Tính Chất (Properties)
Đường Cong-F Đang Hoạt Động (Active F-Curve)
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Bảng (Panel)
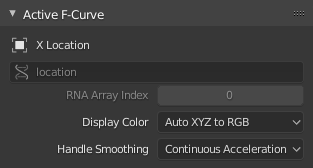
Bảng đường cong-F đang hoạt động.
Bảng này hiển thị các Tính Chất cho Đường Cong-F đang hoạt động.
- Tên Kênh (Channel Name)
Kiểu ID + Tên kênh (Địa điểm X).
- Đường Dẫn Dữ Liệu (Data Path)
Tính Chất của Thao Tác.
- Chỉ Số Mảng RNA (RNA Array Index)
Index to the specific property affected by the F-Curve if applicable.
- Màu Hiển Thị (Display Color)
The method used to determine the color of the F-Curve shown in the Graph editor.
- Tự Động Cầu Vồng Hóa (Auto Rainbow)
Gia tăng sắc màu của Đường Cong-F dựa trên chỉ số của kênh.
- Tự Động XYZ Sang RGB (Auto XYZ to RGB)
Đối với những bộ Tính Chất giống như vị trí của XYZ thì tự động đặt bộ màu thành đỏ, lục, lam.
- Người Dùng Định Nghĩa (User Defined)
Chỉ định màu tùy chọn dành cho Đường Cong-F đang hoạt động.
- Xử Lý Vấn Đề làm Mượt Mà (Handle Smoothing)
Selects the method used to compute automatic Bézier handles (Automatic, Auto Clamped, Vector).
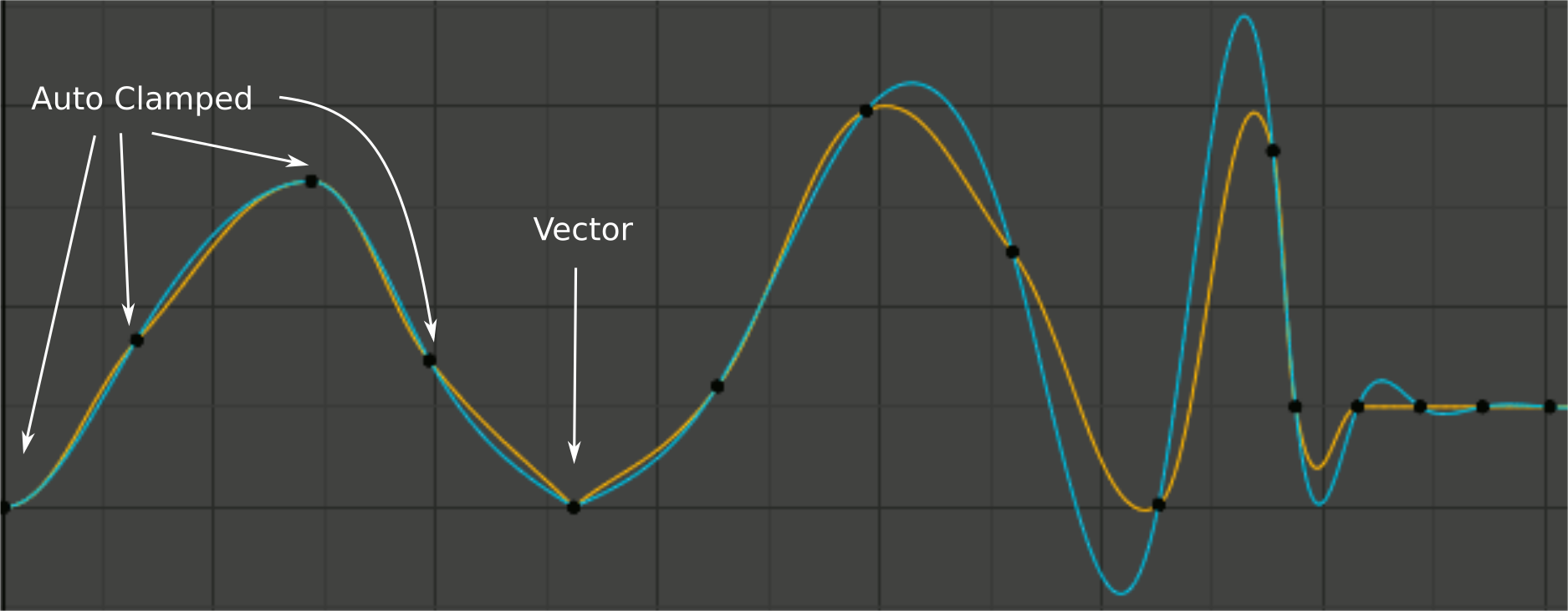
Handle smoothing mode comparison.
