Blocos de dados
The base unit for any Blender project is the data-block. Examples of data-blocks include: meshes, objects, materials, textures, node trees, scenes, texts, brushes, and even Workspaces.
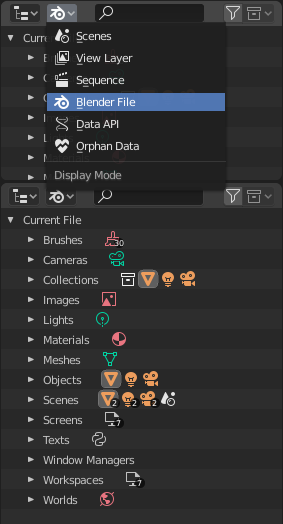
Blender File view of the Outliner.
A data-block is a generic abstraction of very different kinds of data, which features a common set of basic features, properties and behaviors.
Algumas características em comum:
Eles são os conteúdos elementares dos arquivos Blender.
They can reference each other, for reuse and instancing. (Child/parent, object/object-data, materials/images, in modifiers or constraints too…)
Their names are unique within a blend-file, for a given type.
Eles podem ser adicionados, removidos, editados e duplicados.
Eles podem ser vinculados entre arquivos (opção habilitada somente para um conjunto limitado de blocos de dados).
Eles podem ter seus próprios dados de animação.
They can have Custom Properties.
User will typically interact with the higher level data types (objects, meshes, etc.). When doing more complex projects, managing data-blocks becomes more important, especially when inter-linking blend-files. The main editor for that is the Outliner.
Not all data in Blender is a data-block, bones, sequence strips or vertex groups e.g. are not, they belong to armature, scene and mesh types respectively.
Tipos de blocos de dados
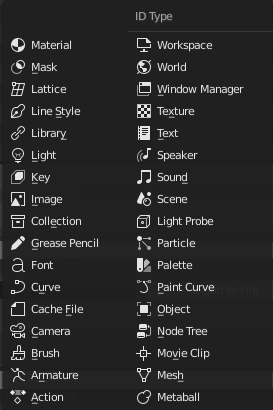
Tipos de blocos de dados com seus respectivos ícones.
Para referência, apresentamos aqui uma tabela de tipos de blocos de dados armazenados em arquivos Blender.
- Vinculações
A vinculação a bibliotecas, suporta também o vínculo a outros arquivos Blender.
- Pack
File Packing, supports file contents being packed into the blend-file (not applicable for most data-blocks which have no file reference).
Tipo |
Vinculações |
Pack |
Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
✓ |
Stores animation F-Curves.
Usados como blocos de dados para os dados de animação,
and the Nonlinear Animation editor.
|
||
✓ |
Uma espécie de esqueleto para deformar malhas.
Used as data of armature objects, and by the Armature Modifier.
|
||
✓ |
Usado pelas ferramentas de pintura.
|
||
✓ |
Used as data by camera objects.
|
||
✓ |
Used by Mesh Cache modifiers.
|
||
✓ |
Used as data by curve, font & surface objects.
|
||
✓ |
✓ |
Referencia arquivos de fonte.
Used by curve object-data of text objects.
|
|
✓ |
2D/3D sketch data used by Grease Pencil objects.
Usado como uma sobreposição auxiliar de informações, pelos editores
3D Viewport, Image, Sequencer & Movie Clip editors.
|
||
✓ |
Group and organize objects in scenes.
Used to instance objects, and in library linking.
|
||
✓ |
✓ |
Arquivos de imagem.
Used by shader nodes and textures.
|
|
✗ |
Armazenam formatos de geometrias, que podem ser animadas.
Usados pelos objetos de malha, curvas e treliças.
|
||
✓ |
Used as object data by light objects.
|
||
✗ |
✓ |
References to an external blend-file.
Access from the Outliner’s Blender File view.
|
|
✓ |
Used by the Freestyle renderer.
|
||
✓ |
Deformações por treliças embasadas em grades.
