Thuyên Chuyển Dữ Liệu của Khung Lưới (Transfer Mesh Data)
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Chế Độ (Mode)
Chế Độ Vật Thể (Object Mode)
- Trình Đơn (Menu)
The Data Transfer tool transfers several types of data from one mesh to another. Data types include vertex groups, UV maps, Color Attributes, custom normals... Transfer works by generating a mapping between source mesh's elements (vertices, edges, etc.) and destination ones, either on a one-to-one basis, or mapping several source elements to a single destination one by interpolated mapping.
Transfers data layer(s) from active to selected meshes.
- Ngưng Hoạt Động của Thao Tác (Freeze Operator)
Prevent changes to settings to re-run the operator. This is useful if you are editing several settings at once with heavy geometry.
- Kiểu dữ liệu (Data Type)
Dữ liệu nào để thuyên chuyển sang.
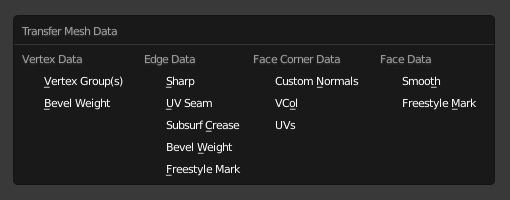
Loại dữ liệu.
- Tạo Dữ Liệu (Create Data)
Thêm tầng dữ liệu vào các khung lưới đích nếu cần.
- Ánh Xạ Điểm Đỉnh (Vertex Mapping)
Method used to map source vertices to destination ones. Because the options change depending on the Data Type options are explained in Vertex Mapping below.
Ánh Xạ Điểm Đỉnh (Vertex Mapping)
Topology (Cấu Trúc Liên Kết)
The simplest option, expects both meshes to have identical number of elements, and match them by order (indices). Useful e.g. between meshes that were identical copies, and got deformed differently.
Ánh Xạ Một-Đối-Một (One-To-One Mappings)
Those always select only one source element for each destination one, often based on shortest distance.
- Vertices (Điểm Đỉnh)
- Điểm đỉnh gần nhất (Nearest Vertex)
Sử dụng điểm đỉnh gần nhất của nguồn.
- Điểm Đỉnh của Cạnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Edge Vertex)
Sử dụng điểm đỉnh gần nhất của cạnh tối cận của nguồn.
- Điểm Đỉnh của Bề Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Face Vertex)
Sử dụng điểm đỉnh gần nhất của bề mặt tối cận của nguồn.
- Cạnh (Edges)
- Điểm Đỉnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Vertices)
Sử dụng cạnh của nguồn có các điểm đỉnh nằm gần nhất với điểm đỉnh cạnh của đích.
- Cạnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Edge)
Uses source's nearest edge (using edge's midpoints).
- Cạnh Bề Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Face Edge)
Uses source's nearest edge of source's nearest face (using edge's midpoints).
- Góc của bề mặt (Face Corners)
A face corner is not a real element by itself, it's some kind of split vertex attached to a specific face. Hence both vertex (location) and face (normal, ...) aspects are used to match them together.
- Góc Tối Cận cùng Pháp Tuyến Giống Nhất (Nearest Corner and Best Matching Normal)
Sử dụng góc của nguồn có pháp tuyến "tách phân" tương đồng nhiều nhất với cái ở đích, từ những cái sử dụng chung điểm đỉnh cận nhất của nguồn.
- Góc Cạnh Gần Nhất và Pháp Tuyến Bề Mặt Giống Nhất (Nearest Corner and Best Matching Face Normal)
Sử dụng góc của nguồn có pháp tuyến "bề mặt" tương đồng nhiều nhất với cái ở đích, từ những cái sử dụng chung điểm đỉnh cận nhất của nguồn.
- Góc Tối Cận của Bề Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Corner of Nearest Face)
Sử dụng góc gần nhất của bề mặt gần nhất của nguồn.
- Bề Mặt (Faces)
- Bề Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Face)
Sử dụng bề mặt gần nhất của nguồn.
- Pháp Tuyến Tương Đồng Nhất (Best Normal-Matching):
Sử dụng bề mặt của nguồn có các pháp tuyến tương đồng nhiều nhất với cái của đích.
Ánh Xạ Nội Suy (Interpolated Mappings)
Those use several source elements for each destination one, interpolating their data during the transfer.
- Vertices (Điểm Đỉnh)
- Cạnh Gần Nhất được Nội Suy (Nearest Edge Interpolated)
Sử dụng điểm cận nhất của cạnh nguồn gần nhất, nội suy dữ liệu từ Toàn bộ các điểm đỉnh cạnh của nguồn đó.
