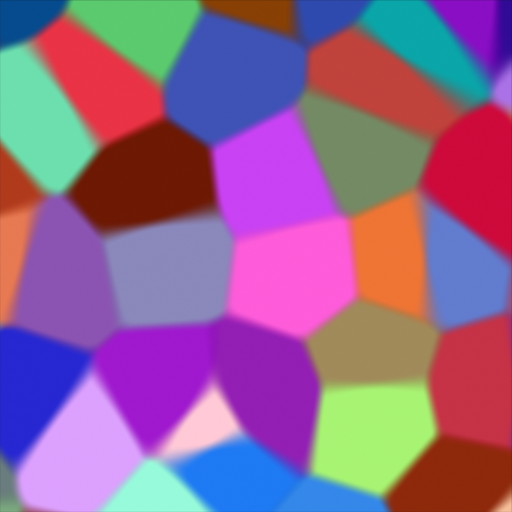
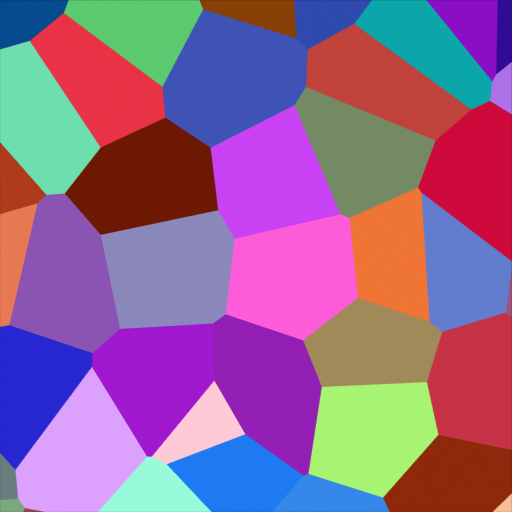
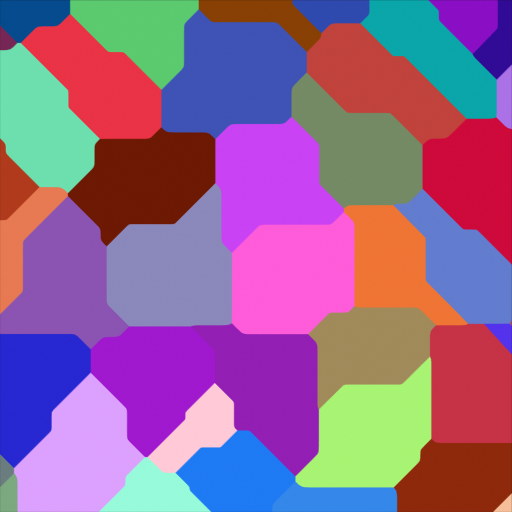
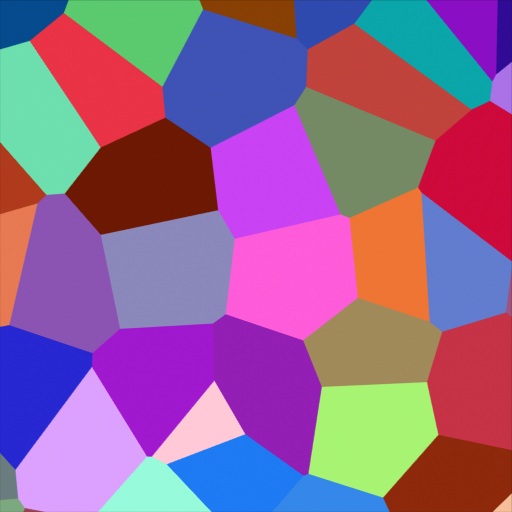
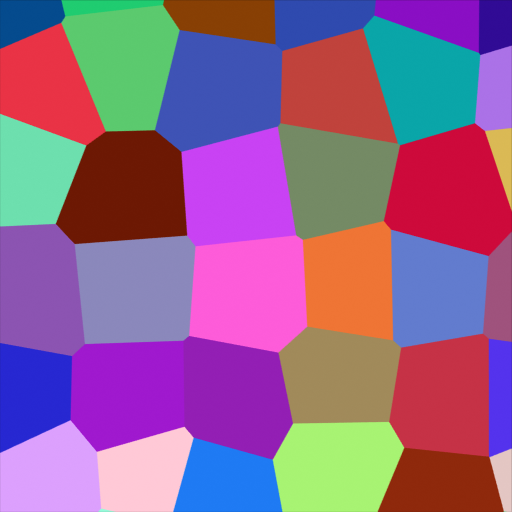
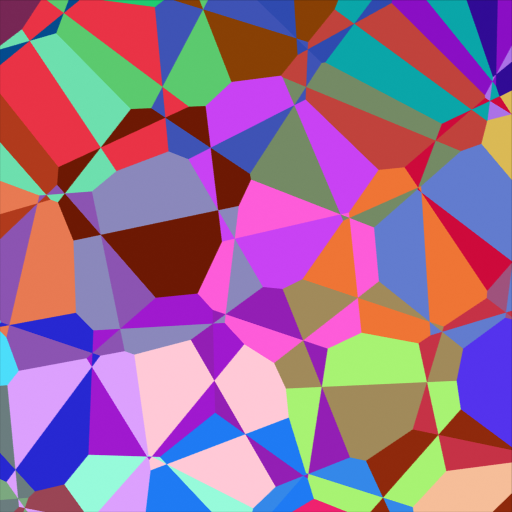
Voronoi Texture Node¶
The Voronoi Texture node evaluates a Worley Noise at the input texture coordinates.
Inputs¶
The inputs are dynamic, they become available if needed depending on the node properties.
- Vector
Texture coordinate to evaluate the noise at; defaults to Generated texture coordinates if the socket is left unconnected.
- W
Texture coordinate to evaluate the noise at.
- Scale
Scale of the noise.
- Detail
Number of noise octaves. The fractional part of the input is multiplied by the magnitude of the highest octave. Higher number of octaves corresponds to a higher evaluation time.
- Roughness
Blend between a smoother noise pattern, and rougher with sharper peaks.
- Lacunarity
