BSDF Principista
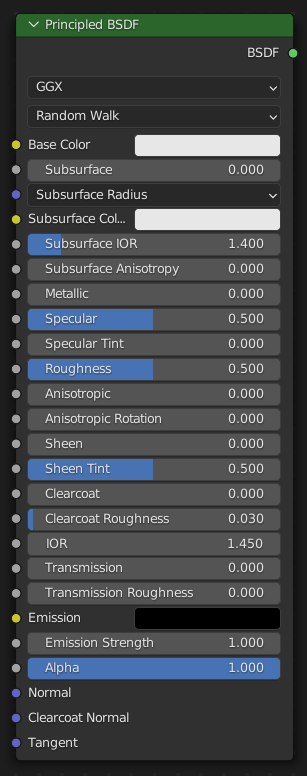
The Principled BSDF that combines multiple layers into a single easy to use node. It is based on the Disney principled model also known as the «PBR» shader, making it compatible with other software such as Pixar’s Renderman® and Unreal Engine®. Image textures painted or baked from software like Substance Painter® may be directly linked to the corresponding parameters in this shader.
This «Uber» shader includes multiple layers to create a wide variety of materials. The base layer is a user controlled mix between diffuse, metal, subsurface scattering and transmission. On top of that there is a specular layer, sheen layer and clearcoat layer.
Nota
The emphasis on compatibility with other software means that it interprets certain input parameters differently from older Blender nodes.
Entradas
- Color Base
Color de la superficie difusa o metálica.
- Transluminiscencia
Mix between diffuse and subsurface scattering. Rather than being a simple mix between Diffuse and Subsurface Scattering, it acts as a multiplier for the Subsurface Radius.
- Subsurface Radius
Factor de distancia que, multiplicado por la Escala, determinará el radio que la luz podrá atravesar por debajo de la superficie, para cada canal de color. Una radio mayor producirá una apariencia más suave, debido a que la luz se filtrará hacia las áreas en sombra y a través del objeto. La distancia de dispersión se especificará de forma separada para cada canal RVA, para posibilitar recrear materiales tales como piel, en los cuales la luz roja se dispersa más que los otros dos componentes. Los valores X, Y, Z serán mapeados respectivamente a valores de R, V, A.
- Subsurface Color
Subsurface scattering base color.
- Subsurface IOR Cycles Only
Índice de refracción para la transluminiscencia.
- Subsurface Anisotropy Cycles Only
Controls the directionality of subsurface scattering.
- Metálico
Permitirá mezclar entre los modelos de material metálico y no metálico. Un valor de 1.0 proporcionará una reflexión completamente especular teñida con el color base, sin reflexión difusa ni transmisión. En 0.0 el material consistirá en una capa base difusa o transmisiva, con una capa de reflexión especular encima.
- Especularidad
Amount of dielectric specular reflection. Specifies facing (along normal) reflectivity in the most common 0 - 8% range.
Consejo
To compute this value for a realistic material with a known index of refraction, you may use this special case of the Fresnel formula: \(specular = ((ior - 1)/(ior + 1))^2 / 0.08\)
Por ejemplo:
water: ior = 1.33, specular = 0.25
glass: ior = 1.5, specular = 0.5
diamond: ior = 2.417, specular = 2.15
Since materials with reflectivity above 8% do exist, the field allows values above 1.
- Specular Tint
Tints the facing specular reflection using the base color, while glancing reflection remains white.
Normal dielectrics have colorless reflection, so this parameter is not technically physically correct and is provided for faking the appearance of materials with complex surface structure.
- Rugosidad
Especifica la rugosidad de las microfacetas de la superficie, para definir la reflexión difusa y especular.
