Bàn Giao Tiếp Python (Python Console)
The Python Console is a quick way to execute commands,
with access to the entire Python API, command history and auto-complete.
The command prompt is typical for Python 3.x,
the interpreter is loaded and is ready to accept commands at the prompt >>>.
The Python Console is a good way to explore the possibilities of Blender built-in Python. The Python Console can be used to test small bits of Python code which can then be pasted into larger scripts.
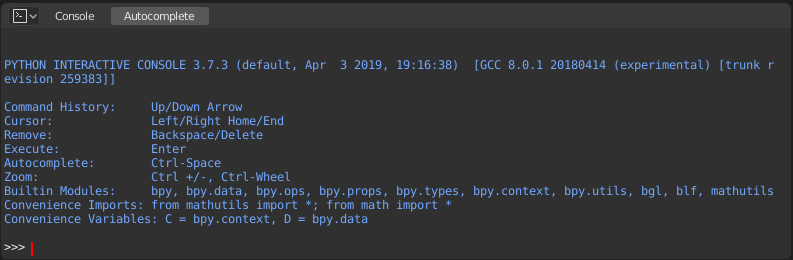
Bàn Giao Tiếp Python.
Giao Diện (Interface)
Khung Nhìn Chính (Main View)
Những Bố Trí Phím (Key Bindings)
Left / Right -- Cursor motion.
Ctrl-Left / Ctrl-Right -- Cursor motion, by word.
Phím Lùi (BackSpace)/Xóa (Delete) - Xóa ký tự.
Ctrl-Phím Lùi (BackSpace)/Ctrl-Xóa (Delete) - Xóa từ.
Return - Thực hiện lệnh.
Shift-Return - Thêm vào lịch sử lệnh mà không cần thực thi.
Cách Sử Dụng (Usage)
Bí Danh (Aliases)
Một số biến số và mô-đun có sẵn để sử dụng thuận tiện:
C: Truy cập nhanh vàobpy.context.D: Truy cập nhanh vàobpy.data.bpy: Mô-đun ở cấp bậc cao nhất trong API Python của Blender.
Làm Quen với Môi Trường Bàn Giao Tiếp (First Look at the Console Environment)
To check what is loaded into the interpreter environment, type dir()
at the prompt and execute it.
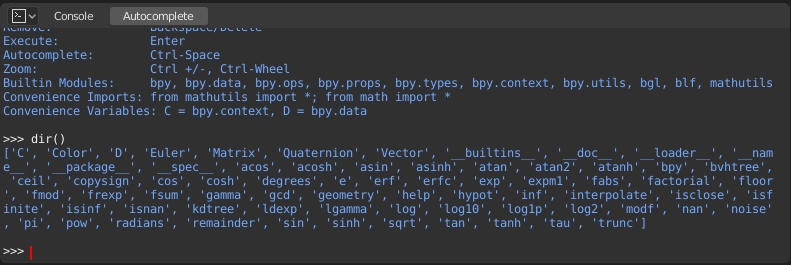
Tự Động Hoàn Chỉnh (Auto Completion)
Now, type bpy. and then press Tab and you will see the Console
auto-complete feature in action.
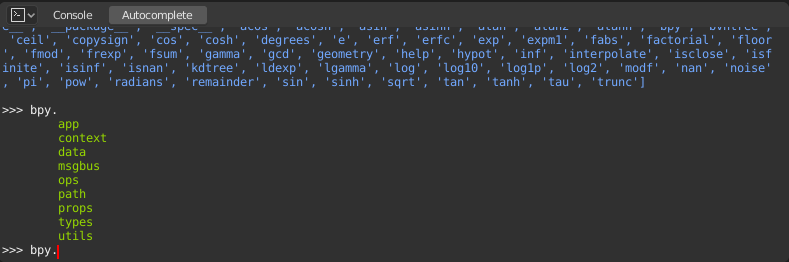
You will notice that a list of submodules inside of bpy appear. These modules encapsulate all
that we can do with Blender Python API and are very powerful tools.
Lets list all the contents of bpy.app module.
Notice the green output above the prompt where you enabled auto-completion.
What you see is the result of auto completion listing.
In the above listing all are module attributed names,
but if you see any name end with (, then that is a function.
We will make use of this a lot to help our learning the API faster.
Now that you got a hang of this, lets proceed to investigate some of modules in bpy.
Before Tinkering with the Modules
If you look at the 3D Viewport in the default Blender scene, you will notice three objects: Cube, Light and Camera.
All objects exist in a context and there can be various modes under which they are operated upon.
At any instance, only one object is active and there can be more than one selected object.
All objects are data in the blend-file.
There are operators/functions that create and modify these objects.
For all the scenarios listed above (not all were listed, mind you...)
the bpy module provides functionality to access and modify data.
Một Số Ví Dụ (Examples)
bpy.context
Ghi chú
Để các lệnh bên dưới hiển thị đầu ra chỉnh tru thì xin hãy đảm bảo rằng bạn đã chọn (các) đối tượng trong Cổng Nhìn 3D.
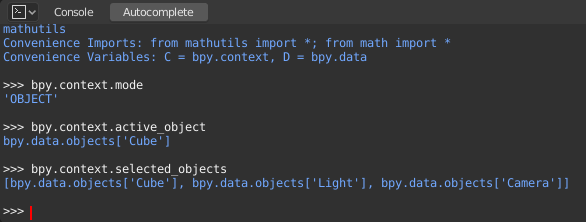
bpy.context.modeWill print the current 3D Viewport mode (Object, Edit, Sculpt, etc.).
bpy.context.objectorbpy.context.active_objectWill give you access to the active object in the 3D Viewport.
Change the X location to a value of 1:
bpy.context.object.location.x = 1
Move the object from previous X location by 0.5 unit:
bpy.context.object.location.x += 0.5
Change the X, Y, Z location:
bpy.context.object.location = (1, 2, 3)
Change only the X, Y components:
bpy.context.object.location.xy = (1, 2)
The data type of object's location:
type(bpy.context.object.location)
Now that is a lot of data that you have access to:
dir(bpy.context.object.location)
bpy.context.selected_objectsWill give access to a list of all selected objects.
Type this and then press Tab:
bpy.context.selected_objects
To print out the name of first object in the list:
bpy.context.selected_objects[0]
The complex one... But this prints a list of objects not including the active object:
[obj for obj in bpy.context.selected_objects if obj != bpy.context.object]
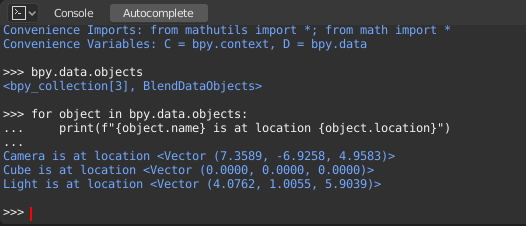
bpy.data
bpy.data has functions and attributes that give you access to all the data in the blend-file.
You can access following data in the current blend-file: objects, meshes, materials, textures, scenes, screens, sounds, scripts, etc.
That is a lot of data.
bpy.ops
The tool system is built around the concept of operators. Operators are typically executed from buttons or menus but can be called directly from Python too.
See the bpy.ops API documentation for a list of all operators.