The difference between the scale of each two consecutive octaves. Larger values corresponds to larger scale for higher octaves.
- Smoothness
The smoothness of the noise.
- Exponent
Exponent of the Minkowski distance metric.
- Randomness
The randomness of the noise.
Properties¶
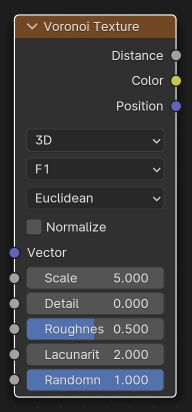
- Dimensions
The dimensions of the space to evaluate the noise in.
- 1D:
Evaluate the noise in 1D space at the input W.
- 2D:
Evaluate the noise in 2D space at the input Vector. The Z component is ignored.
- 3D:
Evaluate the noise in 3D space at the input Vector.
- 4D:
Evaluate the noise in 4D space at the input Vector and the input W as the fourth dimension.
Higher dimensions corresponds to higher render time, so lower dimensions should be used unless higher dimensions are necessary.
- Feature
The Voronoi feature that the node will compute.
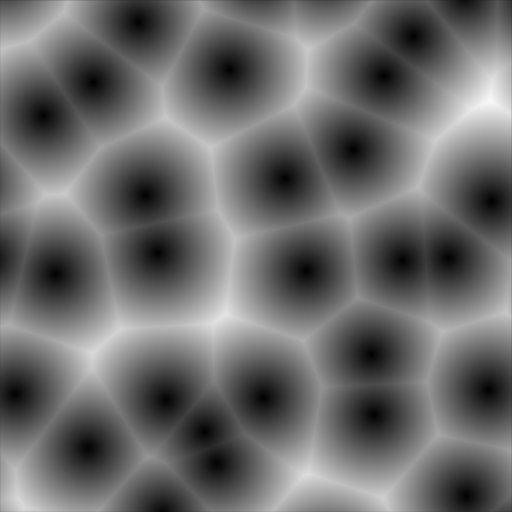
- F1:
The distance to the closest feature point as well as its position and color.