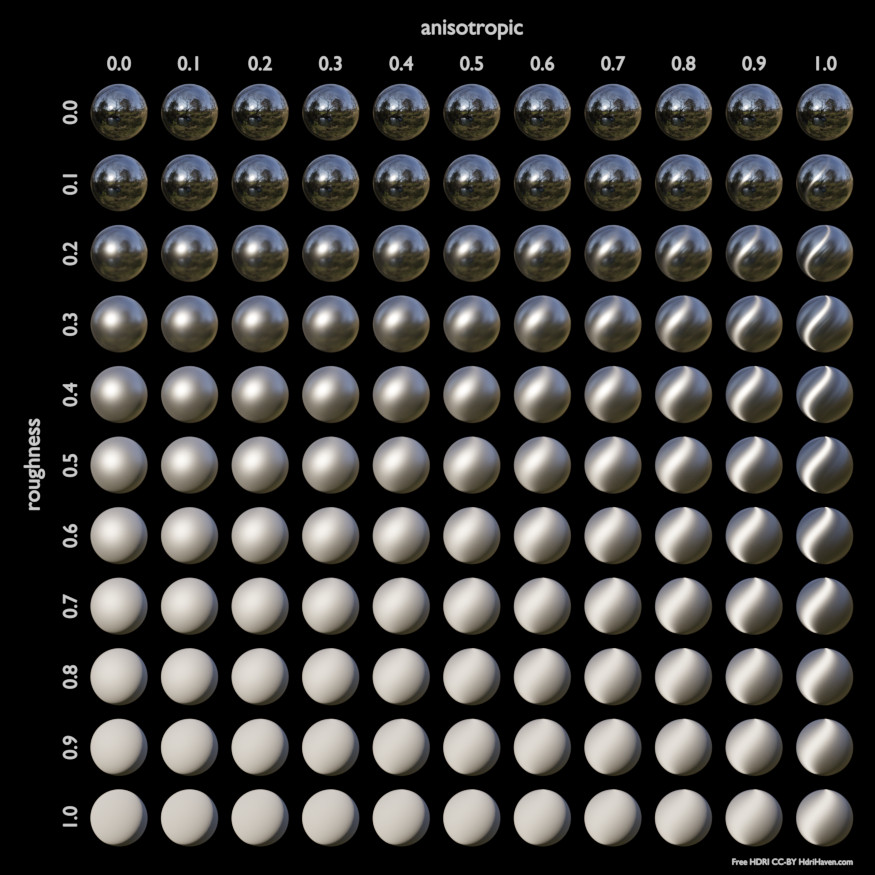
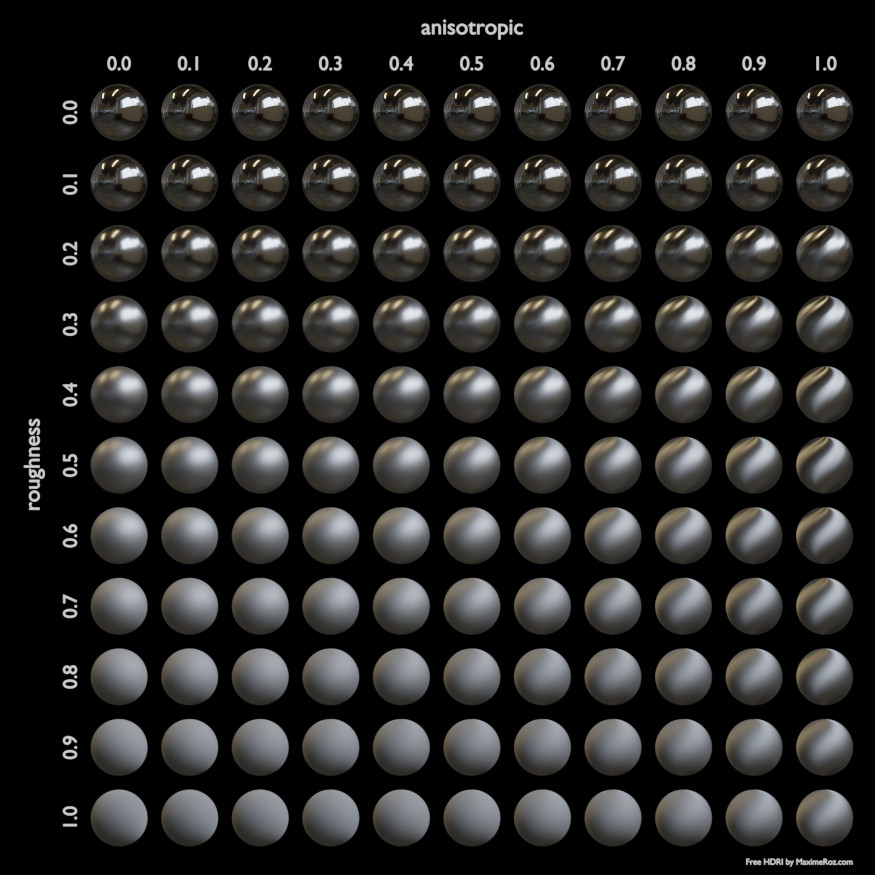
- Anisotropía sólo en Cycles
Cantidad de anisotropía para la reflexión especular. Valores mayores (positivos) producirán brillos especulares alargados en dirección tangencial; valores negativos producirán brillos especulares alargados en dirección perpendicular a la dirección tangencial.
- Rotación de anisotropía sólo en Cycles
Permite rotar la dirección de la anisotropía, con un valor de 1.0 produciendo un círculo completo.
Consejo
Comparado con el nodo BSDF Anisótropo, la dirección de elongación de los brillos especulares se encuentra rotada 90°. Agregar 0.25 al valor para compensarlo.
- Brillo tangencial
Amount of soft velvet like reflection near edges, for simulating materials such as cloth.
- Sheen Tint
Mix between white and using base color for sheen reflection.
- Barniz
Capa adicional de reflexión especular blanca, sobre las otras capas. Esto resultará útil para materiales como pintura de automóvil y otras similares.
- Clearcoat Roughness:
Roughness of clearcoat specular.
- IR
Index of refraction for transmission.
- Transmisión
Mix between fully opaque surface at zero and fully glass like transmission at one.
- Transmission Roughness Cycles Only
With GGX distribution controls roughness used for transmitted light.
- Emisión
Light emission from the surface, like the Emission shader.