Used as data of lattice objects, and by the Lattice Modifier.
|
||
✓ |
Curvas 2D animadas para máscaras.
Usado pelos nós de composição e pelas faixas do editor de sequências.
|
||
✓ |
Define as propriedades de renderização, texturas e sombreamentos.
Usado por objetos, malhas e curvas.
|
||
✓ |
Uma superfície isométrica no espaço 3D.
Used as data of metaball objects.
|
||
✓ |
Geometry made of vertices/edges/faces.
Used as data of mesh objects.
|
||
✓ |
✗ |
Guardam referências a sequências de imagens ou arquivos de vídeo.
Used in the Movie Clip editor.
|
|
✓ |
Groups of re-usable nodes.
Used in the node editors.
|
||
✓ |
Uma entidade dentro da cena com localização,
escala e rotação.
Used by scenes & collections.
|
||
✓ |
Stores a paint or sculpt stroke.
Acesso a partir das ferramentas de pintura.
|
||
✓ |
Guarda predefinições de cores.
Acesso a partir das ferramentas de pintura.
|
||
✓ |
Definições de partículas
Utilizado por sistemas de partículas.
|
||
✓ |
Help achieve complex real-time lighting in Eevee.
|
||
✓ |
O armazenamento inicial de todos os dados exibidos e animados.
Usado como um armazenamento de alto nível para objetos e animações.
|
||
✓ |
✓ |
Reference to sound files.
Used as data of speaker objects.
|
|
✓ |
Fontes de sons para cenas 3D.
Used as data of speaker object.
|
||
✓ |
✗ |
Dados de texto.
Usados por scripts Python, e sombreadores OSL.
|
|
✓ |
Texturas 2D e 3D.
Used by brushes and modifiers.
|
||
✗ |
The overarching manager for all of Blender’s user interface.
Includes Workspaces, notification system, operators, and keymaps.
|
||
✓ |
Define global render environment settings.
|
||
✗ |
UI layout.
Used by each window, which has its own workspace.
|
Life Time
Every data-block has its usage counted (reference count), when there is more than one, you can see the number of current users of a data-block to the right of its name in the interface. Blender follows the general rule that unused data is eventually removed.
Since it is common to add and remove a lot of data while working, this has the advantage of not having to manually manage every single data-block. This works by skipping zero user data-blocks when writing blend-files.
Protected
Devido ao fato dos blocos de dados sem quaisquer usuários (ou usuários zero) não ser salvos, existem muitas ocasiões onde você poderá querer forçar o mantenimento desses dados independentemente de haver ou não usuários.
If you are building a blend-file to serve as a library of assets that you intend to link to and from other files, you will need to make sure that they do not accidentally get deleted from the library file.
To protect a data-block, use the button with the shield icon next to its name. The data-block will then never be silently deleted by Blender, but you can still manually remove it if needed.
Making Single User
When a data-block is shared between several users, you can make a copy of it for a given user. To do so, click on the user count button to the right of its name. This will duplicate that data-block and assign the newly created copy to that usage only.
Nota
Objects have a set of more advanced actions to become single-user, see their documentation.
Removendo blocos de dados
As covered in Life Time, data-blocks are typically removed when they are no longer used. They can also be manually unlinked or deleted.
Unlinking a data-block means that its user won’t use it anymore. This can be achieved by clicking on the «X» icon next to a data-block’s name. If you unlink a data-block from all of its users, it will eventually be deleted by Blender as described above (unless it is a protected one).
Deleting a data-block directly erases it from the blend-file, automatically unlinking it from all of its users. This can be achieved by Shift-LMB on the «X» icon next to its name.
Aviso
Deleting some data-blocks can lead to deletion of some of its users, which would become invalid without them. The main example is that object-data deletion (like mesh, curve, camera…) will also delete all objects using it.
Those two operations are also available in the context menu when RMB-clicking on a data-block in the Outliner.
Propriedades personalizadas
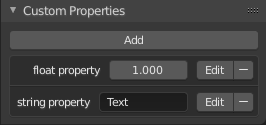
Custom Properties panel.
