Giới Thiệu (Introduction)
Animation (Hoạt Họa)
Animation is making an object move or change shape over time. Objects can be animated in many ways:
- Di chuyển toàn bộ như một vật thể (Moving as a whole object)
Thay đổi vị trí, định hướng hoặc kích thước của chúng theo thời gian;
- Biến dạng chúng (Deforming them)
Animating their vertices or control points;
- Thừa Kế (Inherited animation)
Causing the object to move based on the movement of another object (e.g. its parent, hook, armature, etc.).
In this chapter, we will cover the first two, but the basics given here are actually vital for understanding the following chapters as well.
Animation is typically achieved with the use of keyframes.
Màu cho Trạng Thái (State Colors)
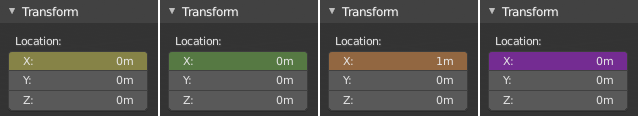
State colors of properties.
Properties have different colors and menu items for different states.
Màu Ghi/Xám hóa |
Chưa hoạt họa/Không hoạt họa/hình |
Màu Vàng (Yellow) |
Keyframed on the current frame |
Lục (Green) |
Keyframed on a different frame |
Màu Da Cam (Orange) |
Changed from the keyframed value |
Màu Tím |
Controlled by a driver |
The changed value highlight currently doesn't work with NLA.
Dựng Giàn Điều Khiển (Rigging)
Rigging is a general term used for adding controls to objects, typically for the purpose of animation.
Rigging often involves using one or more of the following features:
- Cốt (Armatures) (Armatures)
This allows mesh objects to have flexible joints and is often used for skeletal animation.
- Ràng Buộc (Constraints) (Constraints)
To control the kinds of motions that make sense and add functionality to the rig.
- Bộ Điều Chỉnh Vật Thể (Object Modifiers) (Object Modifiers)
Mesh deformation can be quite involved, there are multiple modifiers that help control this.
- Hình Mẫu (Shape Keys) (Shape Keys)
To support different target shapes (such as facial expressions) to be controlled.
- Điều Vận (Drivers) (Drivers)
So your rig can control many different values at once, as well as making some properties automatically update based on changes elsewhere.
Rigging can be as advanced as your project requires, rigs are effectively defining own user interface for the animator to use, without having to be concerned the underlying mechanisms.
Một Số Ví Dụ (Examples)
An armature is often used with a modifier to deform a mesh for character animation.
A camera rig can be used instead of animating the camera object directly to simulate real-world camera rigs (with a boom arm, mounted on a rotating pedestal for example, effects such as camera jitter can be added too).
Xem thêm
The content of this chapter is simply a reference to how rigging is accomplished in Blender. It should be paired with additional resources such as Nathan Vegdahl's excellent introduction to the fundamental concepts of character rigging, Humane Rigging.