Partes del Nodo¶
Todos los nodos en Blender están basados en una construcción similar. Esto se aplica a cualquier tipo de nodo. Estas partes incluyen el Título, Conectores, Previsualización y más.
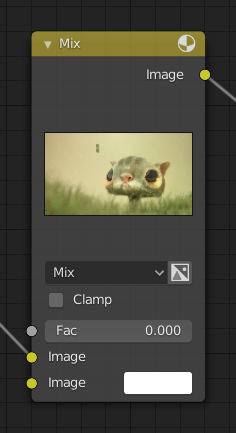
Título¶
El título muestra el nombre/tipo del nodo, puede ser reemplazado cambiando la Etiqueta del nodo. En el lado izquierdo del título está el botón colapsar que se puede emplear para colapsar el nodo. Esto puede hacerse también con H.
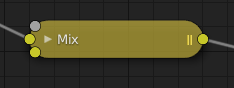
Cómo aparece un nodo cuando está colapsado.¶
Conectores¶
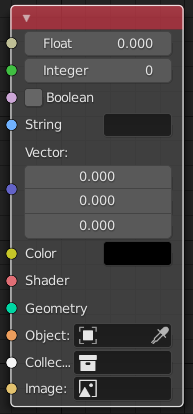
The sockets input and output values from the node. They appear as little colored circles on either side of the node. Unused sockets can be hidden with Ctrl-H. There are two kinds of sockets: inputs and outputs.
Cada conector tiene un código de color dependiendo de qué tipo de dato maneja.
- Decimal (gris)
Indicates numeric value’s information. It can either be a single numerical value or a so-called «value map». (You can think of a value map as a gray-scale map where the different amount of bright/dark reflects the value for each point.) If a single value is used as an input for a «value map» socket, all points of the map are set to this same value. Common use: Alpha maps and value options for a node.
- Entero (verde lima)
Utilizado para pasar un valor entero (un número sin un componente fraccional).
- Booleano (rosa)
Usado para pasar un valor verdadero o falso.
- Cadena (azul claro)
Usado para pasar un valor de texto.
- Vector (azul oscuro)
Indica información vectorial, de coordenadas y normal.
- Color (amarillo)
Indicates that color information needs to be input or will be output from the node. Depending on the node tree type, the color has an alpha channel or not.
- Sombreador (verde brillante)
- Geometría (turquesa)
Usado en Nodos de Geometría.
- Objeto (naranja)
Usado para pasar un bloque de datos de un objeto.
- Colección (blanco)
Utilizado para pasar un bloque de datos de una colección.
- Imagen (albaricoque)
Utilizado para pasar un bloque de datos de una imagen.
Entradas¶
The inputs are located on bottom left side of the node, and provide the data the node needs to perform its function. Each input socket, except for the green shader input, when disconnected, has a default value which can be edited via a color, numeric, or vector interface input. In the screenshot of the node above, the second color option is set by a color interface input.
Some nodes have special sockets that can accept multiple inputs into a single socket. These sockets will have an ellipsis shape rather than a circle to indicate its special behavior.
Salidas¶
Las salidas están ubicadas en el lado superior derecho del nodo y pueden conectarse a entradas de nodos posteriores bajo el árbol de nodos.
Conversión¶
Some socket types can be converted to other socket types either implicitly or explicitly. Implicit conversion can happen automatically without the need of a conversion node.
For example, color and float sockets can both be placed into one another. Once a socket conversion is made data may be lost and cannot be retrieved later down the node tree. Implicit socket conversion can sometimes change the data units as well. When plugging a Value input node into an angle socket will default to use radians regardless of the scene Unidades. This happens because the value node has no unit while the angle input does.
Conversiones válidas:
Between color and vector – in this case the using individual color channels to store the vector.
Between color and float – the color data is converted to its gray scale equivalent.
Color/float/vector to Shader – implicitly converts to color and gives the result of using an emission node.
Explicit conversion requires the use of a conversion node for example the Sombreador a RVA node or the Nodo RVA a Grises node. The Nodo Operar (Math) node also contains some functions to convert between degrees and radians.
Propiedades¶
Muchos nodos tienen configuraciones que pueden afectar el modo en el interactúan con entradas y salidas. Las propiedades de los nodos están ubicadas bajo las salidas y sobre las entradas.
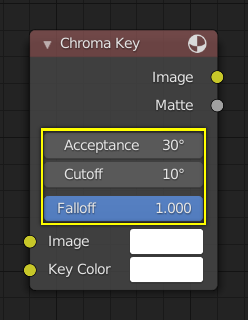
Un ejemplo de controles en el nodo Recortar por Croma (Chroma Key).¶
Previsualización¶
On some nodes this shows a preview image of how the output data for a certain channel will appear. Usually it shows color data.
The preview can be toggled using the icon on the very top right-hand corner of the node, next to the title.
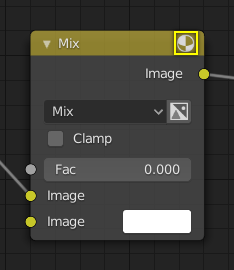
Cómo aparece un nodo sin la previsualización.¶