Attribute Vector Math¶
Modify an attribute with a math operation.
The Attribute Vector Math Node.¶
Inputs¶
- Geometria
Entrada padrão de geometria.
- A, B, C
The inputs to the math operations. Depending on the operation one, two, or all three of the inputs will be used. The attribute types are all vectors of three values, except for the Scale operation, where the second input uses a float type.
- Result
The name of the attribute where the computed result it stored. A new attribute with that name is added if it does not exist yet. If it does exist, the values of the existing attribute are overridden.
Properties¶
- Operação
The math function to perform.
- Adicionar
The sum of A and B.
- Subtract
The difference between A and B.
- Multiplicar
The entrywise product of A and B. \((A.x * B.x, A.y * B.y, A.z * B.z)\)
- Divide
The entrywise division of A by B. Division by zero results in zero. \((A.x / B.x, A.y / B.y, A.z / B.z)\)
- Cross Product
The cross product of A and B.
- Project
A projeção de A em B.
- Reflect
A reflexão de A em torno da normal B. B não precisa ser normalizado.
- Refract
For a given incident vector A, surface normal B and ratio of indices of refraction (IOR) refract outputs the refraction vector R.
- Faceforward
Orienta um vetor A para apontar para longe da superfície B como definido por sua normal C. Computa \((dot(B, C) < 0) ? A : -A\).
- Dot Product
The dot product of A and B.
- Distância
A distância entre A e B.
- Length
The length of A.
- Scale
The result of multiplying A by the scalar input Scale.
- Normalizar
The result of normalizing A.
- Envolver
Wrap.
- Snap
O resultado de arredondar A para o maior inteiro múltiplo de B menor ou igual a A.
- Floor
The entrywise floor of A.
- Ceil
The entrywise ceiling of A.
- Modulo
O módulo elemento-sábio de A por B.
- Fraction
The fractional part of A.
- Absolute
O valor elemento-sábio absoluto de A.
- Mínimo
The entrywise minimum from A and B.
- Máximo
The entrywise maximum from A and B.
- Senoide
O Sine elemento-sábio de A.
- Cossenoide
O Cosine elemento-sábio de A.
- Tangente
A Tangente elemento-sábio de A.
Nota
Attributes are converted implicitly to the input data type.
- A, B, C
- Attribute
A text field to input an attribute name.
- Vector
The input is a vector of three float numbers.
Saída¶
- Geometria
Saída padrão de geometria.
Exemplo¶
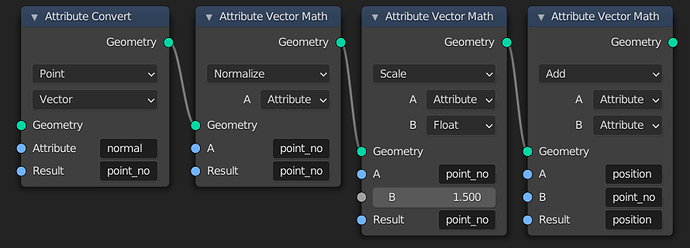
Here are nodes to move points along the normals of a mesh or points from the Point Distribute node. First the normal attribute is moved to the Point domain. Then it is normalized, the length is changed, and it is added to the position. The Factor input could instead be an attribute to vary the displacement per point.