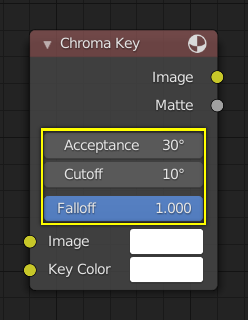
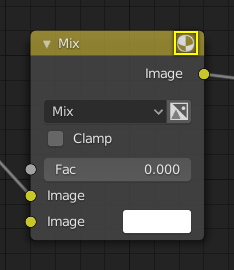
Éléments d’un nœud¶
Tous les nœuds dans Blender sont basés sur une construction similaire. Cela s’applique à tout type de nœud. Ces parties comprennent le titre, les prises, l’aperçu et plus encore.
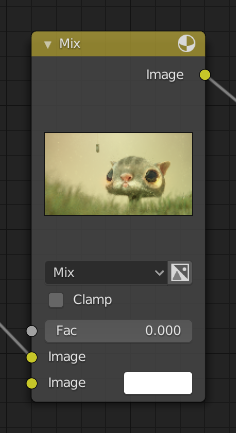
Titre¶
Affiche le nom/type du nœud; il peut être remplacé en modifiant le Label du nœud. Sur le côté gauche du titre se trouve la bascule de réduction qui peut être utilisée pour réduire le nœud. Cela peut également être fait avec H.
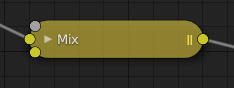
Un nœud replié apparaît ainsi.¶
Prises¶
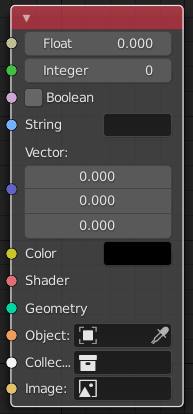
The sockets input and output values from the node. They appear as little colored circles on either side of the node. Unused sockets can be hidden with Ctrl-H. There are two kinds of sockets: inputs and outputs.
Chaque prise a une couleur codée selon le type de donnée qu’elle gère.
- Float (gris)
Indicates numeric value’s information. It can either be a single numerical value or a so-called « value map ». (You can think of a value map as a gray-scale map where the different amount of bright/dark reflects the value for each point.) If a single value is used as an input for a « value map » socket, all points of the map are set to this same value. Common use: Alpha maps and value options for a node.
- Integer (vert citron)
Utilisé pour passer une valeur entière (un nombre sans partie fractionnaire).
- Boolean (rose)
Utilisé pour passer une valeur vraie ou fausse.
- Chaîne (bleu pâle)
Utilisé pour passer une valeur texte.
- Vector (bleu foncé)
Indique les informations sur le vecteur, coordonnées et normale.
- Color (jaune)
Indicates that color information needs to be input or will be output from the node. Depending on the node tree type, the color has an alpha channel or not.
- Shader (vert vif)
- Geometry (turquoise)
Utilisé dans Geometry Nodes.
- Object (orange)
Utilisé pour passer un bloc de données d’objet.
- Collection (white)
Utilisé pour passer le bloc de données d’une collection.
- Image (abricot)
Utilisé pour passer un bloc de données d’image.
Entrées¶
The inputs are located on bottom left side of the node, and provide the data the node needs to perform its function. Each input socket, except for the green shader input, when disconnected, has a default value which can be edited via a color, numeric, or vector interface input. In the screenshot of the node above, the second color option is set by a color interface input.
Some nodes have special sockets that can accept multiple inputs into a single socket. These sockets will have an ellipsis shape rather than a circle to indicate its special behavior.
Sorties¶
Les Outputs (sorties) sont localisées sur le côté en haut à droite du nœud, et peuvent être connectées à l’entrée de nœuds situés plus bas dans l’arborescence des nœuds.
Conversion¶
Some socket types can be converted to other socket types either implicitly or explicitly. Implicit conversion can happen automatically without the need of a conversion node.
For example, color and float sockets can both be placed into one another. Once a socket conversion is made data may be lost and cannot be retrieved later down the node tree. Implicit socket conversion can sometimes change the data units as well. When plugging a Value input node into an angle socket will default to use radians regardless of the scene Unités. This happens because the value node has no unit while the angle input does.
Conversions valides :
Between color and vector – in this case the using individual color channels to store the vector.
Between color and float – the color data is converted to its gray scale equivalent.
Color/float/vector to Shader – implicitly converts to color and gives the result of using an emission node.
Explicit conversion requires the use of a conversion node for example the Nœud Shader To RGB node or the Nœud RGB to BW node. The Nœud Math node also contains some functions to convert between degrees and radians.