- Bề Mặt Gần Nhất được Nội Suy (Nearest Face Interpolated)
Sử dụng điểm cận nhất của bề mặt nguồn gần nhất, nội suy dữ liệu từ Toàn bộ các điểm đỉnh bề mặt của nguồn đó.
- Bề mặt Phóng Chiếu được Nội Suy (Projected Face Interpolated)
Sử dụng điểm trên bề mặt của nguồn, tức điểm mà sự phóng chiếu điểm đỉnh của đích dọc theo pháp tuyến của riêng nó đập vào, nội suy dữ liệu từ Toàn bộ các điểm đỉnh bề mặt của nguồn đó.
- Cạnh (Edges)
- Cạnh Phóng Chiếu Nội Suy (Projected Edge Interpolated)
Đây là một quy trình lấy mẫu vật. Một số tia xạ được phóng chiếu dọc theo cạnh đích (nội suy cả hai pháp tuyến điểm đỉnh của cạnh), và nếu số lượng tia xạ đập vào một cạnh nguồn cao vừa đủ thì Toàn bộ các dữ liệu của cạnh nguồn sẽ được nội suy thành cái ở đích.
- Góc của bề mặt (Face Corners)
A face corner is not a real element by itself, it's some kind of split vertex attached to a specific face. Hence both vertex (location) and face (normal, ...) aspects are used to match them together.
- Bề Mặt Gần Nhất được Nội Suy (Nearest Face Interpolated)
Sử dụng điểm cận nhất của bề mặt nguồn gần nhất, nội suy dữ liệu từ Toàn bộ các góc bề mặt của nguồn đó.
- Bề mặt Phóng Chiếu được Nội Suy (Projected Face Interpolated)
Sử dụng điểm cận nhất của bề mặt nguồn, tức điểm mà sự phóng chiếu góc của đích dọc theo pháp tuyến của riêng nó đập vào, nội suy dữ liệu từ Toàn bộ các góc bề mặt của nguồn đó.
- Bề Mặt (Faces)
- Bề mặt Phóng Chiếu được Nội Suy (Projected Face Interpolated)
Đây là một quy trình lấy mẫu vật. Một số tia xạ được phóng chiếu từ Toàn bộ các bề mặt đích (dọc theo pháp tuyến của bản thân nó), và nếu số lượng tia xạ đập vào một bề mặt nguồn cao vừa đủ thì Toàn bộ các dữ liệu của bề mặt nguồn sẽ được nội suy thành cái ở đích.
Tùy Chọn Khác (Further Options)
- Tự Động Biến Hóa (Auto Transform)
Automatically computes the transformation to get the best possible match between source and destination meshes.
This allows to match and transfer data between two meshes with similar shape, but transformed differently. Note that you'll get best results with exact copies of the same mesh. Otherwise, you'll likely get better results if you "visually" make them match in 3D space (and use Object Transform) instead.
- Biến Hóa Vật Thể (Object Transform)
Ước tính khung lưới nguồn và đích trong không gian toàn cầu.
- Duy Hình Học Lân Cận (Only Neighbor Geometry)
Các thành phần nguồn cần phải gần hơn khoảng cách đã cho với cái ở đích.
- Khoảng Cách Tối Đa (Max Distance)
Maximum allowed distance between source and destination element (for non-topology mappings).
- Bán Kính của Tia Xạ (Ray Radius)
The starting ray radius to use when Ray Casting against vertices or edges. When transferring data between meshes Blender performs a series of ray casts to generate mappings. Blender starts with a ray with the radius defined here, if that does not detect a hit then the radius is progressively increased until a positive hit or a limit is reached.
This property acts as an accuracy/performance control; using a lower ray radius will be more accurate however, might take longer if Blender has to progressively increase the limit. Lower values will work better for dense meshes with lots of detail while larger values are probably better suited for simple meshes.
- Chế Độ Pha Trộn (Mix Mode)
Phương pháp tác động các phần tử ở đích dùng các giá trị nguồn.
- Toàn Bộ (All)
Replaces everything in destination (note that Mix Factor is still used).
- Giới Hạn Trên (Above Threshold)
Only replaces destination value if it is above given threshold Mix Factor. How that threshold is interpreted depends on data type, note that for Boolean values this option fakes a logical AND.
- Giới Hạn Dưới (Below Threshold)
Only replaces destination value if it is below given threshold Mix Factor. How that threshold is interpreted depends on data type, note that for Boolean values this option fakes a logical OR.
- Pha Trộn, Cộng, Trừ, Nhân (Mix, Add, Subtract, Multiply)
Apply that operation, using mix factor to control how much of source or destination value to use. Only available for a few types (vertex groups, Color Attributes).
- Hệ Số Pha Trộn (Mix Factor)
How much of the transferred data gets mixed into existing one (not supported by all data types).