Transformações¶
Transformações¶
We will not detail here the various transformations of bones, nor things like axis locking, pivot points, and so on, as they are common to most object editing, and already described in the mesh section. The same goes for mirroring, as it is nearly the same as with mesh editing. Just keep in mind that bones” roots and tips behave more or less like meshes” vertices, and bones themselves act like edges in a mesh.
As you know, bones can have two types of relationships: They can be parented, and in addition connected. Parented bones behave in Edit Mode exactly as if they had no relations. They can be moved, rotated, scaled, etc. without affecting their descendants. However, connected bones must always have parent’s tips connected to child’s roots, so by transforming a bone, you will affect all its connected parent/children/siblings.
Em relação a outras ferramentas de transformação, os «eixos locais» significam os eixos do objeto, mas aqui eles são os próprios eixos dos ossos (quando você bloqueia em um eixo local, pela utilização do atalho relacionado duas vezes, a restrição será aplicada ao longo dos eixos do osso selecionado, e não em relação ao eixo de objeto da armação de ossos como um todo).
Finally, you can edit in the Transform panel in the Sidebar region the positions and radius of both joints of the active selected bone, as well as its roll rotation.
Escalonar raio¶
Referência
| Mode: | Edit Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: | |
| Hotkey: | Alt-S |
Você pode alterar o raio que um osso possui pela seleção de sua cabeça, corpo ou base, e então pressionar o atalho Alt-S e mover o mouse para a esquerda ou para a direita. Caso o corpo do osso seja selecionado, o seu raio mediano será escalonado. Como usual em relação aos ossos conectados, a escala será alterada ao mesmo tempo para o raio das terminações do parente e das bases ou raízes associadas as suas crianças.
You can also alter the bone radius by selecting the tail or head of the bone you wish to alter, then navigate to and entering new values for the Tail and Head number fields.
Um único osso selecionado em modo de visualização do tipo Octaedro. |
Após o escalonamento normal. |

Um único osso selecionado sendo mostrado na visualização tipo Envelope. |
Após o raio escalonado. O seu comprimento permanece o mesmo, mas o raio de suas juntas está bem maior. |
Note that, when you resize a bone (either by directly scaling it, or by moving one of its joints), Blender automatically adjusts the end-radii of its envelope proportionally to the size of the modification. Therefore, it is advisable to place all the bones first, and only then edit their properties.
Escalonar distância do envelope¶
Referência
| Mode: | Edit Mode and Pose Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: | |
| Hotkey: | Ctrl-Alt-S |
You can alter the size of the Bone Envelope volume by clicking on the body of the bone you want to alter, Ctrl-Alt-S then drag your mouse left or right and the Bone Envelope volume will alter accordingly.
You can also alter the Bone Envelope volume by selecting the Bone you wish to alter and then navigate to then enter a new value into it.
Altering the Bone Envelope volume does not alter the size of the bone just the range within which it can influence vertices of child objects.

