Configurações de imagem
Image Panel
- Imagem
Menu de blocos de dados.
- Novo
+ O botão de Nova imagem abre uma caixa de diálogo para que possa ser definida uma imagem do tipo Generated.
- Novo
Fonte
See about Formatos gráficos suportados.
Single Image
Uma imagem estática ou um único quadro.
Image Sequence
Each frame is stored in a separate file. How to Abrindo uma sequência de imagem. For options see Movie below.
Filme
Quadros empacotados em um contêiner.
- Quadros
Define o intervalo de quadros a ser usado.
- Combinar com o comprimento do filme
This button sets the movies frames to the length of the selected movie.
- Início
Global starting frame of the sequence, when the playback should start. This is a global setting which means it affects all clip users such as the Movie Clip editor itself, motion tracking constraints and Compositor nodes.
- Deslocamento
Desloca o primeiro quadro do clipe. Essa definição adiciona um deslocamento extra para o número de quadros durante as conversões de quadros da cena para o número de quadros dentro do nome dos arquivos. Esta opção não afeta os dados de rastreamento ou quaisquer outros dados associados.
- Cíclico(a)
Inicia novamente e repete novamente a reprodução após o último quadro para criar um ciclo contínuo.
- Atualização automática
Atualiza automaticamente as imagens durante as mudanças de quadro.
- Desentrelaçar
Removes fields in a video file. For example, if it is an analog video and it has even or odd interlacing fields.
Gerado
Image generated in Blender.
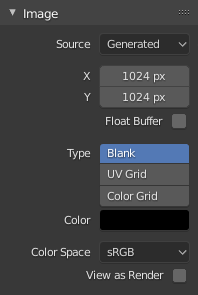
O painel de imagem para a fonte de imagens geradas. |
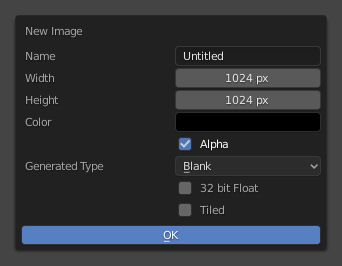
O menu para criar Nova imagem na caixa de diálogo. |
- Largura e altura
O tamanho da imagem em pixeis.
- Color
Define o preenchimento de cor caso esteja criando uma imagem em branco.
- Tipo
- Em branco
Cria uma imagem em branco composta de uma única cor especificada.
- Grade UV
Cria um padrão quadriculado usando cruzes colorizadas (+) em cada um dos quadrados.
- Grade de cor
Cria uma grade colorizada um pouco mais complexa usando cores e números denotando as localizações na grade. Ela pode ser usada para testar como as UVs foram mapeadas e para a redução de esticamentos ou distorções.
- 32-bit Float
Creates a 32-bit image. This is a larger file size, but holds much more color information than the standard 8-bit image. For close-ups and large gradients, it may be better to use a 32-bit image.
- Ladrilhado
Creates an image with support for UDIMs. This option creates the first
1001tile; more tiles can be added later in the UDIM Tiles panel.
Opções comuns
- Arquivo
Utilizado para substituição ou empacotamento de arquivos.
- Pack
Embute o recurso dentro do arquivo Blender atual.
- Caminho
O caminho para o arquivo vinculado.
- Abrir
Opens the File Browser to select a file from a drive.
- Recarregar
Reloads the file. Useful when a file has been reworked in an external application.
- Usar múltipla visualização
See Multi-View.
- Color Space
The Color Space the image file was saved in. Once loaded into Blender, the color will be treated as linear color. This option ensure the correct conversion to linear color is used.
Texture’s color, and final renders are often stored in sRGB, while OpenEXR images are stored in a linear color space. Some images such as normal, bump or stencil maps do not strictly contain “colors”, and on such values, no color space conversion should ever be applied. For such images, the color space should be set to Non-Color.
The list of color spaces depends on the active OCIO config. The default supported color spaces are described in detail here: Default OpenColorIO Configuration
- Alfa
Representation of the image’s Alpha Channel, to convert to and from when saving and loading the image. This option is only available if the input format support’s encoding transparency.
- Straight
Store RGB and alpha channels separately with alpha acting as a mask, also known as unassociated alpha. Commonly used by image editing applications and file formats like PNG. This preserves colors in parts of the image with zero alpha.
- Premultiplied
Store RGB channels with alpha multiplied in, also known as associated alpha. The natural format for renders and used by file formats like OpenEXR. This can represent purely emissive effects like fire correctly, unlike straight alpha.
- Channel Packed
Different images are packed in the RGB and alpha channels, and they should not affect each other. Channel packing is commonly used by game engines to save memory.
- None
Ignore alpha channel from the file and make image fully opaque.
- Half Float Precision
Load the image as having only a Bit Depth of 16 bits per channel instead of 32 bits which saves memory.
- Visualizar como renderização
Applies color transform when displaying this image on the screen.