Yellow: None, Cyan: Continuous Acceleration. From left to right, four Auto Clamped keys, one Vector, and the rest are Automatic.
- Không (None)
Only directly adjacent key values are considered when computing the handles. Vector handles are pointed directly at the adjacent keyframes.
This older method is very simple and predictable, but it can only produce truly smooth curves in the most trivial cases. Note the kinks in the yellow curve around the keys located between the extremes, and near the Vector handles.
- Tăng Tốc Liên Tục (Continuous Acceleration)
A system of equations is solved in order to avoid or minimize jumps in acceleration at every keyframe. Vector handles are integrated into the curves as smooth transitions to imaginary straight lines beyond the keyframe.
It produces much smoother curves out of the box, but necessarily means that any changes in the key values may affect interpolation over a significant stretch of the curve; although the amount of change decays exponentially with distance. This change propagation is stopped by any key with Free, Aligned, or Vector handles, as well as by extremes with Auto Clamped handles.
The mode also tends to overshoot and oscillate more with fully Automatic handles in some cases (see the right end of the image above). So it is recommended to use Auto Clamped by default, and only switch to Automatic handles in places where this is desired behavior. That effect can also be reduced by adding in-between keys.
Mẹo
Considering the upsides and downsides of each mode, Continuous Acceleration should be better suited for limited animation, which uses a small number of interpolated keys with minimal manual polish. In case of highly polished high key rate animation, the benefits of smoothing may not outweigh the workflow disruption from more extensive change propagation.
Khung Khóa Đang Hoạt Động (Active Keyframe)
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Bảng (Panel)
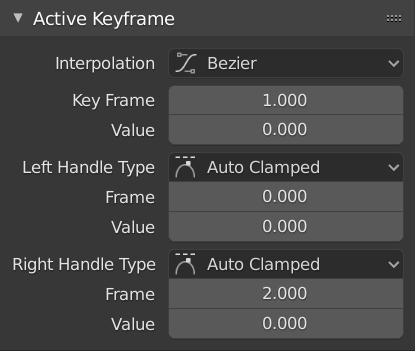
Bảng Khung Khóa đang hoạt động.
- Interpolation (Nội Suy)
Mode for the Interpolation between the current and next keyframe.
Interpolation (Nội Suy)
- Hằng Số/Đồng Đều/Bất Biến (Constant)
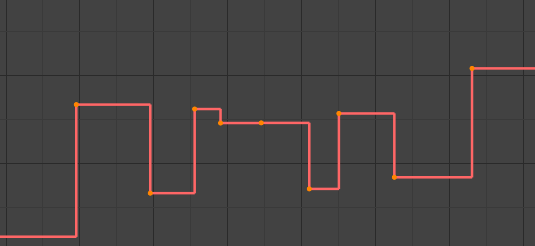
Hằng Số/Đồng Đều/Bất Biến.
There is no interpolation at all. The curve holds the value of its last keyframe, giving a discrete (stairway) "curve". Usually only used during the initial "blocking" stage in pose-to-pose animation workflows.
- Tuyến Tính (Linear)
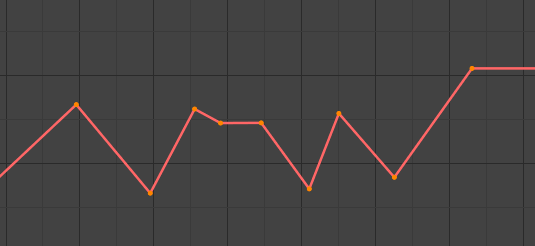
Tuyến Tính.