- Intensidad de emisión
Strength of the emitted light. A value of 1.0 will ensure that the object in the image has the exact same color as the Emission Color, i.e. make it “shadeless”.
- Alfa
Controla la transparencia de la superficie, con 1.0 siendo completamente opaca. Estará usualmente conectada a la salida de Alfa de un nodo de textura de Imagen.
- Normal
Controla las normales de las capas base.
- Clearcoat Normal
Controls the normals of the Clearcoat layer.
- Tangente
Controls the tangent for the Anisotropic layer.
Propiedades
- Distribución
Tipo de distribución de microfacetas a usar.
- GGX:
A method that is faster than Multiple-scattering GGX but is less physically accurate. Selecting it enables the Transmission Roughness input.
- Multiple-scattering GGX:
Takes multiple bounce (scattering) events between microfacets into account. This gives a more energy conserving results, which would otherwise be visible as excessive darkening.
- Método de transluminiscencia
Métodos de procesamiento para simular la transluminiscencia.
Nota
Eevee does use not support the Random Walk methods.
- Christensen-Burley:
Una aproximación a una dispersión volumétrica basada en principios físicos. Este método es menos preciso que Camino aleatorio, sin embargo en algunas situaciones producirá menos ruido en menos tiempo.
- Camino aleatorio (Radio fijo):
Proporcionará resultados precisos en objetos delgados y curvos. El método Camino aleatorio utiliza una verdadera dispersión volumétrica dentro de la malla, lo que significa que funcionará mejor en mallas cerradas. Caras superpuestas y huecos en la malla podrán causar problemas.
- Camino aleatorio:
Behaves similarly to Random Walk (Fixed Radius) but modulates the Subsurface Radius based on the Color, Subsurface Anisotropy, and Subsurface IOR. This method thereby attempts to retain greater surface detail and color than Random Walk (Fixed Radius).
Salidas
- BSDF
Salida estándar de sombreador.
Ejemplos
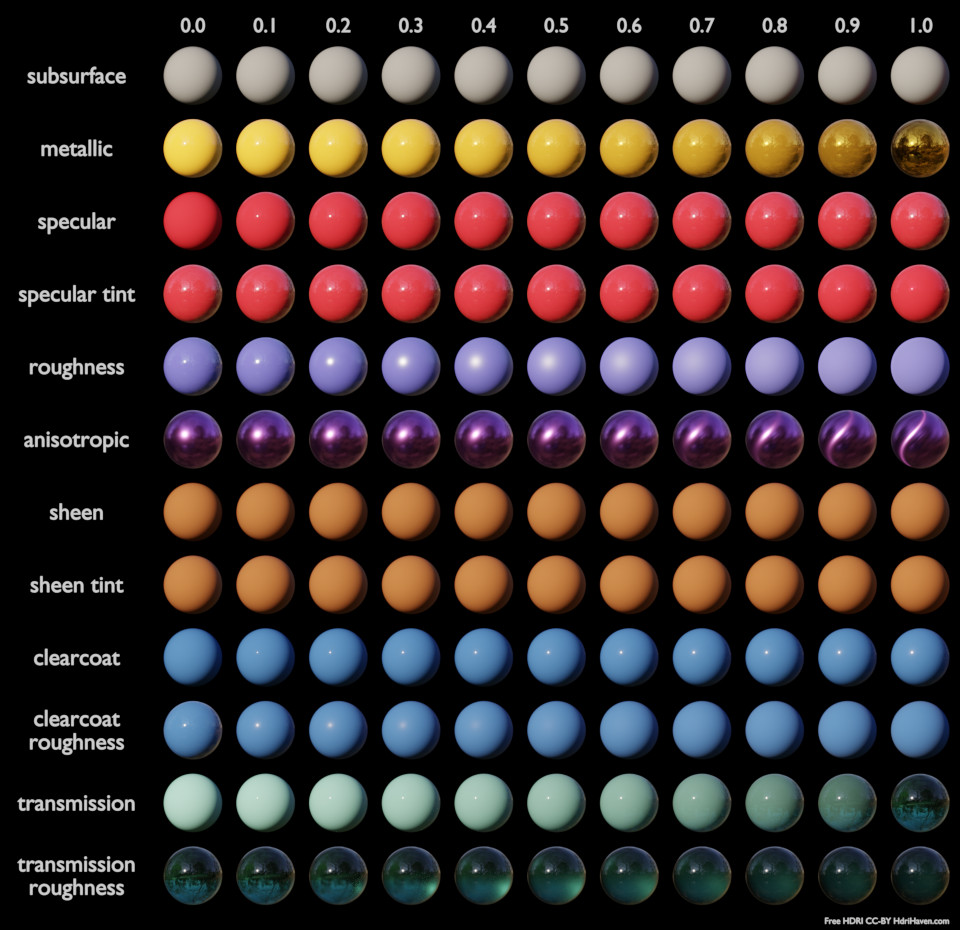
Below are some examples of how all the Principled BSDF’s parameters interact with each other.