Custom properties are a way to store your own data in Blender’s data-blocks. It can be used for rigging (where bones and objects can have custom properties driving other properties), and Python scripts, where it’s common to define new settings not available in Blender. It is also possible to access custom properties from materials via the Attribute Node.
Only certain data supports custom properties:
All data-blocks types.
Bones and pose bones.
Sequence strips.
To add a custom property, search for the Custom Properties panel, found at the bottom of most Properties or Sidebar region, and click New. Properties can be removed from the same location with the delete icon. Once properties are added they can be configured via the edit icon to work for a particular use case; see Editing Properties for more information.
Editing Properties
Interface do usuário
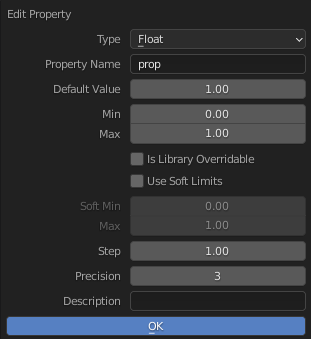
Custom Properties edit pop-up.
Custom properties can be edited using the panel available for data types that support it. Editing the properties allows you to configure things such as default values, ranges, and even add a custom tooltip.
- Tipo
The data type of the property; different data types have can only have specific data properties.
- Float
A numeric value with decimals e.g. 3.141, 5.0, or 6.125.
- Float Array
A collection of multiple float data types e.g.
[3.141, 5.0, 6.125]. This data type can also be used for data that can be represented as a float array such as colors. These special float arrays can be set in the Subtype selector.- Integer
A numeric value without any decimals e.g. 1, 2, 3, or 4.
- Integer Array
A collection of multiple integer data types e.g.
[1, 2, 3, 4].- String
A sequence of characters such as «Some Text».
- Python
Edit a Python data type directly, used for unsupported data types.
Nota
Boolean values must be handled as integers and only work when using Min/Max values that are integers and that are no more than 1 apart.
At this point, the Boolean values will still look like integers but behave like a Boolean having one lower, off, value and a higher, on, value.
- Array Length
The number of elements in the array. Note that if the array length is greater than 7 you cannot directly edit its elements, you must press Edit Value to edit the elements of the array.
- Property Name
The text that is displayed to the left of the value. This name is also used to access the property via Python.
- Default Value
This sets the default value of the property used by the Reset to Default Value operator.
Aviso
Default values are used as the basis of NLA blending, and a nonsensical default (e.g. 0 for a property used for scaling) on a property intended for being keyframed is likely to cause issues.
- Mínimo, Máximo
The minimum/maximum value the custom property can take.
- Is Library Overridable
Allow the property to be overridden when the data-block is linked.
- Use Soft Limits
Enables limits that the Property Value slider can be adjusted to without having to input the value numerically.
- Soft Min, Max
The minimum/maximum value for the soft limit.
- Passos
A multiplier to control how much the data type is incremented at a time. The internal step size for floats is 0.01, so a Step value of 5 will increment at a rate of 0.05 and a Step value of 100 will increment by 1.0. For integers the internal step size is 1.
- Precisão
The number of digits after the decimal to display in the user interface for float data types.
- Subtype
Specifies the type of data the property contains, which affects how it appears in the user interface. In order for this property to appear the Property Value must be a vector of floats. For either of the color subtypes to work the Property Value must be a vector with three or four values depending on the availability of an Alpha Channel.
- Plane Data
Data values do not have any special behavior.
- Linear Color
Color in linear color space.
- Gamma-Corrected Color
Color in gamma corrected color space.
- Euler Angles
Euler Rotation angles.
- Quaternion Angles
Quaternion Rotation angles.
- Descrição
Allows you to write a custom Tooltip for your property.
Python Access
Custom properties can be accessed in a similar way to dictionaries, with the constraints that keys can only be strings, and values can only be strings, numbers, arrays of such, or nested properties.
See the API documentation for details.