This simple interpolation creates a straight segment, giving a non-continuous line. It can be useful when using only two keyframes and the Extrapolation extend mode, to easily get an infinite straight line (i.e. a linear curve).
- Bézier (Đường Cong Bézier)
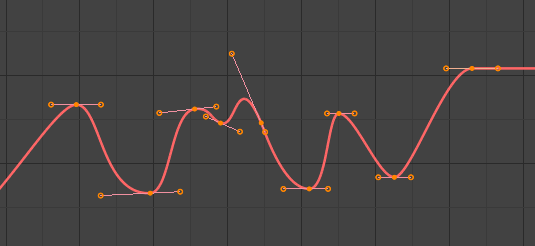
Bézier.
The more powerful and useful interpolation, and the default one. It gives nicely smoothed curves, i.e. smooth animations!
Ghi chú
Remember that some F-Curves can only take discrete values, in which case they are always shown as if constant interpolated, whatever option you chose.
Nới Lỏng [theo mức độ] (Easing [by strength])
Different methods of easing interpolations for F-Curve segment. The "Robert Penner easing equations" (basically, equations which define some preset ways that one keyframe transitions to another) which reduce the amount of manual work (inserting and tweaking keyframes) to achieve certain common effects. For example, snappy movements.
Tuyến Tính (Linear)
Sin
Bình Phương (Quadratic)
Lập Phương (Cubic)
Bậc Bốn
Bậc Năm
Lũy Thừa
Vòng Tròn (Circular)
Xem thêm
For more info and a few live demos, see https://easings.net and http://robertpenner.com/easing/
Hiệu Ứng Năng Động (Dynamic Effects)
These additional easing types imitate (fake) physics-based effects like bouncing/springing effects. The corresponding settings can be found in the .
- Sau (Back)
Cubic easing with overshoot and settle. Use this one when you want a bit of an overshoot coming into the next keyframe, or perhaps for some wind-up anticipation.
- Sau (Back)
The back property controls the size and direction (i.e. above/below the curve) of the overshoot.
- Nẩy (Bounce)
Exponentially decaying parabolic bounce, like when objects collide. e.g. for Bouncing balls, etc.
- Elastic (Đàn Hồi)
Exponentially decaying sine wave, like an elastic band. This is like bending a stiff pole stuck to some surface, and watching it rebound and settle back to its original state.
- Biên Độ (Amplitude)
The amplitude property controls how strongly the oscillation diverges from the basic curve. At 0.0, there is no oscillation (i.e. it just snaps to the B-value like an extreme exponential transition), and at 1.0 a profile similar to the one shown in the icon occurs.
- Chu Kỳ (Period)
The period property controls the frequency with which oscillations occur. Higher values result in denser oscillations.
- Nới Lỏng/Chậm Rãi (Easing)
The Easing Type controls which end of the segment between the two keyframes that the easing effects apply to. It has no effect if the Interpolation Mode is set to either Constant, Linear, or Bézier.
- Tự Động Nới Lỏng/Chậm Rãi (Automatic Easing)
The most commonly expected of the below behaviors is used. For the transitional effects, this is basically ease in, while for the physics effects it is ease out.
- Vào Nới Lỏng/Làm Dịu/Chậm Rãi/Mềm Mại (Ease In)
Effect builds up to the second keyframe.
- Làm Chậm Rãi Ra (Ease Out)
Hiệu Ứng mờ dần ra khỏi khung khóa đầu tiên.
- Vào và Ra Nới Lỏng/Làm Dịu/Chậm Rãi/Mềm Mại (Ease In Out)
Ảnh hưởng xảy ra ở hai đầu của phân đoạn.
- Khung Khóa (Key Frame)
Đặt khung hình cho khung khóa đang hoạt động.
- Value (Giá Trị)
Đặt giá trị cho khung khóa đang hoạt động.
