Data-Blocks¶
The base unit for any Blender project is the data-block. Examples of data-blocks include: meshes, objects, materials, textures, node trees, scenes, texts, brushes, and even Workspaces.
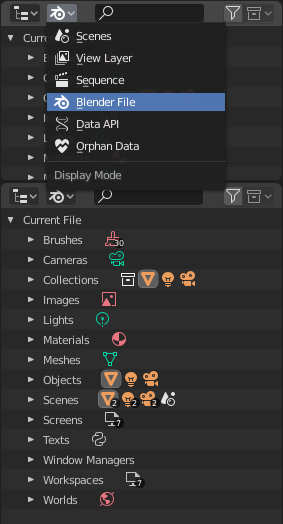
Blender File view of the Outliner.
A data-block is a generic abstraction of very different kinds of data, which features a common set of basic features, properties and behaviors.
Some common characteristics:
- They are the primary contents of the blend-file.
- They can reference to each other, for reuse and instancing. (Child/parent, object/object-data, materials/images, in modifiers or constraints too…)
- Their names are unique within a blend-file, for a given type.
- They can be added/removed/edited/duplicated.
- They can be linked between files (only enabled for a limited set of data-blocks).
- They can have their own animation data.
- They can have Custom Properties.
User will typically interact with the higher level data types (objects, meshes, etc.). When doing more complex projects, managing data-blocks becomes more important, especially when inter-linking blend-files. The main editor for that is the Outliner.
Not every data in Blender is a data-block, bones, sequence strips or vertex groups e.g. are not, they belong to armature, scene and mesh types respectively.
Life Time¶
Every data-block has its usage counted (reference count), when there is more than one, you can see the number of current users of a data-block to the right of its name in the UI.
Blender follows the general rule that unused data is eventually removed.
Since it is common to add and remove a lot of data while working, this has the advantage of not having to manually manage every single data-block.
This works by skipping zero user data-blocks when writing blend-files.
Protected¶
Since zero user data-blocks are not saved, there are times when you want to force the data to be kept irrespective of its users.
If you are building a blend-file to serve as a library of things that you intend to link to and from other files, you will need to make sure that they do not accidentally get deleted from the library file.
To protect a data-block, use the button with the shield icon next to its name. The data-block will then never be silently deleted by Blender, but you can still do it manually if needed.
Sharing¶
Data-blocks can be shared among other data-blocks.
Examples where sharing data is common:
- Sharing textures among materials.
- Sharing meshes between objects (instances).
- Sharing animated actions between objects, for example to make all the lights dim together.
You can also share data-blocks between files, see:
Making Single User¶
When a data-block is shared between several users, you can make a copy of it for a given user. To do so, click on the user-count button to the right of its name. This will duplicate that data-block and assign the newly created copy to that usage only.
Nota
Objects have a set of more advanced actions to become single-user, see their documentation.
Removing Data-Blocks¶
As covered in Life Time, data-blocks are typically removed when they are no longer used.
They can also be manually unlinked or deleted.
Unlinking a data-block means that its user won’t use it anymore. This can be achieved by clicking on the «X» icon next to a data-block’s name.
If you unlink a data-block from all of its users, it will eventually be deleted by Blender as described above (unless it is a protected one).
Deleting a data-block directly erases it from the blend-file, automatically unlinking it from all of its users. This can be achieved by Shift-LMB on the «X» icon next to its name.
Advertencia
Deleting some data-blocks can lead to deletion of some of its users, which would become invalid without it. The main example is that object-data deletion (like mesh, curve, camera…) will also delete all objects using it.
Those two operations are also available in the context menu when RMB-clicking on a data-block in the Outliner.
Data-Block Types¶
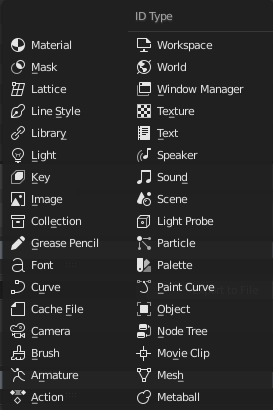
Data-blocks types with their icon.
For reference, here is a table of data-blocks types stored in blend-files.
| Link: | Library Linking, supports being linked into other blend-files. |
|---|---|
| Pack: | File Packing, supports file contents being packed into the blend-file (not applicable for most data-blocks which have no file reference). |
| Type | Link | Pack | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Action | ✓ | — | Stores animation F-curves.
Used as data-block animation data,
and the Non-Linear Animation editor.
|
| Armature | ✓ | — | Skeleton used to deform meshes.
Used as data of armature objects, and by the Armature Modifier.
|
| Brush | ✓ | — | Used by paint tools.
|
| Camera | ✓ | — | Used as data by camera objects.
|
| Cache File | ✓ | — | Used by Mesh Cache modifiers.
|
| Curve | ✓ | — | Used as data by curve, font & surface objects.
|
| Font | ✓ | ✓ | References font files.
Used by curve object-data of text objects.
|
| Grease Pencil | ✓ | — | 2D/3D sketch data used by Grease Pencil objects.