- F2:
The distance to the second closest feature point as well as its position and color.
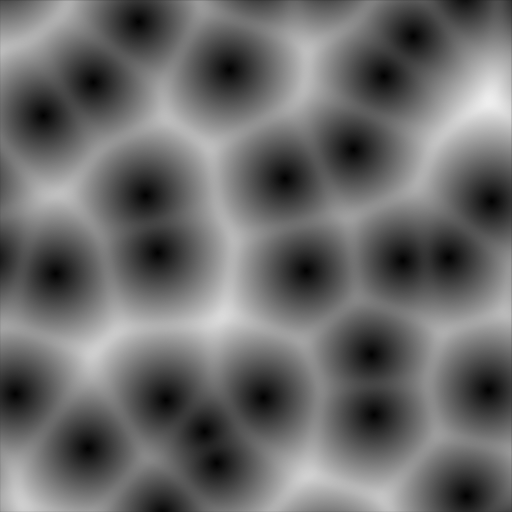
- Smooth F1:
A smooth version of F1.
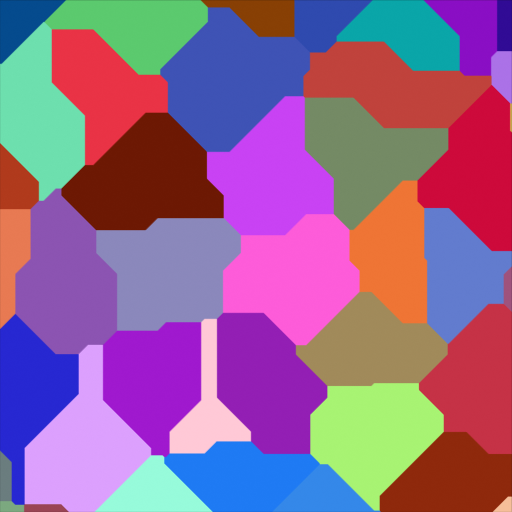
- Distance to Edge:
The distance to the edges of the Voronoi cells.
- N-Sphere Radius:
The radius of the n-sphere inscribed in the Voronoi cells. In other words, it is half the distance between the closest feature point and the feature point closest to it.
- Distance Metric
The distance metric used to compute the texture.
- Euclidean:
Use the Euclidean distance metric.
- Manhattan:
Use the Manhattan distance metric.
- Chebychev:
Use the Chebychev distance metric.
- Minkowski:
Use the Minkowski distance metric. The Minkowski distance is a generalization of the aforementioned metrics with an Exponent as a parameter. Minkowski with an exponent of one is equivalent to the Manhattan distance metric. Minkowski with an exponent of two is equivalent to the Euclidean distance metric. Minkowski with an infinite exponent is equivalent to the Chebychev distance metric.
- Normalize
If enabled, ensures that the output values stay in the range 0.0 to 1.0. In rare cases, the output value may be outside that range when Feature is F2.
Outputs¶
- Distance
Distance.