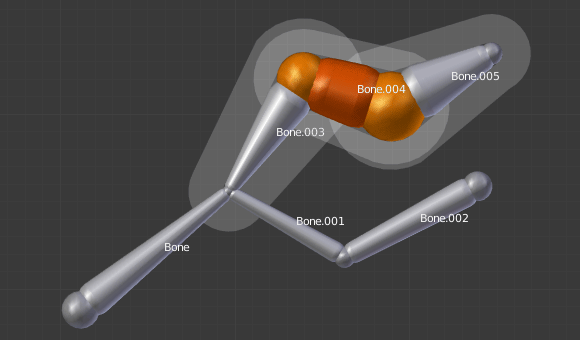
A single bone selected in Envelope visualization. |
Its envelope distance scaled. |
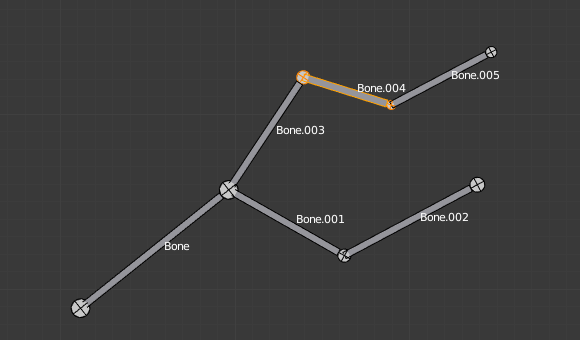
A single «default size» bone selected in B-Bone visualization. |
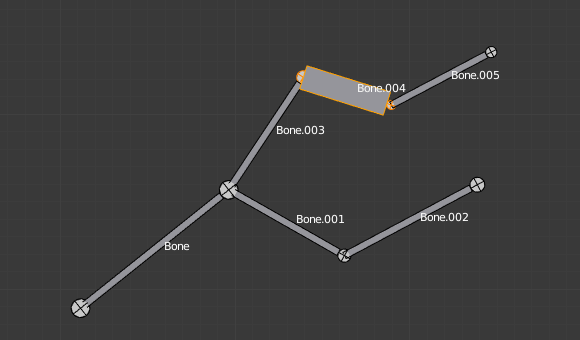
Its envelope distance scaled. |
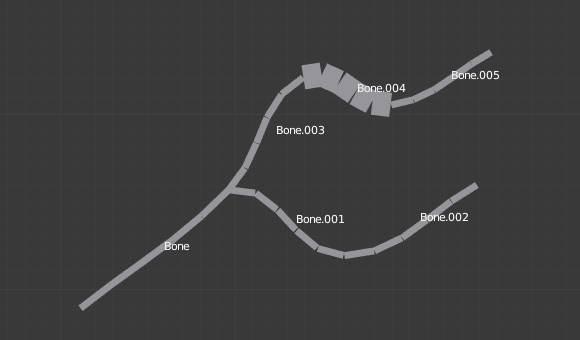
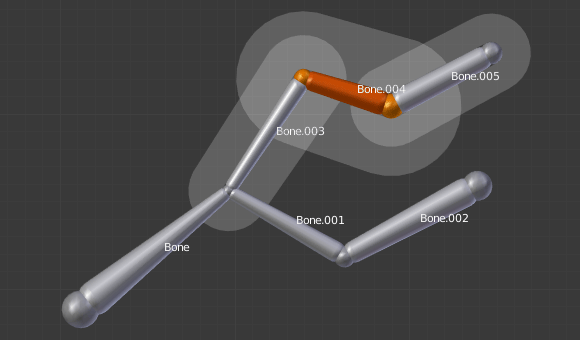
The same armature in Object Mode and B-Bone visualization, with Bone.004’s size scaled up. |
Align Bones¶
Referência
| Mode: | Edit Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: | |
| Hotkey: | Ctrl-Alt-A |
Rotates the selected bones to achieve the same orientation as the active one.
Rolagem de ossos¶
In Edit Mode, you can control the bone roll (i.e. the rotation around the Y axis of the bone).
Contudo, após a edição das armações, ou durante as utilizações das rotações tipo Euler (Arranjos de cardans), você provavelmente irá querer definir a rolagem dos ossos.
Definindo a rolagem dos ossos¶
Referência
| Mode: | Edit Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: | |
| Hotkey: | Ctrl-R |
Este é um modo de transformação onde você poderá editar a rolagem de todos os ossos selecionados.
Recalculando a rolagem dos ossos¶
Referência
| Mode: | Edit Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: | |
| Hotkey: | Ctrl-N |
- Orientação dos eixos
- Tangente local
Alinha a rolagem relativamente ao eixo definido pelo osso e seu parente.
X, Z
- Eixo global
Alinhando a rolagem aos eixos X, Y e Z.
X, Y, Z
- Osso ativo
- Segue a rotação do osso ativo.
- Eixos exibidos
- Set the roll to align with the viewport.
