Attribute Vector Math¶
Modify an attribute with a math operation.
The Attribute Vector Math Node.¶
输入¶
- 几何数据(Geometry)
标准的几何图形输入。
- A, B, C
The inputs to the math operations. Depending on the operation one, two, or all three of the inputs will be used. The attribute types are all vectors of three values, except for the Scale operation, where the second input uses a float type.
- 结果
The name of the attribute where the computed result it stored. A new attribute with that name is added if it does not exist yet. If it does exist, the values of the existing attribute are overridden.
属性¶
- 操作
The math function to perform.
- 相加
The sum of A and B.
- 相减
The difference between A and B.
- 正片叠底(相乘)
The entrywise product of A and B. \((A.x * B.x, A.y * B.y, A.z * B.z)\)
- 相除
The entrywise division of A by B. Division by zero results in zero. \((A.x / B.x, A.y / B.y, A.z / B.z)\)
- 叉乘
The cross product of A and B.
- 投影
A在B上的投影。
- 反射
A 围绕正常 B 的反射不需要归一化。
- 折射
For a given incident vector A, surface normal B and ratio of indices of refraction (IOR) refract outputs the refraction vector R.
- 面朝前
将矢量 A 定向到远离由其正态 C 定义的曲面 B 的方向 <。答:-答`
- 点乘
The dot product of A and B.
- 距离
A和B之间的距离。
- 长度
The length of A.
- 比例|缩放
The result of multiplying A by the scalar input Scale.
- 规格化
The result of normalizing A.
- 包裹
Wrap.
- 吸附
将A舍入为B小于或等于A的最大整数倍的结果。
- 基面
The entrywise floor of A.
- 向上取整
The entrywise ceiling of A.
- 模数
A通过B逐项取模。
- 分数
The fractional part of A.
- 绝对
A的逐项取绝对值。
- 最小值
The entrywise minimum from A and B.
- 最大值
The entrywise maximum from A and B.
- 正弦
输入值的 正弦。
- 余弦
余弦 .
- 切向(正切)
切向(正切) .
Note
Attributes are converted implicitly to the input data type.
- A, B, C
- 属性
A text field to input an attribute name.
- 矢量
The input is a vector of three float numbers.
输出¶
- 几何数据(Geometry)
标准的几何体输出。
例子¶
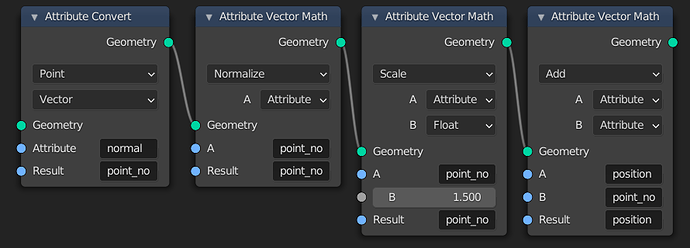
Here are nodes to move points along the normals of a mesh or points from the Point Distribute node. First the normal attribute is moved to the Point domain. Then it is normalized, the length is changed, and it is added to the position. The Factor input could instead be an attribute to vary the displacement per point.