Bàn Giao Tiếp Python
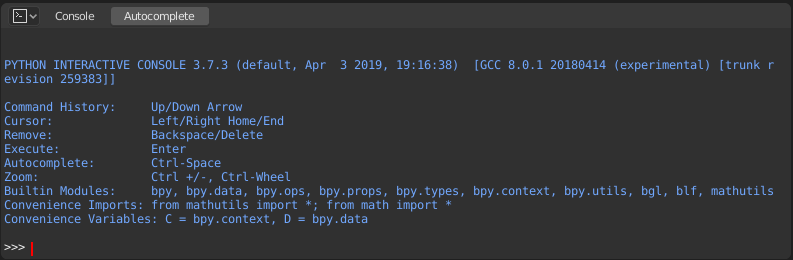
The Python Console is a quick way to execute commands,
with access to the entire Python API, command history and auto-complete.
The command prompt is typical for Python 3.x,
the interpreter is loaded and is ready to accept commands at the prompt >>>.
The Python Console is a good way to explore the possibilities of Blender built-in Python. The Python Console can be used to test small bits of Python code which can then be pasted into larger scripts.
Bàn Giao Tiếp Python.
Giao Diện
Khung Nhìn Chính
Những Tổ Hợp Phím
Left / Right -- Cursor motion.
Ctrl-Left / Ctrl-Right -- Cursor motion, by word.
Backspace / Delete -- Erase characters.
Ctrl-Backspace / Ctrl-Delete -- Erase words.
Return -- Execute command.
Shift-Return -- Add to command history without executing.
Sử Dụng
Bí Danh
Some variables and modules are available for convenience:
C: Quick access tobpy.context.D: Quick access tobpy.data.bpy: Top level Blender Python API module.
Làm Quen với Môi Trường Bàn Giao Tiếp
To check what is loaded into the interpreter environment, type dir()
at the prompt and execute it.
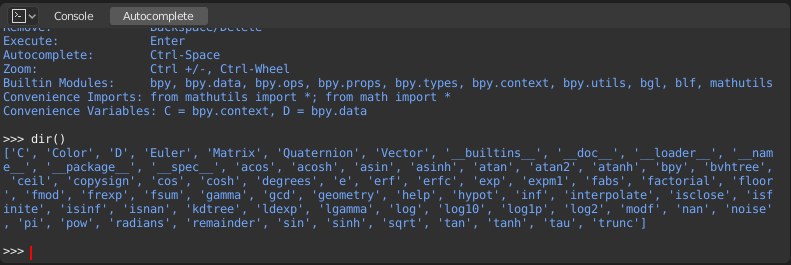
Tự động Hoàn Chỉnh
Now, type bpy. and then press Tab and you will see the Console
auto-complete feature in action.
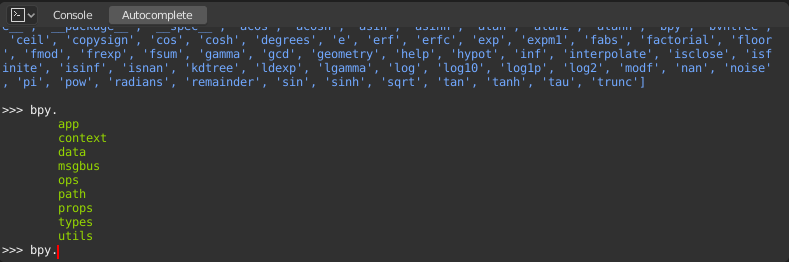
You will notice that a list of submodules inside of bpy appear. These modules encapsulate all
that we can do with Blender Python API and are very powerful tools.
Lets list all the contents of bpy.app module.
Notice the green output above the prompt where you enabled auto-completion.
What you see is the result of auto completion listing.
In the above listing all are module attributed names,
but if you see any name end with (, then that is a function.
We will make use of this a lot to help our learning the API faster.
Now that you got a hang of this, lets proceed to investigate some of modules in bpy.
Trước khi thí nghiệm với các Mô-Đun
If you look at the 3D Viewport in the default Blender scene, you will notice three objects: Cube, Light and Camera.
All objects exist in a context and there can be various modes under which they are operated upon.
At any instance, only one object is active and there can be more than one selected object.
All objects are data in the blend-file.
There are operators/functions that create and modify these objects.
For all the scenarios listed above (not all were listed, mind you...)
the bpy module provides functionality to access and modify data.
Ví Dụ
bpy.context
Ghi chú
For the commands below to show the proper output, make sure you have selected object(s) in the 3D Viewport.
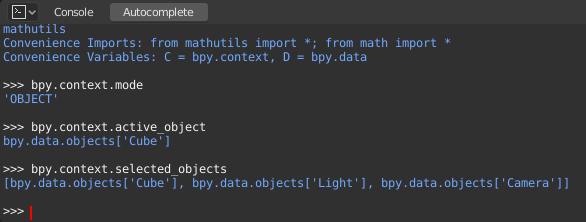
bpy.context.modeWill print the current 3D Viewport mode (Object, Edit, Sculpt, etc.).
bpy.context.objectorbpy.context.active_objectCông Cụ dành cho việc đo lường các vật thể trong Cổng Nhìn 3D.
Change the X location to a value of 1:
bpy.context.object.location.x = 1
Move the object from previous X location by 0.5 unit:
bpy.context.object.location.x += 0.5
Change the X, Y, Z location:
bpy.context.object.location = (1, 2, 3)
Change only the X, Y components:
bpy.context.object.location.xy = (1, 2)
The data type of object's location:
type(bpy.context.object.location)
Now that is a lot of data that you have access to:
dir(bpy.context.object.location)
bpy.context.selected_objectsWill give access to a list of all selected objects.
Type this and then press Tab:
bpy.context.selected_objects
To print out the name of first object in the list:
bpy.context.selected_objects[0]
The complex one... But this prints a list of objects not including the active object:
[obj for obj in bpy.context.selected_objects if obj != bpy.context.object]
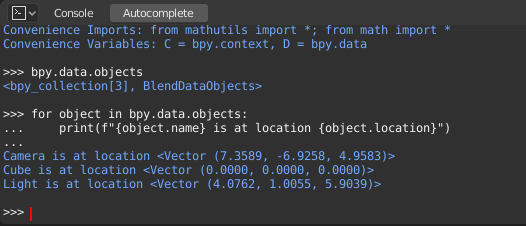
bpy.data
bpy.data has functions and attributes that give you access to all the data in the blend-file.
You can access following data in the current blend-file: objects, meshes, materials, textures, scenes, screens, sounds, scripts, etc.
That is a lot of data.
bpy.ops
The tool system is built around the concept of operators. Operators are typically executed from buttons or menus but can be called directly from Python too.
Xin xem thêm bài bpy.ops.wm để xem toàn bộ danh sách.