Viewport¶
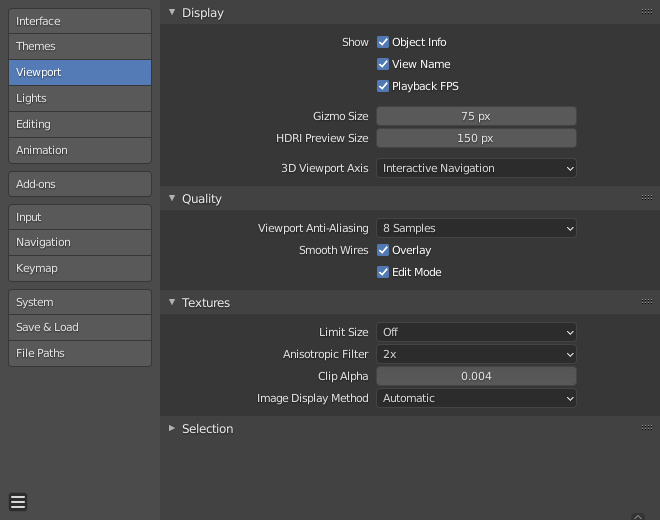
Blender Preferences Viewport section.¶
Display¶
- Show
- Object Info
Display the active Object name and frame number at the top left of the 3D Viewport.
- View Name
Display the name and type of the current view in the top left corner of the 3D Viewport. For example: "User Perspective" or "Top Orthographic".
- Playback FPS
Show the frames per second screen refresh rate while an animation is played back. It appears in the top left of the 3D Viewport, displaying red if the frame rate set cannot be reached.
- Gizmo Size
Diameter of the gizmo.
- HDRI Preview Size
Diameter of the HDRI sphere overlay.
- 3D Viewport Axis
- Interactive Navigation
Display the axis as an interactive gizmo.
- Click
Sets the viewport to display along this axis.
- Drag
Orbit the view.
- Simple Axis
Display simple, less intrusive axis in the viewport.
- Size
Size of the simple axis.
- Brightness
How vivid the colors of the simple axis are.
- Off
Disables the viewport axis.
Quality¶
- Viewport Anti-Aliasing
Control the Anti-Aliasing for higher quality rendering.
- Smooth Wires
- Overlay
Display overlays with smooth wire, without this wires will be rendered aliased. To increase the visibility you can disable this and Edit Mode, since edges do not blend into other shaded regions.
- Edit Mode
Display smooth wire in Edit Mode, without this wires will be rendered aliased.
Textures¶
- Limit Size
Limit the maximum resolution for pictures used in textured display to save memory. The limit options are specified in a square of pixels (e.g: the option 256 means a texture of 256×256 pixels). This is useful for game engineers, whereas the texture limit matches paging blocks of the textures in the target graphic card memory.
- Anisotropic Filtering
Sets the level of anisotropic filtering. This improves the quality of textures that are rendered at the cost of performance.
- Clip Alpha
Clip alpha below this threshold in the 3D Viewport. Note that, the default is set to a low value to prevent issues on some GPUs.
- Image Display Method
Method to render images; the following options are supported:
- Automatic
Automatically use GLSL which runs on the GPU for performance but falls back to the CPU for large images which might be slow when loaded with the GPU.
- 2D Texture
Uses CPU for display transform and render images as a 2D texture.
- GLSL
Fastest method using GLSL for display transform and render images as a 2D texture.
Selection¶
- OpenGL Depth Picking
This option uses an alternative method of picking which uses depth information to select the front-most elements. It is only used for selecting with the cursor (not box select, lasso, circle select, etc.).
Performance varies depending on your OpenGL hardware and drivers.