Smooth Corrective Modifier¶
The Smooth Corrective modifier is used to reduce highly distorted areas of a mesh by smoothing the deformations.
This is typically useful after an Armature modifier, where distortion around joints may be hard to avoid, even with careful weight painting.
To use this modifier effectively, it is important to understand the basics of how it works.
- Rest State
Used as a reference to detect highly distorted areas. The original vertex locations are used by default.
- Làm Mịn -- Smoothing
Many options for this modifier relate to smoothing which is used internally to correct the distorted regions.
Tùy Chọn -- Options¶
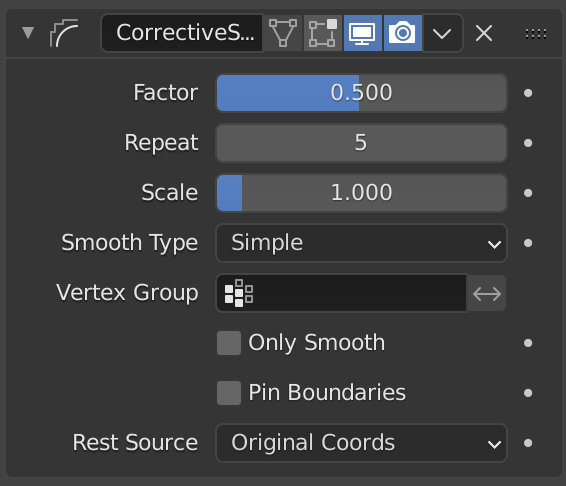
The Smooth Corrective modifier.¶
- Hệ Số -- Factor
The factor to control the smoothing amount. Higher values will increase the effect.
Values outside expected range (above 1.0 or below 0.0) will distort the mesh.
- Lặp Lại -- Repeat
The number of smoothing iterations, equivalent to executing the Smooth tool multiple times.
- Scale
Additional scaling factor to increase the size of the mesh. This is useful because sometimes the Smooth Corrective modifier will introduce volume loss, especially when used with a rig.
- Loại Mịn Hóa -- Smooth Type
Select the smoothing method used.
- Đơn Giản -- Simple
This simply relaxes vertices to their connected edges.
- Trọng Lượng tùy Chiều Dài -- Length Weight
Uses a method of relaxing that weights by the distance of surrounding vertices. This option can give higher quality smoothing in some cases, by better preserving the shape of the original form.
- Nhóm Điểm Đỉnh -- Vertex Group
If set, restrict the effect to the only vertices in that vertex group. This allows for selective, real-time smoothing, by painting vertex weights.
- Chỉ Làm Mịn Thôi -- Only Smooth
This option is included to preview the smoothing used, before correction is applied.
- Giữ Ranh Giới -- Pin Boundaries
Prevent boundary vertices from smoothing.
- Nguồn cho Tư Thế Nghỉ -- Rest Source
Select the source for reference vertex positions that defines the undeformed state.
- Original Coordinates
Use the original input vertex positions. This relies on the original mesh having the same number of vertices as the input, modified mesh.
- Bind Coordinates
Optionally you may bind the modifier to a specific state. This is required when there are constructive modifiers such as Subdivision Surface or Mirror in the stack before this modifier.