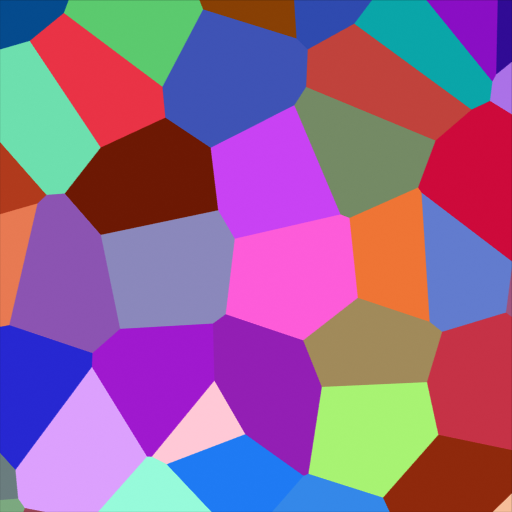
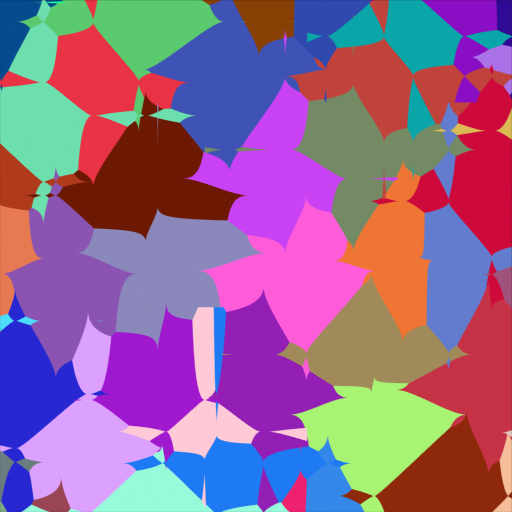
- Color
Cell color. The color is arbitrary.
- Pozicioniranje
Position of feature point.
- W
Position of feature point.
- Radius
N-Sphere radius.
Notes¶
In some configurations of the node, especially for low values of Randomness, rendering artifacts may occur. This happens due to the same reasons described in the Notes section in