Attribute Vector Math¶
Modify an attribute with a math operation.
The Attribute Vector Math Node.¶
Entrées¶
- Geometry
Entrée géométrie standard.
- A, B, C
The inputs to the math operations. Depending on the operation one, two, or all three of the inputs will be used. The attribute types are all vectors of three values, except for the Scale operation, where the second input uses a float type.
- Result
The name of the attribute where the computed result it stored. A new attribute with that name is added if it does not exist yet. If it does exist, the values of the existing attribute are overridden.
Propriétés¶
- Operation
The math function to perform.
- Add
The sum of A and B.
- Subtract
The difference between A and B.
- Multiply
The entrywise product of A and B. (A.x∗B.x,A.y∗B.y,A.z∗B.z)
- Divide
The entrywise division of A by B. Division by zero results in zero. (A.x/B.x,A.y/B.y,A.z/B.z)
- Cross Product (produit vectoriel)
The cross product of A and B.
- Project
La projection de A sur B.
- Reflect
La réflexion de A autour de la normale B. B n’a pas besoin d’être normalisée.
- Refract
For a given incident vector A, surface normal B and ratio of indices of refraction (IOR) refract outputs the refraction vector R.
- Faceforward
Oriente un vecteur A pour qu’il pointe loin d’une surface B telle que définie par sa normale C. Calcule (dot(B,C)<0)?A:−A.
- Dot Product (produit scalaire)
The dot product of A and B.
- Distance
La distance entre A et B.
- Length
The length of A.
- Scale
The result of multiplying A by the scalar input Scale.
- Normalize
The result of normalizing A.
- Wrap
Wrap.
- Snap
Le résultat de l’arrondi de A au plus grand multiple entier de B inférieur ou égal à A.
- Floor
The entrywise floor of A.
- Ceil
The entrywise ceiling of A.
- Modulo
Le modulo de A par B.
- Fraction
The fractional part of A.
- Absolute
La valeur absolue de A.
- Minimum
The entrywise minimum from A and B.
- Maximum
The entrywise maximum from A and B.
- Sine (sinus)
Le Sinus de A.
- Cosine (cosinus)
Le Cosinus de A.
- Tangent (tangente)
La Tangente de A.
Note
Attributes are converted implicitly to the input data type.
- A, B, C
- Attribute
A text field to input an attribute name.
- Vector
The input is a vector of three float numbers.
Sortie¶
- Geometry
Sortie de géométrie standard.
Exemple¶
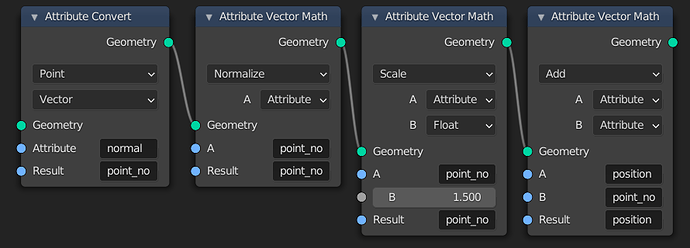
Here are nodes to move points along the normals of a mesh or points from the Point Distribute node. First the normal attribute is moved to the Point domain. Then it is normalized, the length is changed, and it is added to the position. The Factor input could instead be an attribute to vary the displacement per point.