- Cursor
- Define a rolagem na direção do cursor 3D.
- Inverter eixos
- Inverte a direção dos eixos.
- Rotação mais curta
- Evita a rolagem do osso mais que 90 graus em relação ao seu valor atual.
Trocar direção¶
Referência
| Mode: | Edit Mode |
|---|---|
| Menu: | , |
| Hotkey: | Alt-F |
This tool allows you to switch the direction of the selected bones (i.e. their root will become their tip, and vice versa).
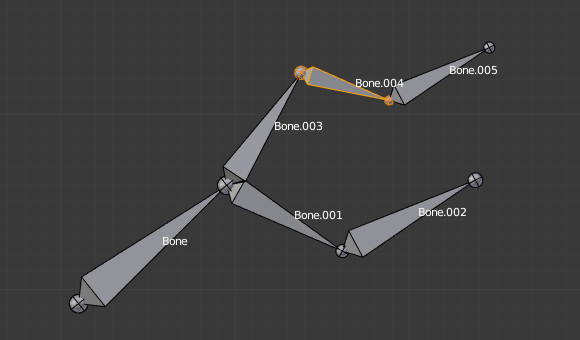
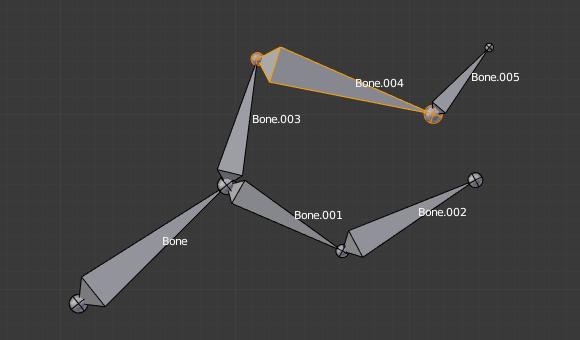
Trocar a direção de um osso em geral irá quebrar a cadeia de osso(s) a qual ele pertence. Contudo, caso você troque um conjunto integral (ou seja, uma parte ou uma área regional) da cadeia, os ossos com suas direções trocadas ainda estarão parenteados e conectados, mas na sua «ordem reversa». Veja a imagem Switching example..
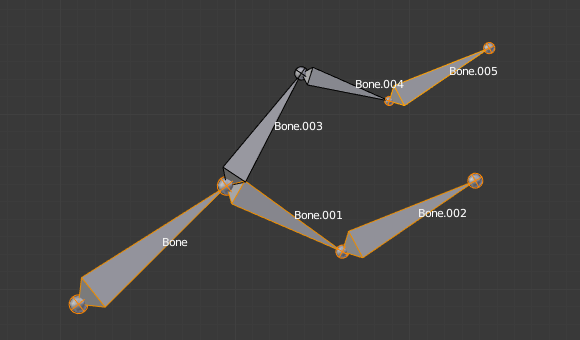
Uma armação de ossos com um osso selecionado, e um encadeamento de três ossos selecionados, antes da troca de direção. |
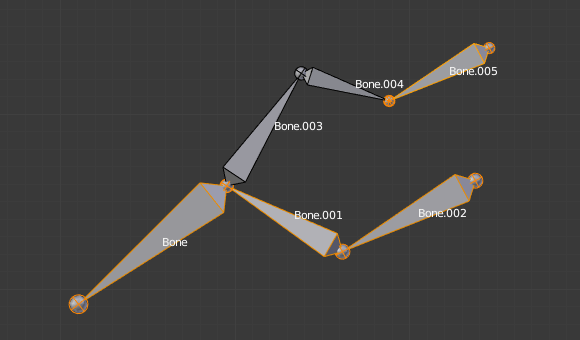
The selected bones have been switched. Bone.005 is no more connected nor parented to anything. The chain of switched bones still exists, but reversed (now Bone.002 is its root, and Bone is its tip). Bone.003 is now a free bone. |