Used as overlay helper info, by the
3D View, Image, Sequencer & Movie Clip editors.
|
| Collection | ✓ | — | Group and organize objects in scenes.
Used to instance objects, and in library linking.
|
| Image | ✓ | ✓ | Image files.
Used by shader nodes and textures.
|
| Keys (Shape Keys) | ✗ | — | Geometry shape storage, which can be animated.
Used by mesh, curve, and lattice objects.
|
| Light | ✓ | — | Used as object data by light objects.
|
| Library | ✗ | ✓ | References to an external blend-file.
Access from the Outliner’s Blender File view.
|
| Line Style | ✓ | — | Used by the Freestyle renderer.
|
| Lattice | ✓ | — | Grid based lattice deformation.
Used as data of lattice objects, and by the Lattice Modifier.
|
| Mask | ✓ | — | 2D animated mask curves.
Used by compositing nodes & sequencer strip.
|
| Material | ✓ | — | Set shading and texturing render properties.
Used by objects, meshes & curves.
|
| Metaball | ✓ | — | An isosurface in 3D space.
Used as data of metaball objects.
|
| Mesh | ✓ | — | Geometry made of vertices/edges/faces.
Used as data of mesh objects.
|
| Movie Clip | ✓ | ✗ | Reference to an image sequence or video file.
Used in the Movie Clip editor.
|
| Node Tree | ✓ | — | Groups of re-usable nodes.
Used in the node editors.
|
| Object | ✓ | — | An entity in the scene with location,
scale, rotation.
Used by scenes & collections.
|
| Paint Curve | ✓ | — | Stores a paint or sculpt stroke.
Access from the paint tools.
|
| Palette | ✓ | — | Store color presets.
Access from the paint tools.
|
| Particle | ✓ | — | Particle settings.
Used by particle systems.
|
| Light Probe | ✓ | — | Help achieve complex real-time lighting in Eevee.
|
| Scene | ✓ | — | Primary store of all data displayed and animated.
Used as top-level storage for objects & animation.
|
| Sounds | ✓ | ✓ | Reference to sound files.
Used as data of speaker objects.
|
| Speaker | ✓ | — | Sound sources for a 3D scene.
Used as data of speaker object.
|
| Text | ✓ | ✗ | Text data.
Used by Python scripts and OSL shaders.
|
| Texture | ✓ | — | 2D/3D textures.
Used by brushes and modifiers.
|
| Window Manager | ✗ | — | The overarching manager for all of Blender’s UI.
Includes Workspaces, notification system, operators, and key-maps.
|
| World | ✓ | — | Define global render environment settings.
|
| Workspace | ✗ | — | UI layout.
Used by each window, which has its own workspace.
|
Custom Properties¶
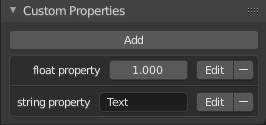
Custom Properties panel.
Custom properties are a way to store your own data in Blender’s data-blocks. It can be used for rigging (where bones and objects can have custom properties driving other properties), and Python scripts, where it’s common to define new settings not available in Blender.
Only certain data supports custom properties:
- All data-blocks types.
- Bones and pose bones.
- Sequence strips.
To add a custom property, search for the Custom Properties panel, found at the bottom of most Properties Editor or Sidebar region, and hit Add.
Editing Properties¶
User Interface¶
Custom properties can be edited using the panel available for data types that support it.
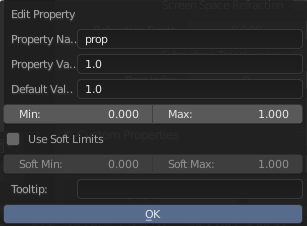
Custom Properties edit pop-up.
- Property Name
- The name of the custom property.
- Property Value
This does two things: first it sets the current value of the custom property, and second, it defines the data type of the property. Custom properties can be of the following types: Integers, Floats, Strings or Booleans. See the table below for a list of examples for each:
Integers: 1, 2, 3, 4, Floats: 3.141, 5.0, 6.125, Strings: any text, Booleans: True,FalseNota
Booleans are handled very similar to integers and only work when using Min/Max values that are integers and that are no more than 1 apart.
At this point, the booleans will still look like integers but behave like booleans having one lower, off, value and a higher, on, value.
- Default Value
This sets the default value of the property used by the Reset to Default Value operator.
Advertencia
Default values are used as the basis of NLA blending, and a nonsensical default (e.g. 0 for a property used for scaling) on a property intended for being keyframed is likely to cause issues.
- Min
- The minimum value the custom property can take.
- Max
- The maximum value the custom property can take.
- Use Soft Limits
Enables limits that the Property Value slider can be adjusted to without having to input the value numerically.
- Soft Min
- The minimum value for the soft limit.
- Soft Max
- The maximum value for the soft limit.
- Tooltip
- Allows you to write a custom Tooltip for your property.
Python Access¶
Custom properties can be accessed in a similar way to dictionaries, with the constraints that keys can only be strings, and values can only be strings, numbers, arrays of such, or nested properties.
See the API documentation for details.