Color Ramp Node
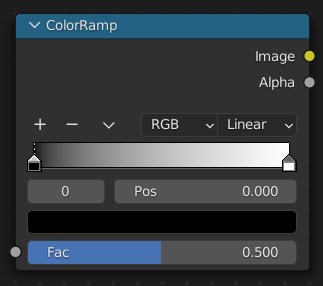
The Color Ramp Node is used for mapping values to colors with the use of a gradient.
Inputs
- Fator
The Factor input is used as an index for the color ramp.
Properties
- Color Ramp
For controls see Gradiente de cores.
Saídas
- Imagem
Standard color output.
- Alfa
Standard alpha output.
Examples
Creating an Alpha Mask
An often overlooked use case of the Color Ramp is to create an alpha mask, or a mask that is overlaid on top of another image. Such a mask allows you to select parts of the background to be shown through.
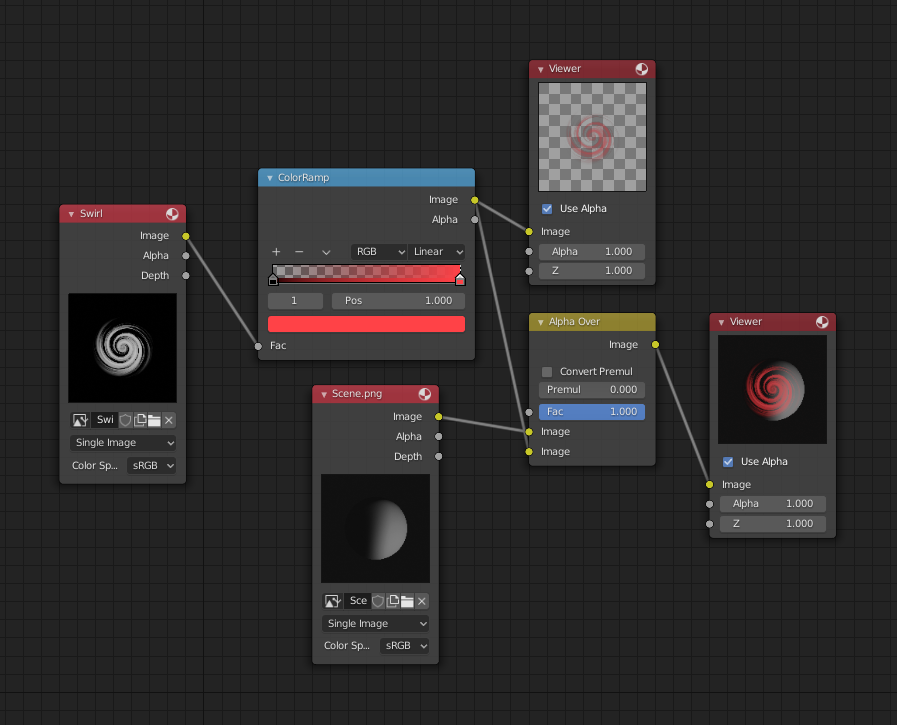
Using the Color Ramp node to create an alpha mask.
In the map above, a black-and-white swirl image, which is lacking an alpha channel, is fed into the Color Ramp node as a Factor.
The Color Ramp node is set to a purely transparent color on the left end of the gradient, and a fully red color on the right. As you can see in the Viewer node, the Color Ramp node puts out a mask that is fully transparent where the image is black. Black is zero, so Color Ramp outputs the color at the left end of the gradient, which is set to transparent. The Color Ramp image is fully red and opaque where the image is white (which is 1).
You can verify that the output image mask is indeed transparent by overlaying it on top of another image.
Colorizing an Image
In this example multiple colors are added to the color gradient converting a black-and-white image into a flaming swirl.
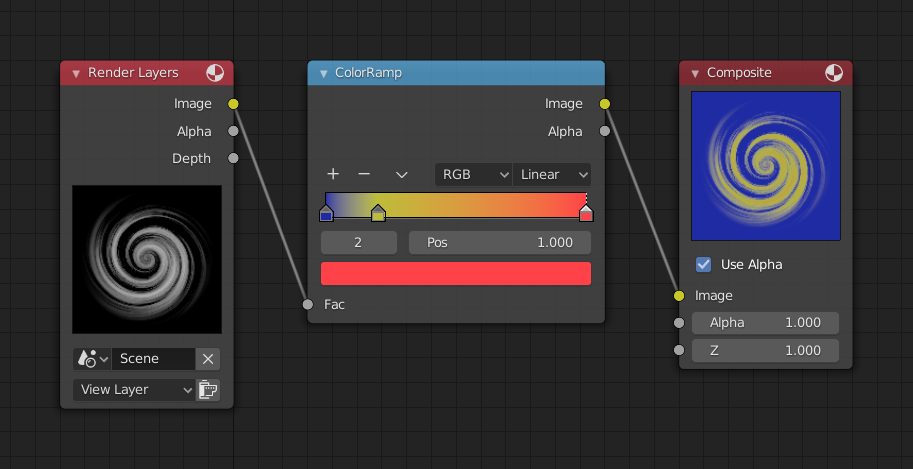
The shades of gray in the input image are mapped to three colors: blue, yellow, and red, all fully opaque (alpha of 1). Where the image is black, Color Ramp substitutes blue (the first color stop). Where it is some shade of gray, Color Ramp outputs a corresponding color from the gradient (bluish, yellow, to reddish). Where the image is fully white, the Color Ramp outputs red.