- Thể Loại Tay Cầm Trái / Phải (Left/Right Handle Type)
Khi sử dụng các đường cong nội suy Bézier, chúng ta có thể kiểm soát độ dốc của đường cong tại các điểm điều khiển. Việc làm này được thực hiện thông qua các điểm "tay cầm" của đường cong; bạn có thể đặt kiểu tay cầm để sử dụng cho các điểm đường cong bằng cách nhấn phím V hoặc chọn Khóa, Loại Tay Cầm trong trình đơn của Trình Biên Soạn Đồ Thị. Mỗi điểm đường cong có thể có một kiểu tay cầm khác nhau, ngay cả trên cùng một đường cong nữa.
Có ba chế độ tự động, "Tự Động", "Tự Động Hạn Định" và "Véctơ", trong đó Blender tự động xác định độ dốc của đường cong tại mỗi điểm điều khiển. Các điểm điều khiển lân cận bị ảnh hưởng của độ dốc tác động nhiều nhất và các điểm ở xa hơn có ảnh hưởng ít hơn. Điều này có thể được kiểm soát trên Đường Cong-F với tính chất Tự Động Mịn Hóa Tay Cầm (Auto Handle Smoothing).
Bằng cách sử dụng các chế độ khác, không tự động, bạn có toàn quyền điều khiển độ dốc một cách thủ công.
- Tự Động (Automatic)
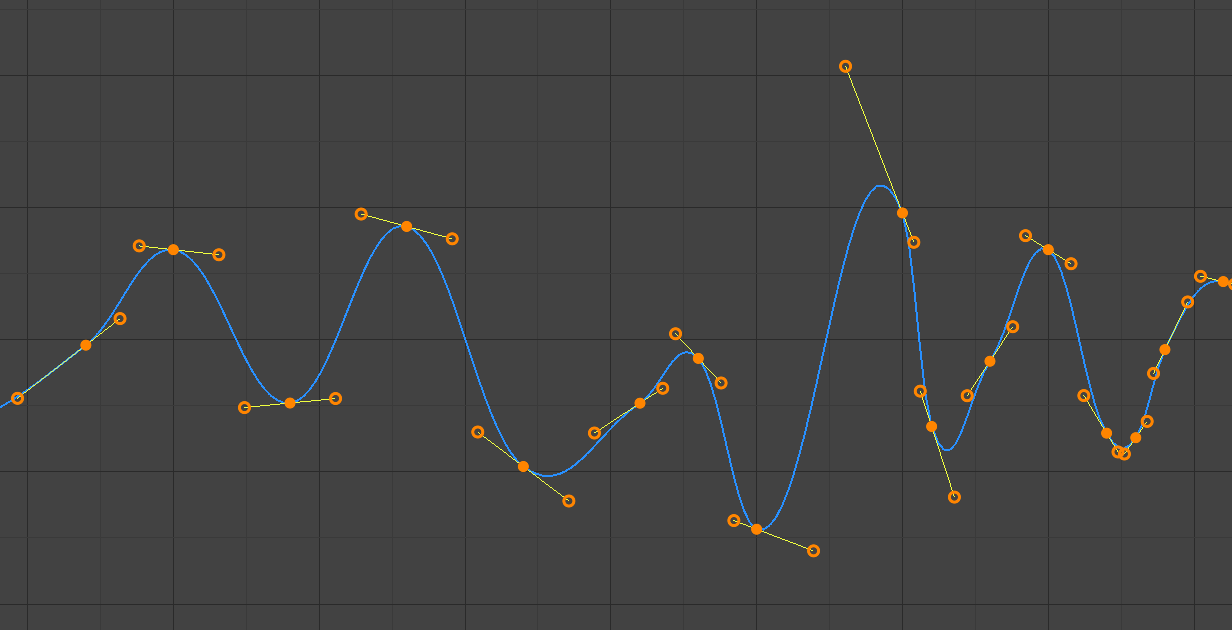
Các tay cầm tự động.
Các vị trí tay cầm được chọn tự động để tạo ra các đường cong mượt mà.