the White Noise Texture page and can be fixed in a similar manner as described there.
Examples¶
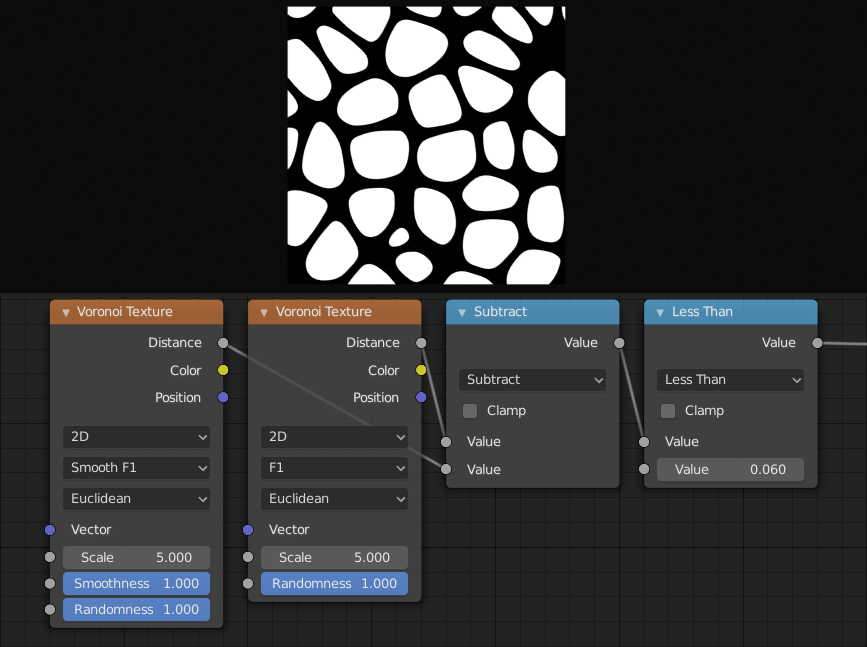
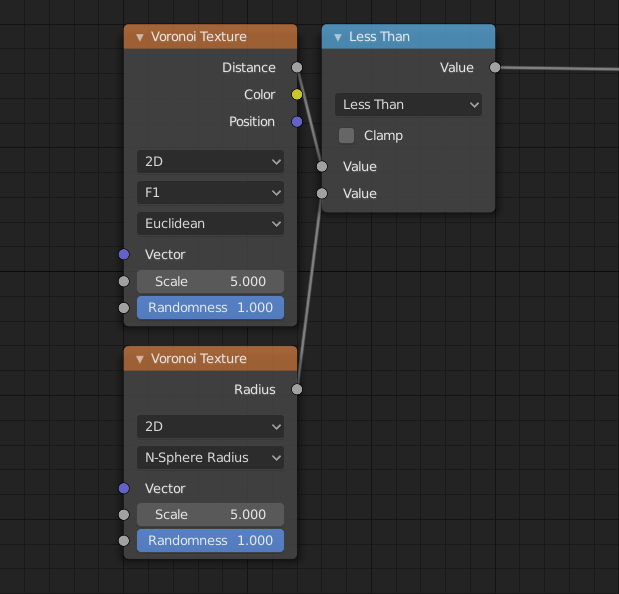
The difference between F1 and Smooth F1 can be used to create beveled Voronoi cells.¶
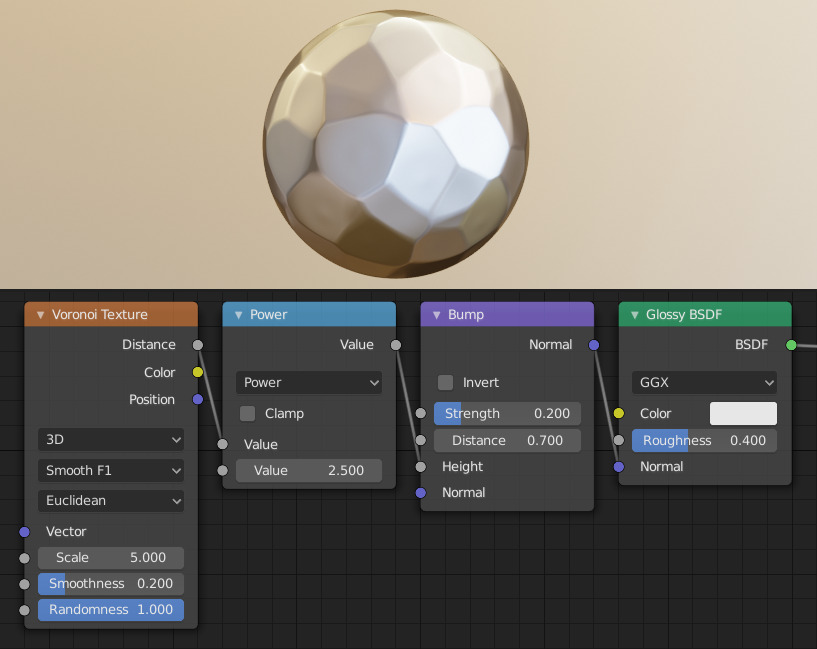
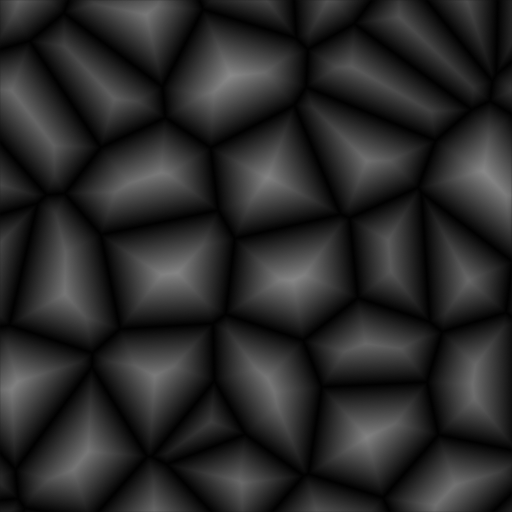
Creating a hammered metal shader using the Voronoi Texture node.¶