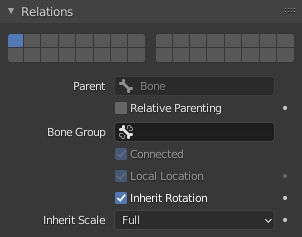
关系面板。
In this panel you can arrange sets of bones in different layers for easier manipulation.
骨骼层
Moving Bones between Layers
Obviously, you have to be in Edit Mode or Pose Mode to move bones between layers. Note that as with objects, bones can lay in several layers at once, just use the usual Shift-LMB clicks... First of all, you have to select the chosen bone(s)!
In the Properties, use the "layer buttons" of each selected bone Relations panel (Bones tab) to control in which layer(s) it lays.
In the 3D Viewport, use the menu or or press M to show the usual pop-up layers menu. Note that this way, you assign the same layers to all selected bones.
父级
- 父级
数据 ID 选择要设为父级的骨骼。
- 相对父级 仅限姿态模式
更改骨骼的变换应用于其子对象的方式。
- 骨骼组 仅姿态模式
To assign a selected bone to a given bone group use the Bone Group data ID.
- 相连项
相连项(Connected)复选框设置要与其父级根部连接的骨骼。
Transformations 变换
骨骼关系对变换行为的影响。
默认情况下,子骨骼继承:
其父位置与自身的偏移量。
其父旋转的角度 (即他们保持恒定旋转相对于其父级)。
其父缩放,与自身偏移量。
就像标准的子对象。你可以 骨骼 标签的关系面板在前面的骨骼的基础上修改此行为:
- 锁定坐标
禁用时,将在父骨骼的局部空间中计算位置变换属性,而不是使用骨骼自身的 静置姿态 局部空间坐标。
- Inherit Rotation 继承旋转
禁用时,这将 "破坏" 与骨骼的父级的旋转关系。这意味着当它的父级旋转时,子级将在骨架对象空间中保持旋转。
- 继承缩放
指定骨骼继承的父级缩放效果:
- 完整:
骨骼继承父级缩放和剪切的所有效果。
- 修复切变:
将完整的父级效果应用于子级的静置状态,之后以保留骨骼方向、长度和体积的方式去除任何剪切,并且最小程度地影响平均滚动。结果与子级的自身变换相结合。
如果继承的比例不均匀,这不会阻止剪切由于子级骨骼或其子级的局部旋转而重新出现。
- 对齐:
父级缩放是继承的,如同子级的方向与父级相同,始终在子级 X缩放基础上应用父级 X 缩放,等等。
- 平均:
继承表示父级体积总体变化的均匀缩放系数。
- 无:
忽略父级的所有缩放和剪切。
- 无(旧版):
忽略所有缩放,前提是父级未被切。如果是,则不能保证。
此选项将复制旧 “继承缩放” 复选框的行为,并可能在将来的版本中删除。
这些继承行为将沿骨骼的层次结构传播。所以当你缩小骨骼时,它的所有后代子级按默认值相应缩小。但是,如果在此 "系列" 中设置了一个骨骼的 继承缩放 或 继承旋转 属性,这将打破继承传播,当你缩小它的祖先(父级)时,这个骨骼 和它所有的后代(所有的子级) 将不再受到影响。
Tip
各种 继承缩放 选项作为工具提供,以避免由不均匀缩放与育儿和旋转结合引起的剪切。没有明显的最佳方式来实现这一目标,因此不同的选择对不同的局势是有用的。
- 无
Useful for gaining full control over the scaling of the child in order to e.g. manually overwrite it with constraints.
- 平均
Useful to block squash and stretch propagation between sub-rigs, while allowing uniform changes in the size and volume to pass through.
- 对齐
Can be used within bone chains, e.g. tentacles, in order to propagate lengthwise scaling as lengthwise, and sideways as sideways, no matter how the tentacle bends. Similar to using None with Copy Scale from parent.
- 修复切变
May be useful at the base of an appendage in order to reallocate squash and stretch between axes based on the difference in rest pose orientations of the parent and child. It behaves closest to Full while suppressing shear.
连接的骨骼具有另一种特异性:它们不能被移动。事实上,由于他们的头端必须在他们父级骨骼的尾端,如果你不移动父级骨骼,你不能移动子级骨骼的根,而只移动它的尖端,这导致子级旋转。这正是当您按下 G 并选择了连接骨骼时发生的情况,Blender会自动切换到旋转操作。
骨骼关系也对多个骨骼的选择在变换时的行为有重要的影响。然而,有许多不同的情况可能不包括在这个名单上,这应该给出一个好主意的问题:
通常,不相关的骨骼被独立化。
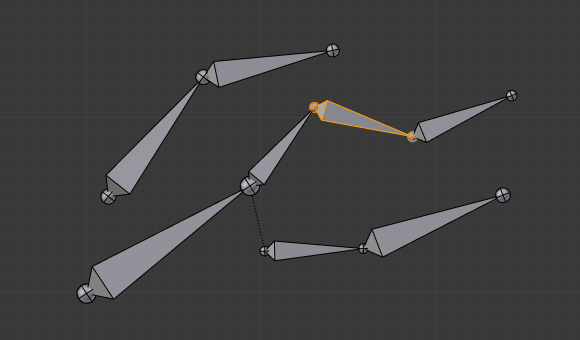
当选择相同 "族" 的几个骨骼时,只有 "最父" 的骨骼才真正被转换 -- 后代只是通过父关系过程处理,就好像它们没有被选中一样(见图 缩放其中一些相关骨骼。 第三个尖端骨骼,以黄色标出,仅通过父关系缩小,与未选择的一样,即使它被选中并激活。否则,它应该是两次小!)
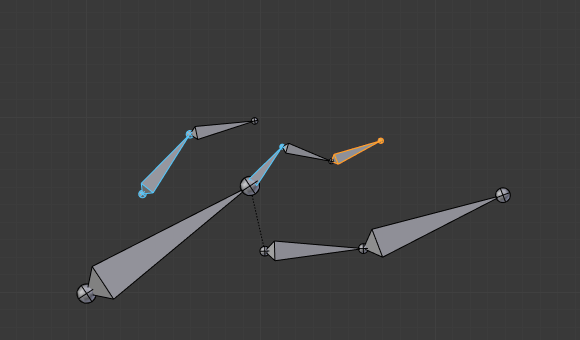
缩放其中一些相关骨骼。
选择已连接和未连接的骨骼后,如果开始移动操作,则只会影响未连接的骨骼。
当子级连接链骨骼选择时,"最多父级" 选择的那个是链接的,当你按 G,什么都没发生,因为Blender仍然在移动操作,这当然对连接的骨骼没有影响。
So, when posing a chain of bones, you should always edit its elements from the root bone to the tip bone. This process is known as Forward Kinematics (FK). We will see in a later page that Blender features another pose method, called Inverse Kinematics (IK), which allows you to pose a whole chain just by moving its tip.
Note
此功能在某种程度上受到来自于 姿态库 的扩展与完善。