- Tự Động Hạn Định (Auto Clamped)
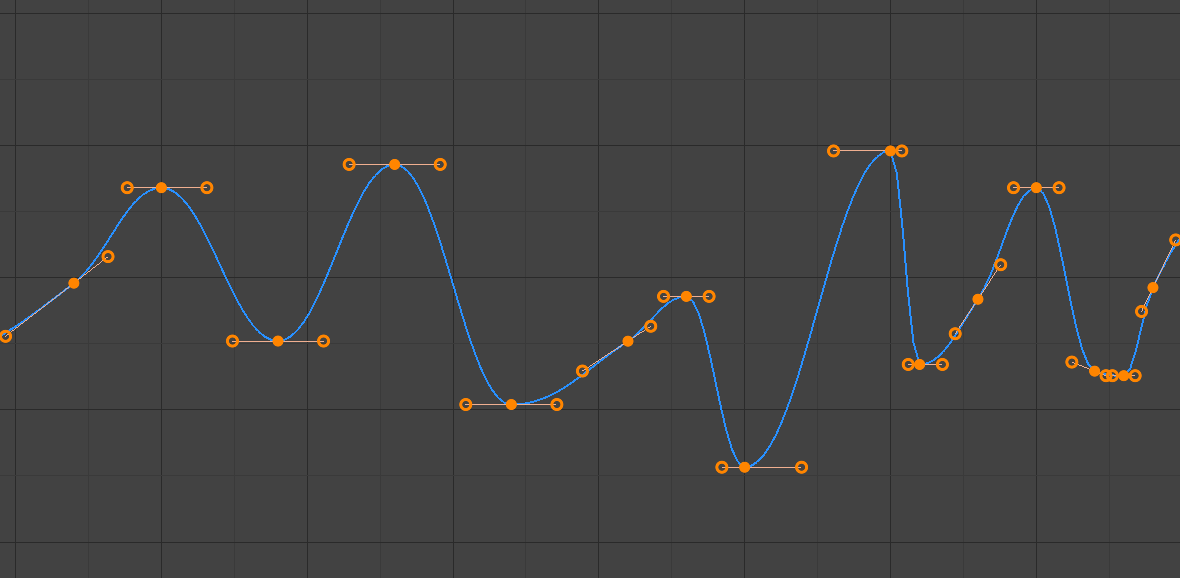
Các tay cầm hạn định.
Tay cầm tự động bị hạn định hòng để ngăn chặn những trường hợp không kiềm chế xảy ra và thay đổi chiều hướng của đường cong giữa các khung khóa (hình chữ-S).
- Véctơ (Vector)
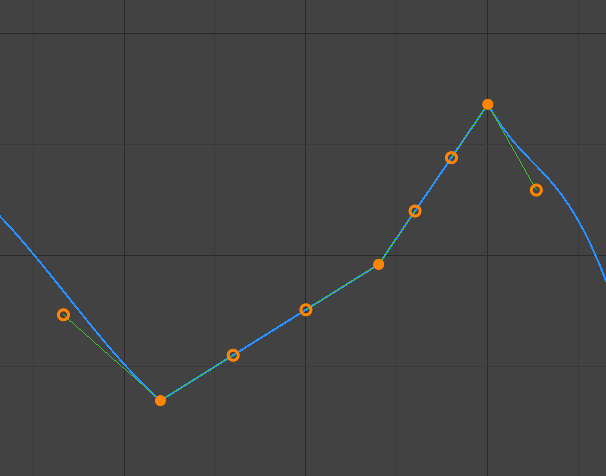
Các tay cầm Véctơ.
Tạo nội suy tuyến tính tự động giữa các khung khóa. Các phân đoạn vẫn giữ nguyên tính chất tuyến tính trong khi các trung tâm khung khóa di chuyển. Tuy nhiên, khi các tay cầm di chuyển thì kiểu tay cầm sẽ được chuyển sang là "Tự Do".
