Transferência de dados¶
The Data Transfer tool transfers several types of data from one mesh to another. Data types include vertex groups, UV maps, vertex colors, custom normals…
Transfer works by generating a mapping between source mesh’s items (vertices, edges, etc.) and destination ones, either on a one-to-one basis, or mapping several source items to a single destination one by interpolated mapping.
Dados¶
Referência
| Mode: | Object Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: |
Transfers data layer(s) from active to selected meshes.
- Congelar operador
- Prevent changes to settings to re-run the operator. This is useful if you are editing several settings at once with heavy geometry.
- Tipo de dados
Quais dados serão transferidos.
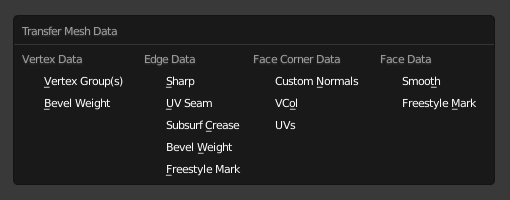
Tipo de dados.
- Criar dados
- Adiciona camadas de dados nas malhas de destinação quando necessário.
- Mapeamento de vértices
- Method used to map source vertices to destination ones. Because the options change depending on the Data Type options are explained in Vertex Mapping below.
Mapeamento de vértices¶
Topologia¶
The simplest option, expects both meshes to have identical number of items, and match them by order (indices). Useful e.g. between meshes that were identical copies, and got deformed differently.
Mapeamentos um a um¶
Those always select only one source item for each destination one, often based on shortest distance.
- Vértices
- Vértices mais próximos
- Usa os vértices da fonte mais próximos.
- Vértices mais próximos das arestas
- Uses source’s nearest vertex of source’s nearest edge.
- Vértices mais próximos das faces
- Uses source’s nearest vertex of source’s nearest face.
- Arestas
- Vértices mais próximos
- Uses source’s edge which vertices are nearest from destination edge’s vertices.
- Arestas mais próximas
- Uses source’s nearest edge (using edge’s midpoints).
- Arestas das faces mais próximas
- Uses source’s nearest edge of source’s nearest face (using edge’s midpoints).
- Junções das faces
A face corner is not a real item by itself, it’s some kind of split vertex attached to a specific face. Hence both vertex (location) and face (normal, …) aspects are used to match them together.
- Junções mais próximas e que combinem melhor com as normais
- Uses source’s corner having the most similar split normal with destination one, from those sharing the nearest source’s vertex.
- Junções mais próximas e que combinem melhor com as normais das faces
- Uses source’s corner having the most similar face normal with destination one, from those sharing the nearest source’s vertex.
- Junções mais próximas das faces mais próximas
- Junções mais próximas e que combinem melhor com as normais das faces
- Faces
- Faces mais próximas
- Usa as faces da fonte mais próximas.
- Melhores combinações das normais:
- Uses source’s face which normal is most similar with destination one.
Arestas interpoladas mais próximas¶
Those use several source items for each destination one, interpolating their data during the transfer.
- Vértices
- Arestas interpoladas mais próximas
- Uses nearest point on nearest source’s edge, interpolates data from both source edge’s vertices.
- Faces interpoladas mais próximas
- Uses nearest point on nearest source’s face, interpolates data from all that source face’s vertices.
- Projeções de faces interpoladas
- Uses point of face on source hit by projection of destination vertex along its own normal, interpolates data from all that source face’s vertices.
- Arestas
- Projeções de arestas interpoladas
- This is a sampling process. Several rays are cast from along the destination’s edge (interpolating both edge’s vertex normals), and if enough of them hit a source’s edge, all hit source edges” data are interpolated into destination one.
- Junções das faces
A face corner is not a real item by itself, it’s some kind of split vertex attached to a specific face. Hence both vertex (location) and face (normal, …) aspects are used to match them together.
- Faces interpoladas mais próximas
- Uses nearest point of nearest source’s face, interpolates data from all that source face’s corners.
- Projeções de faces interpoladas
- Uses point of face on source hit by projection of destination corner along its own normal, interpolates data from all that source face’s corners.
- Faces
- Projeções de faces interpoladas
- This is a sampling process. Several rays are cast from the whole destination’s face (along its own normal), and if enough of them hit a source’s face, all hit source faces” data are interpolated into destination one.
Opções adicionais¶
- Transformações automáticas
Automatically computes the transformation to get the best possible match between source and destination meshes.
This allows to match and transfer data between two meshes with similar shape, but transformed differently. Note that you’ll get best results with exact copies of the same mesh. Otherwise, you’ll likely get better results if you «visually» make them match in 3D space (and use Object Transform) instead.
- Transformações de objeto
- Avalia as malhas de fonte e destinação no espaço global.
- Somente a geometria mais próxima
Os elementos de fonte devem estar mais próximos do que a distância fornecida a partir da destinação.
- Distância máxima
- Distância máxima permitida entre os elementos da fonte e destinação, para mapeamentos não topológicos.
- Raio (largura) para os raios
- Width of rays. Useful when ray casting against vertices or edges.
- Modo de mistura
Permite definir como serão afetados os elementos da destinação com os valores da fonte.
- Todos
- Replaces everything in destination (note that Mix Factor is still used).
- Acima do ajuste
- Only replaces destination value if it is above given threshold Mix Factor. How that threshold is interpreted depends on data type, note that for boolean values this option fakes a logical AND.
- Abaixo do ajuste
- Only replaces destination value if it is below given threshold Mix Factor. How that threshold is interpreted depends on data type, note that for boolean values this option fakes a logical OR.
- Misturar, Adicionar, Subtrair, Multiplicar
- Apply that operation, using mix factor to control how much of source or destination value to use. Only available for a few types (vertex groups, vertex colors).
- Fator de mistura
- How much of the transferred data gets mixed into existing one (not supported by all data types).
Esquema de dados¶
Referência
| Mode: | Object Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: |
Transfere o esquema das camadas de dados das malhas ativas para as selecionadas.
- Tipo de dados
Quais dados serão transferidos.

Tipo de dados.
- Combinação exata
- Também apaga algumas camadas de dados a partir da destinação caso necessário, de maneira que os dados combinem perfeitamente com a fonte.
- Seleção de camadas das fontes
Which layers to transfer, in case of multi-layer types.
- Camada ativa
- Transfere somente as camadas de dados ativas
- Todas as camadas
- Transfere todas as camadas de dados.
- Combinação das camadas de destinação
Permite definir como combinar as camadas de fonte e destinação.
- Definir pelos nomes
- Identifica as camadas de dados dos alvos para serem afetadas pela combinação de nomes.
- Definir pela ordem
- Identifica as camadas de dados dos alvos para ser afetadas pela sua ordem (usando seus índices).
Veja também