Propriétés¶
Panneau Active F-Curve¶
Référence
- Panneau
Panneau Active F-Curve.¶
Ce panneau montre les propriétés de la F-curve active.
- Channel Name
ID Type + Channel name (X Location).
- RNA Path
RNA Path to property + Array index.
- Color Mode
Mode de couleur pour la F-curve active.
- Auto Rainbow
Incrémente le hue de la couleur de la F-curve selon l’indice du canal.
- Auto XYZ to RGB
For property sets like location XYZ, automatically set the set of colors to red, green, blue.
- User Defined
Définir une couleur personnalisée pour la F-curve active.
- Auto Handle Smoothing
Selects the method used to compute automatic Bézier handles (Automatic, Auto Clamped, Vector).
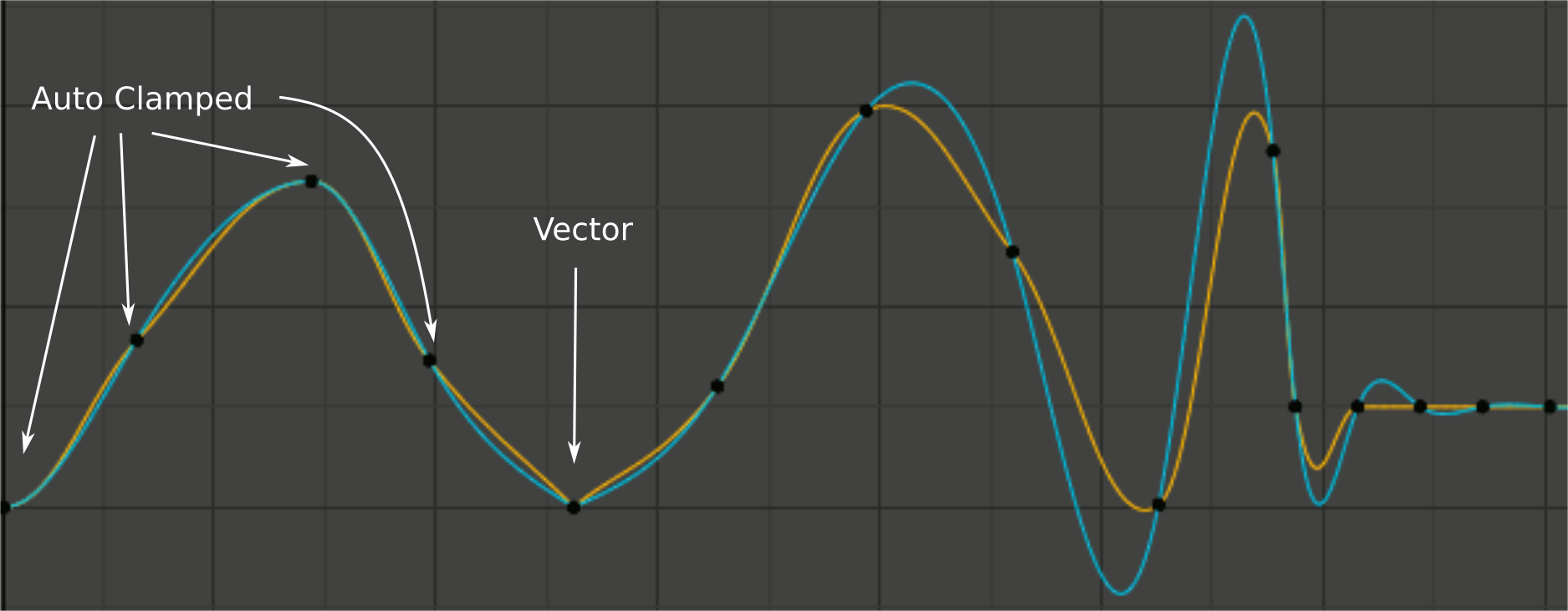
Handle smoothing mode comparison. Yellow: None, Cyan: Continuous Acceleration.¶
From left to right, four Auto Clamped keys, one Vector, and the rest are Automatic.
- None
Only directly adjacent key values are considered when computing the handles. Vector handles are pointed directly at the adjacent keyframes.
This older method is very simple and predictable, but it can only produce truly smooth curves in the most trivial cases. Note the kinks in the yellow curve around the keys located between the extremes, and near the Vector handles.
- Continuous Acceleration
A system of equations is solved in order to avoid or minimize jumps in acceleration at every keyframe. Vector handles are integrated into the curves as smooth transitions to imaginary straight lines beyond the keyframe.
This produces much smoother curves out of the box, but necessarily means that any changes in the key values may affect interpolation over a significant stretch of the curve; although the amount of change decays exponentially with distance. This change propagation is stopped by any key with Free, Aligned, or Vector handles, as well as by extremes with Auto Clamped handles.
This mode also tends to overshoot and oscillate more with fully Automatic handles in some cases (see the right end of the image above), so it is recommended to use Auto Clamped by default, and only switch to Automatic handles in places where this is desired behavior. This effect can also be reduced by adding in-between keys.
Considering the upsides and downsides of each mode, Continuous Acceleration should be better suited for limited animation, which uses a small number of interpolated keys with minimal manual polish. In case of highly polished high key rate animation, the benefits of smoothing may not outweigh the workflow disruption from more extensive change propagation.
Panneau Active Keyframe¶
Référence
- Panneau
Panneau Active Keyframe.¶
- Interpolation
Définissez le Mode d’interpolation pour la trame clé active.
- Easing
Voir Easing Type.
- Touche
- Frame
Définir la trame pour la trame clé active.
- Value
Définir la valeur pour la trame clé active.
- Left/Right Handle
Définir la position de la poignée d’interpolation gauche/droite pour la trame clé active.-
- Handle Type
Voir Handle Types.
View Properties¶
Référence
- Panneau
Propriétés de la vue.¶
- Show Cursor
Commute la visibilité du Curseur 2D.
- Cursor from Selection
Place le curseur 2D au point médian des trames clés sélectionnées.
- Cursor Location
Déplace le curseur à la trame (valeur X) et la valeur (valeur Y) spécifiées.
- To Keys
Applique la position courante du curseur 2D aux trames clés sélectionnées.
Voir aussi
Menu View.de l’Éditeur Graph.