Opções de saída¶
O primeiro passo no processo de renderização é determinar e definir as opções de saída. Isto inclui o tamanho da renderização, a taxa de quadros, a proporção de aspecto dos pixeis, localização da saída e tipo de arquivo.
Painel dimensões¶
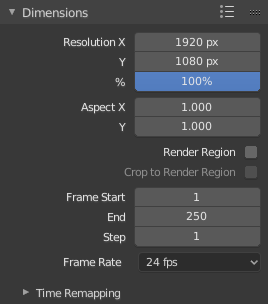
Dimensions panel.
- Predefinições de renderização
- Opções de predefinições de formatos comuns para TVs e telas.
- Resolução
- X/Y
- O número de pixeis horizontalmente e verticalmente na imagem.
- Porcentagem
- Um deslizador numérico para aumentar ou decrescer o tamanho da imagem renderizada relativamente aos valores presentes em X e Y descritos acima. Isto é útil para pequenos testes de renderização que possuem as mesmas proporções da imagem final.
- Proporção de aspecto
Televisores mais antigos podem ter pixeis que não são quadrados, portanto, isto pode ser usado para controlar o formato dos pixeis ao longo dos respectivos eixos. Isto irá fazer uma pré-distorção nas imagens, que parecerão mais esticadas em uma tela de computador, mas que serão mostradas de maneira correta em uma tela de TV mais antiga (CRTs). É importante que vocẽ utilize a proporção de aspecto correta quando for renderizar para evitar o re-escalonamento, resultando em qualidades de imagens mais baixas.
See Video Output for details on pixel aspect ratio.
- Render Region
Renders just a portion of the view instead of the entire frame. See the Render Region documentation to see how to define the size of the render region.
Nota
Isto desabilita a opção Salvar contingenciamentos no painel Performance e a opção Amostragem completa no painel Antisserrilhamento.
- Crop Render Region
- Crops the rendered image to the size of the render region, instead of rendering a transparent background around it.
- Faixa de quadros
- Set the Start and End frames for Rendering Animations. Step controls the number of frames to advance by for each frame in the timeline.
- Taxa de quadros
- For an Animation the frame rate is how many frames will be displayed per second.
- Remapeamento de tempo
- Usado para remapear o comprimento de uma animação.
Painel Saída¶
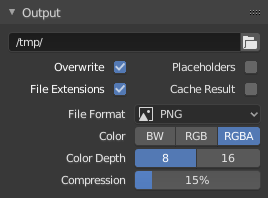
O painel Saída.
This panel provides options for setting the location of rendered frames for animations, and the quality of the saved images.
- Caminho de arquivo
Choose the location to save rendered frames.
When rendering an animation, the frame number is appended at the end of the file name with four padded zeros (e.g.
image0001.png). You can set a custom padding size by adding the appropriate number of#anywhere in the file name (e.g.image_##_test.pngtranslates toimage_01_test.png).This setting expands Relative Paths where a
//prefix represents the directory of the current blend-file.- Sobrescrever
- Sobrescreve os arquivos existentes durante a renderização.
- Substitutivos
- Create empty placeholder frames while rendering.
- Extensões de arquivo
- Adds the correct file extensions per file type to the output files.
- Resultados do cache
- Saves the rendered image and passes to a multi-layer EXR file in temporary location on your hard drive. This allows the compositor to read these to improve the performance, especially for heavy compositing.
- File Format
Choose the file format to save to. Based on which format is used, other options such as channels, bit depth and compression level are available.
For rendering out to images see: saving images, for rendering to videos see rendering to videos.
- Modo de cor
Choose the color format to save the image to. Note that RGBA will not be available for all image formats.
BW, RGB, RGBA
Dica
Primitive Render Farm
An easy way to get multiple machines to share the rendering workload is to:
- Set up a shared directory over a network file system.
- Disable Overwrite, enable Placeholders in the Render Output panel.
- Start as many machines as you wish rendering to that directory.
Post Processing Panel¶
Reference
| Panel: |
|---|
The Post Processing panel is used to control different options used to process your image after rendering.
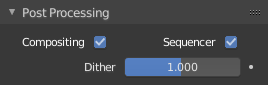
Post Processing panel.
- Sequencer
- Renders the output of the Video Sequence editor, instead of the view from the 3D scene’s active camera. If the sequence contains scene strips, these will also be rendered as part of the pipeline. If Compositing is also enabled, the Scene strip will be the output of the Compositor.
- Compositing
- Renders the output from the compositing node setup, and then pumps all images through the Composite node map, displaying the image fed to the Composite Output node.
Dithering¶
Dithering is a technique for blurring pixels to prevent banding that is seen in areas of gradients, where stair-stepping appears between colors. Banding artifacts are more noticeable when gradients are longer, or less steep. Dithering was developed for graphics with low bit depths, meaning they had a limited range of possible colors.
Dithering works by taking pixel values and comparing them with a threshold and neighboring pixels then does calculations to generate the appropriate color. Dithering creates the perceived effect of a larger color palette by creating a sort of visual color mixing. For example, if you take a grid and distribute red and yellow pixels evenly across it, the image would appear to be orange.
The Dither value ranges from 0 to 2.