- Thẳng Hàng (Aligned)
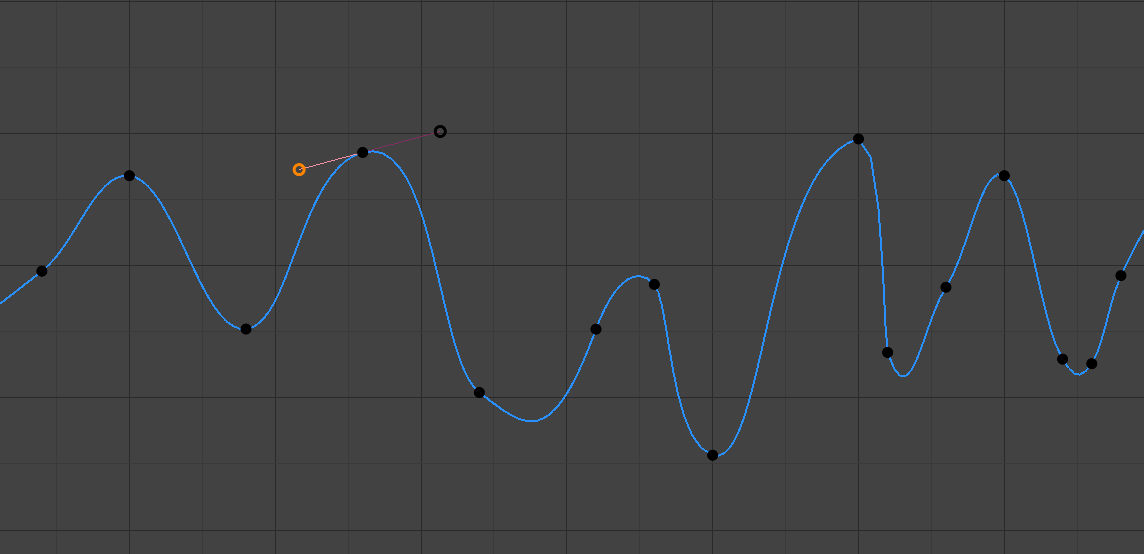
Các tay cầm thẳng hàng .
Hai tay cầm của điểm đường cong được khóa với nhau để luôn hướng về các hướng hoàn toàn ngược nhau. Điều này dẫn đến một đường cong luôn trơn tru tại điểm điều khiển.
- Tự Do (Free)
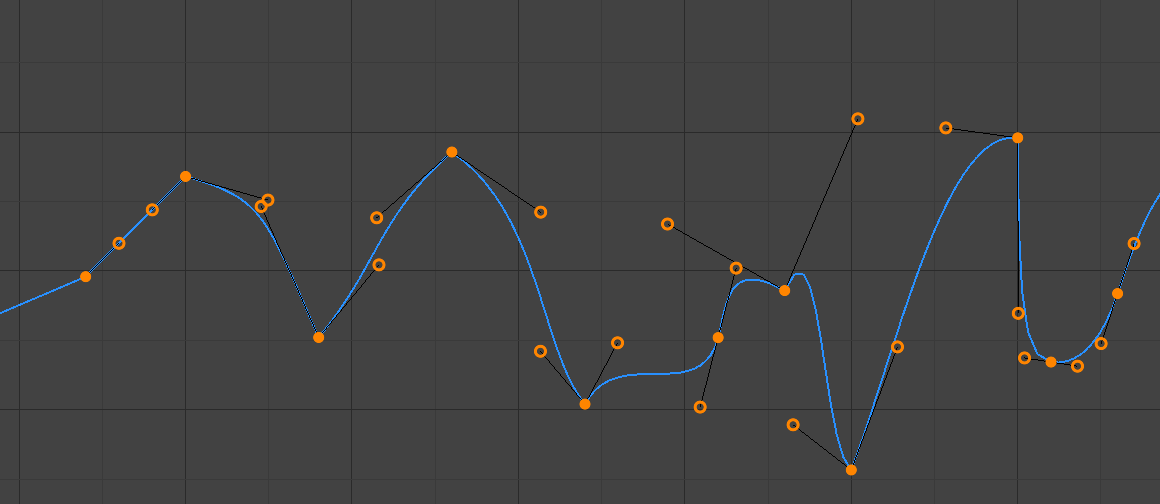
Các tay cầm tự do.
Các tay cầm có thể được di chuyển hoàn toàn độc lập, và do đó có thể dẫn đến sự thay đổi chiều hướng đột ngột.
- Khung Hình, Giá Trị
Đặt khung hình và giá trị cho tay cầm nội suy trái/phải cho khung khóa đang hoạt động.