Follow Path Constraint
The Follow Path constraint places its owner onto a curve target object, and makes it move along this curve (or path). It can also affect its owner’s rotation to follow the curve’s bends, when the Follow Curve option is enabled.
It could be used for complex camera traveling, a train on its rails and most other vehicles can also use «invisible» tracks, the links of a bicycle chain, etc.
The owner is always evaluated in the global (world) space:
Its location (as shown in the Transform panel) is used as an offset from its normal position on the path. E.g. if you have an owner with the (1.0, 1.0, 0.0) location, it will be one unit away from its normal position on the curve, along the X and Y axis. Hence, if you want your owner on its target path, clear its location Alt-G!
This location offset is also proportionally affected by the scale of the target curve. Taking the same (1.0, 1.0, 0.0) offset as above, if the curve has a scale of (2.0, 1.0, 1.0), the owner will be offset two units along the X axis (and one along the Y one)…
When the Follow Curve option is enabled, its rotation is also offset to the one given by the curve. E.g. if you want the Y axis of your object to be aligned with the curve’s direction, it must be in rest, non-constrained state, aligned with the global Y axis. Here again, clearing your owner’s rotation Alt-R might be useful…
The movement of the owner along the target curve/path may be controlled in two different ways:
The most simple is to define the number of frames of the movement, in the Path Animation panel of the Curve tab, via the Frames number field, and its start frame via the constraint’s Offset option (by default, start frame: 1 [= offset of 0], duration: 100).
The second way, much more precise and powerful, is to define an Evaluation Time interpolation curve for the Target path (in the Graph Editor). See the Graph Editor chapter to learn more about F-curves.
If you do not want your owner to move along the path, you can give to the target curve a flat Speed F-curve (its value will control the position of the owner along the path).
Follow Path is another constraint that works well with the Locked Track one. One example is a flying camera on a path. To control the camera’s roll angle, you can use a Locked Track and a target object to specify the up direction, as the camera flies along the path.
Nota
Follow Path & Clamp To
Do not confuse these two constraints. Both of them constraint the location of their owner along a curve, but Follow Path is an «animation-only» constraint, inasmuch as the position of the owner along the curve is determined by the time (i.e. current frame), whereas the Clamp To constraint determines the position of its owner along the curve using one of its location properties” values.
Nota
Note that you also need to keyframe Evaluation Time for the Path. Select the path, go to the Path Animation panel in the curve properties, set the overall frame to the first frame of the path (e.g. frame 1), set the value of Evaluation time to the first frame of the path (e.g. 1), right-click on Evaluation time, select create keyframe, set the overall frame to the last frame of the path (e.g. frame 100), set the value of Evaluation time to the last frame of the path (e.g. 100), right-click on Evaluation time, select create keyframe.
Opzioni
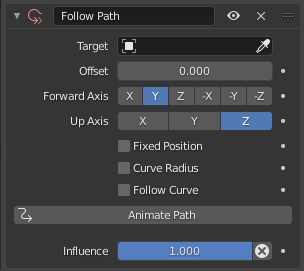
Follow Path panel.
- Target
ID used to select the constraint’s target, which must be a curve object, and is not functional (red state) when it has none. See common constraint properties for more information.
- Offset
The number of frames to offset from the «animation» defined by the path (by default, from frame 1).
- Forward Axis
The axis of the object that has to be aligned with the forward direction of the path (i.e. tangent to the curve at the owner’s position).
- Up Axis
The axis of the object that has to be aligned (as much as possible) with the world Z axis. In fact, with this option activated, the behavior of the owner shares some properties with the one caused by a Locked Track constraint, with the path as «axle», and the world Z axis as «magnet».
- Fixed Position
Object will stay locked to a single point somewhere along the length of the curve regardless of time.
- Curve Radius
Objects scaled by the curve radius. See Curve Editing.
- Follow Curve
If this option is not activated, the owner’s rotation is not modified by the curve; otherwise, it is affected depending on the Forward and Up Axes.
- Animate Path
Adds an F-curve with options for the start and end frame. ToDo: from above.
- Influenza
Controls the percentage of affect the constraint has on the object. See common constraint properties for more information.